Blood Groups and Types
http://www.biosciencenotes.com/blood-group-and-blood-grouping/
Introduction
The term "blood group" refers to the entire blood group system comprising red blood cell antigens whose specificity is controlled by a series of genes which can be allelic or linked. Very closely on the same chromosome.
"Blood type" refers to specific pattern of reaction to testing antisera within a given system.
The main reason to know your blood group are if you you need blood transfusion or if you are pregnant or sick till the extend of needed blood in your blood.
✓Blood Compatibility Testing
Is conducted in medical laboratory to identify potential incompatibility between individuals and blood donor's blood Types, which can occur in blood transfusion.it is also used to diagnose and prevent some complication of pregnancy that can occur when the baby has a different blood group from the mother. Blood Compatibility testing include blood typing, which detects the antigens on red blood cell that determine a person's blood type; testing for unexpected antibodies against blood group antigens (antibody screening and identification); and in the case of blood transfusions, mixing the recipient's plasma with the donor's red blood cell to detect incompatibilities (cross matching). Routine Blood typing involves determining the A B O and RhD (Rh factor) type,
Note 1 involves both identification of ABO antigens on red blood cell (forward grouping) and identification of ABO antibodies in the plasma (reverse grouping) other blood group antigens may be tested for in specific clinical situations.
O positive blood type determined by the tube method from left to right: the patient's red blood cells do not agglutinate With the anti-A and anti-B reagents, but do agglutinate With the anti-D reagent the patient's plasma agglutinates
Type A1 and B red blood cells.
Blood compatibility testing generally makes use of reactions between blood group antigens and antibodies specifically the ability of antibodies to cause red blood cells clump together when they bind to antigens on the cell surface, a phenomenon called agglution techniques that reallying on antigens -antibody reactions are termed serologic methods,and several such methods are available, ranging from manual testing using test tubes or slides to fully automated systems.blood types can also be determined through genetic testing,which is used when conditions that interfere with serologic testing are present or when a high degree of accuracy in antigen identification is required.several conditions can cause false or inconclusive result in blood compatibility testing. When these issue affect typing, they are called ABO discrepancies. ABO discrepancies ABO discrepancies must be investigated and resolved before the person's blood type is reported. Other sources of error include the "weak D" phenomenon, in which people who are positive for the RhD antigen show weak or negative reactions when tested for RhD antigen and the presence of immunoglobuling antibodies on red blood cells, which can interfere with antibody screening cross matching and typing for some blood group antigens.
•Blood Requisition
After the decision to transfuse blood is take the next step should be to order a Requisition during which the following steps need to be remembered.
✓Cross-Matching
Is a test performed before a blood transfusion as part of blood compatibility testing normally, this involves adding the recipient's Blood plasma to a sample donor's red blood cells if the blood is incompatible, the antibodies in the recipient's plasma will bind to antigens on donor red blood cells.this antibody- antigen reaction can be detected through visible clumping or destruction of the red blood cells,or by reaction with anti- human globulin.
Along with blood typing of the donor and recipient and screening for unexpected blood group antibodies crossing the matching is one of a series of step in the pre-Transfusion testing in some circumstances an electronic cross- match can be performed by comparing records of the recipient's ABO and Rh blood type against that of the donor sample.
In emergencies blood may be issued before cross-matching is complete
Cross-matching is also used to determine compatibility between a donor and recipient in organ transplantation.
The main components of blood are:
✓ red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body
✓white blood cells, which play a crucial role in the immune system.
✓plasma, which is yellowish liquid that contain protein and salts
✓platelets, which enable clotting
The blood group will depend on which antigens are on the surface of the red blood cells.
Antigens are molecules they can be either proteins or sugars.the types and features of antigens can vary between individuals, due to small genetic differences.
The antigens in blood have various function including:
•transporting other molecules into and out of the cell.
•maintaining the structure of red blood cells
•detecting unwanted cells that could cause illness
Scientist use two types of antigens to classify blood Types:
•ABO antigens
•Rh antigens
Antigens and antibodies play a role in the immune system defense mechanism.
White blood cells produce antibodies.these antibodies will Target an antigen if they consider it a foreign object.
This is why it is essential to match blood types when a person needs a transfusion.
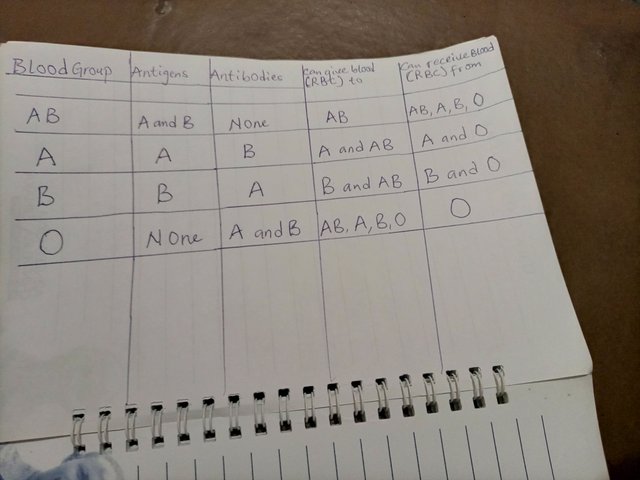
There are four ABO Groups
•group A: the surface of the red blood cells contains A antigen, and the plasma has anti-B antibody. Anti-B antibody would attack blood cells that contain B antigen.
•group B: the surface of the red blood cells contains B antigen, and the plasma has anti-A antibody. Anti-A antibody would attack blood cell that contain A antigen.
•group O : the plasma contains both anti-A and anti-B antibodies, but the surface of the red blood cells does not contain any A or B antigens.since these antigens are not present, a person with any ABO blood type can receive this type of blood.
✓ Blood Group Names
Your blood group depends on which antigens occur on the surface of your red blood cells.
Your genetic make-up,which you inherit from your parents, determines which antigens are present on your red blood cells.your blood group is said to be:
√ A +(A positive) if you have A and rhesus antigens.
√ A - (A negative) if you have A antigens but don't have rhesus antigens.
√ B +(B positive) if you have B and rhesus antigens.
√ B -(B negative) if you have B antigens but don't have rhesus antigens.
√ AB +(AB positive) if you have A,B and rhesus antigens.
√ AB -(AB negative) if you have A and B antigens but don't have rhesus antigens.
√ O +(O positive) if you have neither A nor B antigens but you have rhesus antigens.
√ O -(O negative) if you don't have A, B rhesus antigens.
✓ Donating Blood
Giving blood is sample of and saves lives.the Blood transfusion services nerds people of all blood Groups to donate blood, but especially if you have one of the rarer blood Groups. By donating blood, you will find out what blood group you are.
treatment-medication/blood-tests/blood-groups-and-types
Reference
You have done a great research on blood qroups and type it very necessary for people to know they blood types
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good teacher weldone..I wish I know my blood group self....
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Welcome dear
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Wow.
Great, quiet inspiring
Thanks for sharing with us
We really appreciate dear
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good work done
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
So amazing, thanks for sharing.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit