Understanding Ecology
Ecology is the study of the interactions between organisms with their environment and others. Derived from the Greek word oikos ("habitat") and logos ("science"). Ecology is defined as a science that studies both the interaction between living things and the interaction between living things and their environment.
https://steemitimages.com/DQmVUU8TiAmaXpcvBacFA79JMEPVcCV9ePjpMdntnCeXcz7/51yhdRbgmCL.SX353_BO1%2C204%2C203%2C200.jpg
image source
An organism always interacts with each other and the environment. There is a science that specifically studies the relationship between the organism and its environment. The science is known as Ecology. On this good occasion mimin will discuss about the Definition of Ecology, Principles in Ecology, Ecological Pyramids, Types of Ecology, and Ecological Examples.
Principles of Ecology
The principles adopted in Ecology include:
- Interaction
- Interdependence
- Diversity (diversity)
- Harmony
- Continuous Capability (sustainability)
The Ecological Pyramid
The ecological pyramid is a picture of the inter-tropical arrangement can be based on population density, dry weight, and the ability to store energy in each trophic. The trophic structure can be arranged in accordance with the eating and eating relationships between the trophic which generally show the shape of a cone or a pyramid.
There are three types of ecological pyramids such as number pyramids, biomass pyramids, and energy pyramids.
- Number Pyramid
On the pyramid the number of compositions of organisms, belong to the trophic level presented in the number pyramid. The number pyramid is a pyramid that shows the number of organisms at each trophic level.
Organisms at the first trophic level are usually abundant, while the second, third and subsequent trophic levels are diminishing. Communities that mostly have normal numbers are more plants than herbivor organisms.
Similarly, the number of herbivors is always more than the number of carnivor level I. Level I carnivors are also always more than the level II carnivor and so on.
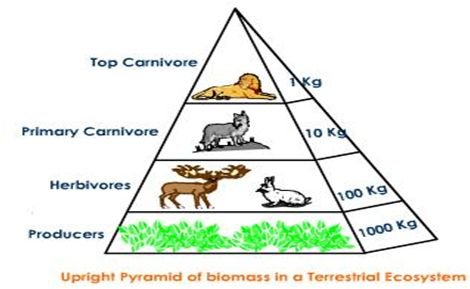
- Biomass Pyramid
Understanding The pyramid of biomass is a pyramid that describes the total dry mass or mass of living organisms from each trophic level in an ecosystem in a given time.
The pyramid of biomass has a more realistic portrayal than the number pyramid. The function of the biomass pyramid is to describe the mass mix of all organisms in a particular habitat, and expressed in grams.
To avoid habitat destruction, it is usually a measurement using the sample method. The sample is measured, then the total of all biomass is calculated by a certain ratio. The assessment, resulting in more accurate information about the ecosystem.
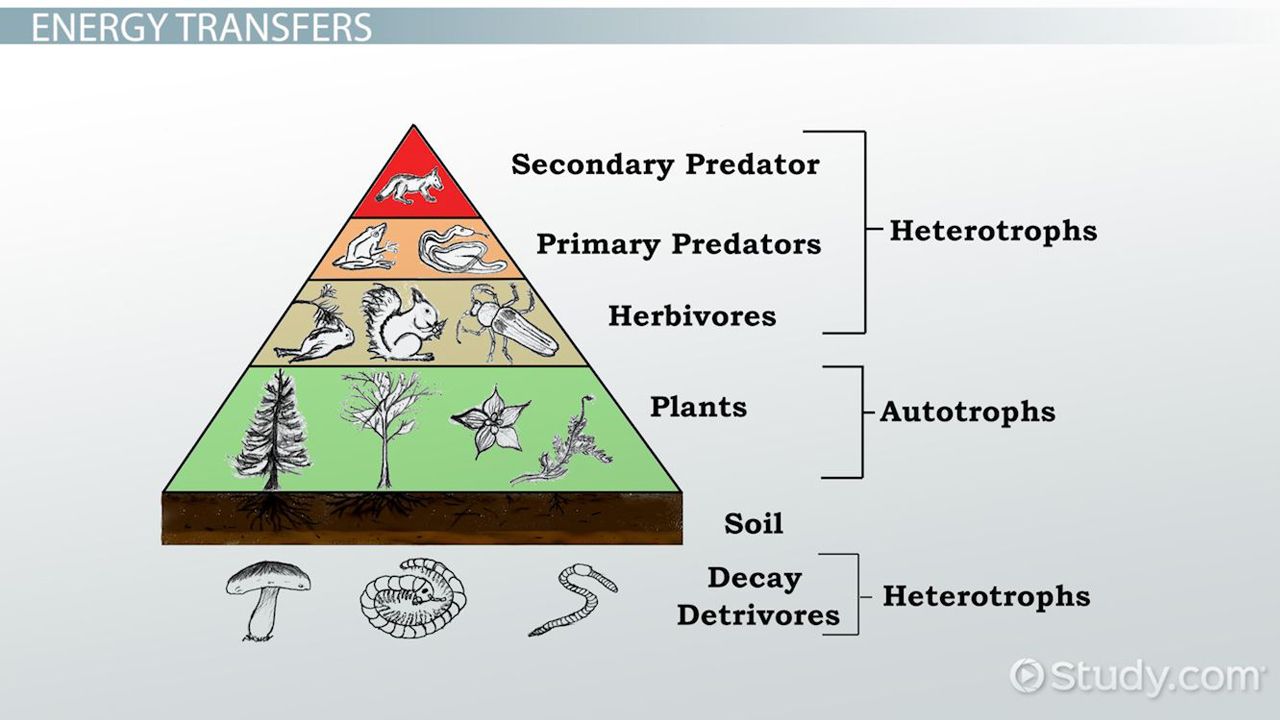
- Energy Pyramid
The definition of the energy pyramid is a pyramid that describes the decrease of energy at each stage of the trophic level. The energy pyramid is based on long-term observations.
At the energy pyramid provides the most illuminating description of the energy flow in the ecosystem of the number pyramid, and the biomass pyramid. At the energy pyramid there is a decrease in the number of energies in a row from the lowest trophic level to the highest trophic level.
The following causes the lack of energy at each trophic level:
- Only partly on the food that is captured and eaten by the next trophic level
- The food eaten will not be entirely digested and some are removed as waste
- Only on the part of the digested food becomes part of the body of the organism, while the rest is used as a source of
energy.
Types of Ecology
There are several types of ecology include:
Forest Ecology
Understanding Forest Ecology is a study that studies the interaction between living things and the environment. This interaction is so strong and complex that it proves that ecology is environmental biology (Eviromentalbiology).
Marine Ecology
Marine ecology is a study of marine ecosystems. Marine water ecosystems are distinguished over oceans, beaches, estuaries, coral reefs, and seagrass beds. Oceanic habitat is characterized by high salinity with a Cl ion reaching 55 {b32ad327e9f68ea504e024eb5395ab8ecfcbdd806be5c18267fa9f55623c3d39} especially in tropical marine areas, due to high temperature and large evaporation.
In the tropics the sea temperature is about 25 ° C. High and low temperature differences are high. The boundary between the hot water layer at the top and the cold water at the bottom is called the termocline area.
Whereas in cold regions, the temperature of the seawater is evenly distributed so that the water can be mixed, the sea surface area remains fertile and many plankton and fish. The movement of water from the shore of the middle causes the upper water to drop down and vice versa, thus allowing the formation of a good food chain. Marine habitats can be distinguished by their depth and surface area horizontally.
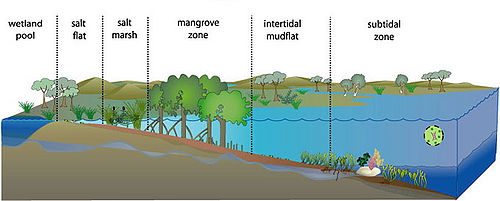
Estuary Ecology
Estuary Ecology (estuary) is where the river with the sea. The estuaries are often limited by large intertidal slabs or salt marshes. The salinity of the water changes gradually from freshwater to sea. This salinity is also influenced by the daily cycle with its tidal water. Nutrien from the river enriches the estuary.
Seagrass Ecology
Seagrass Ecology usually forms a vast seagrass on the seafloor that is still accessible by the sunlight that fills for its growth. Seagrasses live in shallow and clear waters at depths between 2-12 m, with good water circulation. Circulating water is required to transmit nutrients and oxygen, and bring the outcome of seagrass metabolism out of the seagrass beds.