Over the past decades, transplantation has become one of the most studied branches of medicine, its development dates back to the 20th century and has been developing tirelessly throughout this time. And now interesting and optimistic news came from the fields of medical research - scientists working in the field of stem cell research have discovered a new way of obtaining them.
According to a Japanese research team, they managed to obtain pluripotent stem cells by immersing blood in acid. To do this, they used lymphocytes from mice, which were exposed to weak acids for thirty minutes.
The results were positive, and now the group is faced with the task of conducting the same experiment on human cells. Scientists published their research in the journal Nature, where they described their experiment in detail. In their opinion, the new method will allow not only to reduce the cost, but also to significantly speed up the process of stem cell production.
The cells obtained by the new method were called STAP-cells (STAP - acquisition of pluripotency under the influence of stimuli). According to one of the authors of this work, Haruko Obokata of the Japanese laboratory Riken, the results obtained surprised the researchers and gave them additional incentive to work.
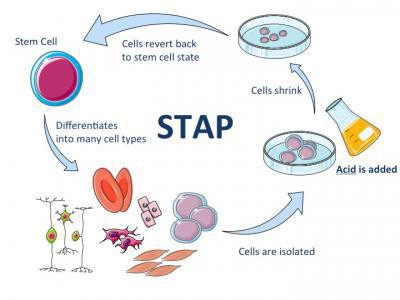
Source
“It's nice to think about the new opportunities that are opening up before us in connection with the results of this study, not only in terms of regenerative medicine, but also in the treatment of cancer” - Haruko Obokata
In turn, Chris Mason, professor of regenerative medicine at University College London, says that if the transformation of human cells by a new method is proved, it will be possible to speak safely about a new era of personalized medicine. Thus, for example, new ways of developing methods of treatment may open up, taking into account the genetic nature of the cells of each individual patient. He also noted that at the moment, stem cell treatment requires serious financial and time costs, so great hopes are pinned on the new method.
His colleague, Professor Robin Lovell-Badge of the British Medical Research Council, also supports and develops Mason's thought, considering this discovery to be revolutionary and breakthrough. However, despite the optimistic mood, the professor still notes that there are still too many questions to be resolved. And he explains that it will be a long time before researchers fully understand the nature of cells and evaluate the possibility of their use. In his opinion, the main mystery remains the process of "transformation" of the cell, that is, how the acidic environment leads to the reprogramming of blood cells, because when we eat lemon or taste vinegar, nothing happens to our ordinary cells.
Interesting:
*The founder of experimental transplantation of vital organs, in particular the heart, is Alexis Carrel, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1912.
*Earlier, Japanese and British scientists received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of a method for transforming skin cells into stem cells using genetic reprogramming.
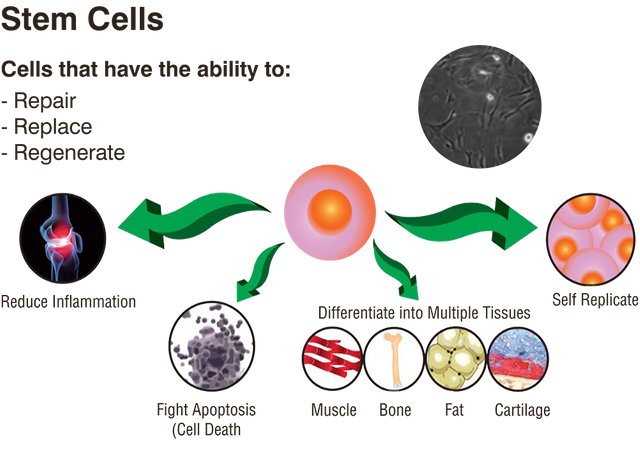
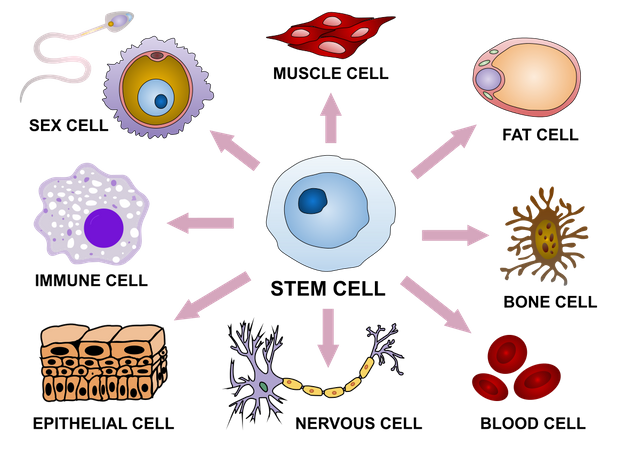
*Since stem cells can transform into cells of any other type, this ability has become a major focus of research in regenerative medicine.
This post was resteemed by @steemvote and received a 5.74% Upvote. Send 0.5 SBD or STEEM to @steemvote
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit