No trust in the DeFi era
DeFi is based on smart contracts on Ethereum and other chains, and Ethereum is a decentralized public chain that requires no permission and cannot be tampered with. This feature brings trustless, permissionless and transparency in the DeFi era. Traditional financial services require trust and permission, and it is difficult to be transparent. With the advent of the DeFi era, all this is changing.
Not only can transactions and lending be decentralized, but asset management can also be decentralized. The Cook protocol attempts to achieve this and build a trustless and transparent asset management protocol. All this can only be done in the DeFi era.
What does trustless asset management services mean
Today’s asset management services require trust in the credibility of the institution itself, and trust in this case means higher costs and lower efficiency. As a result, traditional asset management services are more willing to serve people or institutional investors with more assets. This means that more ordinary users do not receive high-quality asset management services.
Trust-free asset management services are transparent, because the flow of funds and operations are on the chain, which is more efficient and cheaper. Since data is trustless, users can make choices at any time according to their own risk preferences. At the same time, any ordinary user can participate in trustless asset management services, which also does not require permission.
This is a new service in the DeFi era
The development of DeFi makes trustless asset management services possible
The total amount of assets locked in DeFi is currently US$43 billion. In the past 12 months, the total trading volume of DEX has exceeded US$280 billion, and the number of trading users of DEX is close to 1.5 million. Uniswap, Sushiswap and other DEX have more than 4 billion U.S. dollars in liquidity, and the total amount of locked assets in the loan agreement of Maker, Aave, and Compound exceeds 5 billion U.S. dollars. The market value of overall stablecoins such as usdt, usdc, and dai exceeds 57 billion U.S. dollars. This means that although DeFi is still in a very early stage, it is not a barren land. It has begun to take root and the conditions for asset management services on it are ripe.
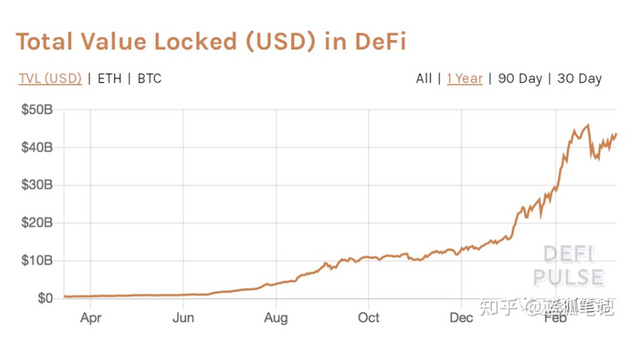
The scale of DeFi's market makes asset management services have the basic conditions. It has sufficient liquidity, a lending market, a derivatives market, a liquid mining market, and a large-scale stablecoin market. In other words, although the field is still expanding and growing, this field is enough to make asset management services possible.
Cook Agreement: Building a universal agreement for trustless asset management
The trustless asset management service means that it is built on the blockchain and it interacts with DeFi. Asset management services are mainly oriented to two groups, one is investment users and the other is fund managers. Investment users have the need to increase returns, while fund managers have the need for funds and more management tools.
The Cook protocol is a DeFi protocol that connects these two groups. Through the Cook protocol, an asset management service market based on chains such as Ethereum, Polkadot, Heco, and BSC can be built. For most ordinary investment users, fund managers have a better understanding of DeFi. Compared with their own operations, they are more likely to be operated by more professional people to obtain higher returns. For fund managers, more funds and more convenient tools are conducive to obtaining higher returns. Both parties have needs for each other.
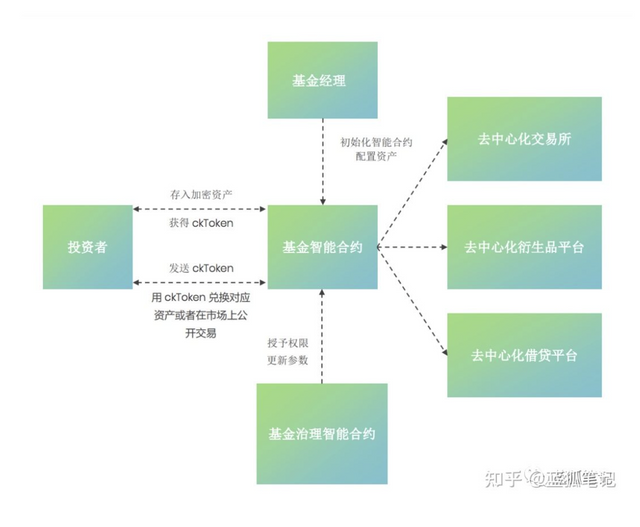
In the Cook agreement, the fund manager will define what kind of encrypted assets it accepts, which DeFi markets to enter, what fee structure to adopt, and what investment strategy to determine. Through these settings, the fund manager can initialize the smart contract. And investment users can choose the corresponding fund according to their own risk preferences. The user participation method is also relatively simple, deposit their encrypted assets into the smart contract, and the fund manager deploys the funds of the smart contract. In terms of deploying funds, the Cook Agreement plans to provide a variety of investment tools to help fund managers execute various strategies.
After the user's funds are deposited into the smart contract, the fund manager only has the right to use it, but not the right to own it. Fund managers cannot withdraw funds from the contract, and the funds in the contract can only be allocated to the DeFi platforms in the whitelist (such as Uniswap, Sushiswap, Compound, Maker, Aave, etc.). In addition, in order to control risks, upper limits on the amount of funds allocated to different agreements will also be set to avoid excessive potential risks caused by hacking incidents. The basic parameters of these smart contracts cannot be modified arbitrarily, and any modification needs to be approved and executed with the approval of fund investment users.
After users deposit their funds into the smart contract of the fund, they will also receive a voucher. And this certificate is the ERC-20 token ckToken, which represents the user’s share in the fund. It will allocate the user’s specific token share based on the overall value of the fund at the time of entry and the value of the user’s deposited encrypted assets. Therefore, ckToken also Represents the proportion of user ownership in the fund.
The user uses ckToken, first, it can be used as an exit certificate to obtain the corresponding income (profit or loss) after exiting, or it can be traded in the secondary market.
When the user withdraws, the exchange rate of ckToken will be obtained by dividing the total value of fund assets at the time of withdrawal by the total amount of ckToken at that time. In addition, upon exit, the contract will destroy the corresponding ckToken and return the corresponding assets.
Like all fund management services, investment users need to pay certain fund management fees to fund managers. This part of the fee is set by the fund manager. Since Cook is a liquid DeFi fund, it can enter or exit at any time, and its income is calculated based on the block time. The management fee will be determined based on the total asset value managed by the fund at a certain block time, the annualized management fee rate, and the number of blocks mined by Ethereum in a year.
In addition, the Cook agreement can also capture fees: fund managers also need to pay 2% of their fund management fees to the agreement as agreement fees. If fund managers use COOK tokens as fund management fees, they can be exempted from paying agreement fees.