The act of speculating on cryptocurrency price movements via a CFD trading account, or buying and selling the underlying coins via an exchange, is known as cryptocurrency trading.
CFD TRADING ON CRYPTOCURRENCIES
CFD trading is a type of derivative that allows you to bet on bitcoin price changes without having to possess the underlying currencies. You can go long ('buy) if you believe the value of a cryptocurrency will rise, or short ('sell') if you believe the value will fall.
Both are leveraged instruments, which means you only need a little deposit (known as margin) to have full exposure to the underlying market. Because your profit or loss is still determined based on the total size of your investment, leverage magnifies both earnings and losses.
BUYING AND SELLING CRYPTOCURRENCIES VIA AN EXCHANGE
When you buy cryptocurrencies on an exchange, you're actually buying the coins. To begin a position, you'll need to open an exchange account, deposit the full value of the asset, and keep the cryptocurrency tokens in your own wallet until you're ready to sell.
Exchanges have their own high learning curve because you'll need to wrap your head around the technology and figure out how to interpret the data. Many exchanges also have limits on the amount of money you can deposit, and maintaining an account can be costly.
HOW DO CRYPTOCURRENCY MARKETS WORK?
Cryptocurrency markets are decentralized, meaning they are neither issued nor supported by a central authority like a government. Instead, they're distributed across a computer network. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, can be purchased and sold on exchanges and held in 'wallets.'
Cryptocurrencies, unlike traditional currencies, only exist as a shared digital record of ownership maintained on a blockchain. A user sends bitcoin units to another user's digital wallet. The transaction isn't deemed complete until it's validated and added to the blockchain, which is done through a process known as mining. New cryptocurrency tokens are frequently created in this manner.
WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN?
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger of data. This is the transaction history for each bitcoin unit, showing how ownership has changed over time. Blockchain records transactions in 'blocks,' with fresh blocks added to the chain's front end.
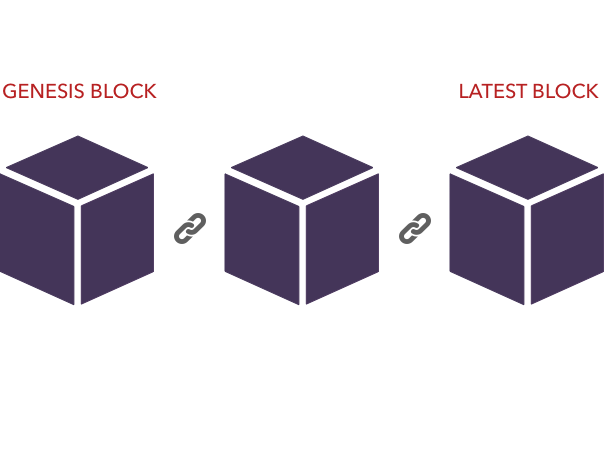
Normal computer files do not have the security features that blockchain technology does.
NETWORK CONSENSUS
A blockchain file is always saved on numerous computers across a network, rather than in a single location, and is usually visible by all members of the network. This makes it both transparent and difficult to change, as there is no single weak point susceptible to hacking, human or software error.
CRYPTOGRAPHY
Cryptography - a combination of advanced mathematics and computer science – connects the blocks. Any effort to change data breaks the cryptographic linkages between blocks, and computers in the network can rapidly identify it as false.
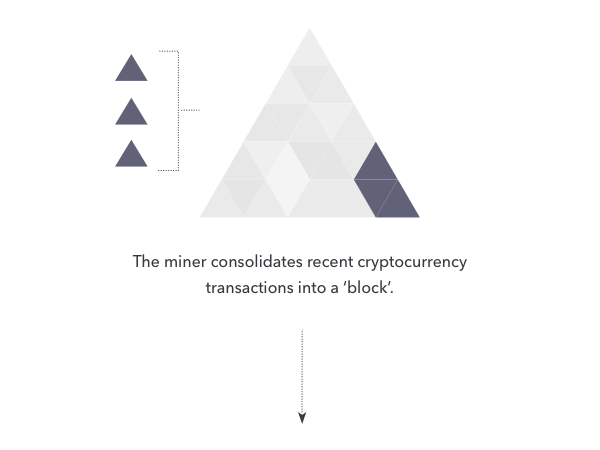
WHAT IS CRYPTOCURRENCY MINING?
The process of checking recent bitcoin transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain is known as cryptocurrency mining.
CHECKING TRANSACTIONS
Mining computers choose pending transactions from a pool and confirm that the sender has sufficient funds to complete the transaction. This is accomplished by comparing transaction data with the blockchain's transaction history. A second check ensures that the sender authorized the cash transfer using their private key.
CREATING A NEW BLOCK
Mining computers compile legitimate transactions into a new block and try to discover a solution to the difficult process to generate the cryptographic link to the previous block. When a machine successfully generates the link, it saves the block to its own copy of the blockchain file and broadcasts the change to the rest of the network.


WHAT MOVES CRYPTOCURRENCY MARKETS?
Markets for cryptocurrencies are driven by supply and demand. Due to their decentralized nature, they are immune to many of the economic and political issues that plague traditional currencies. While there is still a great deal of ambiguity surrounding cryptocurrencies, the following factors can have a big impact on their prices:
• Market capitalization: the overall value of all the coins in existence and how users believe this to be developing • Press: the way the cryptocurrency is depicted in the media and how much publicity it is getting
• Integration: the ease with which a cryptocurrency can be integrated into existing infrastructure, like payment systems for e-commerce.
• Major events: regulatory revisions, security breaches, and economic setbacks are all examples of key events.
HOW DOES CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING WORK?
You can trade cryptocurrencies with IG using a CFD account, which are derivative instruments that allow you to guess whether the value of your selected cryptocurrency will rise or decline. Prices are expressed in traditional currencies, such as the US dollar, and you never possess the cryptocurrency.
CFDs are leveraged products, meaning you can open a position for a portion of the trade's entire value. Leveraged products can increase your profits, but they can also increase your losses if the market goes against you.
WHAT IS THE SPREAD IN CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING?
The spread is the difference between a cryptocurrency's advertised buy and sale prices. When you open a position on a bitcoin market, you'll be given two prices, just like many other financial marketplaces. You trade at the buy price, which is slightly above the market price, to begin a long position. You trade at the selling price, which is somewhat below the market price if you want to initiate a short position.
WHAT IS A LOT IN CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING?
Lots - batches of cryptocurrency tokens designed to standardize the size of trades – are frequently employed in cryptocurrency trading. Because cryptocurrencies are so volatile, lots are often relatively small: the majority is only one unit of the base cryptocurrency. Some cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are traded in larger lots.
WHAT IS LEVERAGE IN CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING?
Leverage is a method of acquiring access to huge sums of cryptocurrencies without having to pay the entire worth of your trade upfront. Instead, you make a tiny down payment known as margin. When you terminate a leveraged position, the full magnitude of the trade determines your profit or loss.
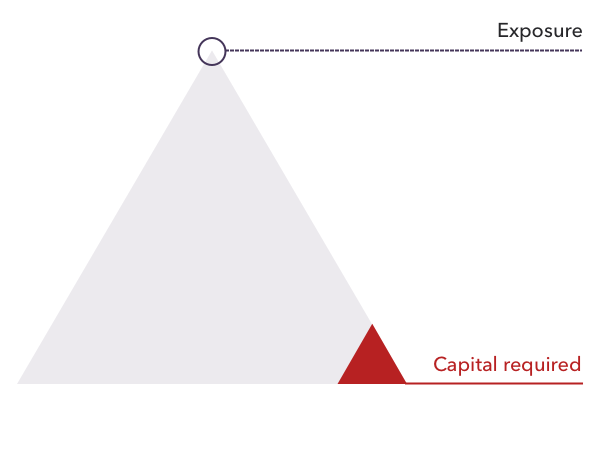
While leverage increases your profits, it also increases your risk of losses, potentially losses that surpass your margin on a single trade. As a result, learning how to manage risk is critical when using leveraged trading.
WHAT IS THE MARGIN IN CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING?
Margin is an important component in leveraged trading. It's the word for the first deposit you make to begin and keep a leveraged position open. When trading cryptocurrencies on margin, keep in mind that your margin requirements will vary based on your broker and the size of your trade.
In most cases, the margin is expressed as a percentage of the total position. For example, trade on bitcoin (BTC) may require payment of 15% of the total value of the position before it can be opened. As a result, instead of $5000, you'd only need to deposit $750.
WHAT IS A PIP IN CRYPTOCURRENCY TRADING?
Pips are the units used to measure price movement in cryptocurrencies, and they correspond to a one-digit change in price at a given level. In general, valuable cryptocurrencies are traded at the 'dollar' level, thus a price change of a single pip from $190.00 to $191.00, for example, would be considered significant. Some lower-value cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are traded on multiple scales, with a pip ranging from a cent to a fraction of a cent.
Before you place a trade, make sure you read the instructions on your selected trading platform to ensure you understand the level at which price movements will be measured.
Now Check Here to Learn More About the Benefits of Trading Cryptocurrencies and High Conversion Forex Trading Signal: bitdotly/3ra9Naf (Copy and Paste in a New Tap and Remove DOT with actual .)