First of all, hello to all, where I love today. Share this beautiful job. My mission is to explore the human brain for everyone to benefit. Welcome, my friends, let's start
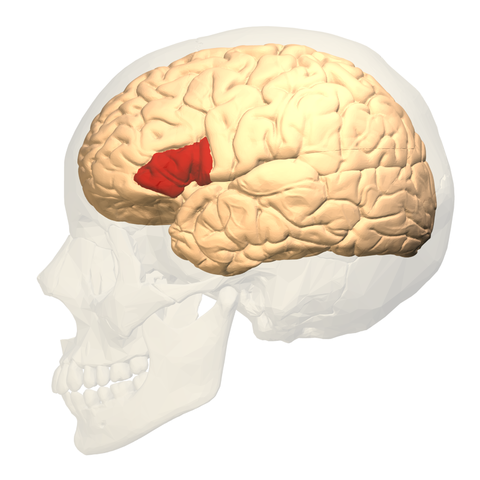
Stimulate the body's tonsillus (tonsils) by electromagnetic pulses - the human brain area responsible for memory and emotional behavior, improves image recognition. Neurologists conducted such an experiment and found that after a day, after stimulation, the subject begins to recall things that show him better than immediately after the presentation!
It reminds us of some inhuman experiences with anatomy, but in fact everything is not too scary. Experiments were conducted at Emory University Hospital in 14 patients with epilepsy. Here, for these patients, an intracranial control procedure is performed by diagnosing invasive out-of-seizures, during which the sensor electrodes are injected into the brain. Along with epilepsy, doctors conduct a variety of experiments, often no analogues in the history of science.
They describe their findings for the first time as a result of electrical stimulation of certain parts of the brain, which consists of an additional short-term improvement in human memory. Within a few minutes, there is a marked increase in the ability to recognize objects that have already been displayed.
Recognition only improved the initial images, which were fixed devices, which were parts of the brain involved in the "reading." In the interval between the demonstration of this initial stimulus and stimulation of the brain region, patients showed a control group of other subjects. After electrostimulation of the brain, it turned out that patients remember only the best first group, but not the second.
In fact, it turned out that scientists were able to revive the memories of "necessary", and one day to induce the person's consciousness to remember them, not some other information. This was said by the main author of the work, Dr. Currie Inman (Currie Inman) of the Department of Neurosurgery.
Once this discovery is possible, it will be possible to create a device designed to provide medical care to patients with serious memory disabilities, for example, painful brain injuries. Also, such treatment will help patients with moderate cognitive impairment associated with various degenerative neurological diseases. Now of course this is not yet a question, but the first steps have been taken in this direction, establishing the theoretical basis for future therapeutic devices begins.
Scientists are looking at this study as a basis for further study of the possibilities of improving brain function in humans. Perhaps for us, healthy people, this sounds like a surplus, but there are people suffering from amnesia who need such treatment.
Stimulating the deep brain (molasses) with a direct current generated by a brain implanted device has already become a clinically proven means of treating movement disorders in Parkinson's disease, and this method is being tested to help with psychological disorders such as deep depression.
In contrast to non-invasive methods (without brain interference), deep brain stimulation allows to selectively work on specific sites, without unnecessary stimulation of other regions that can give unpredictable side effects.
The researchers have carefully studied the main functions of the mezuzah in emotional responses and learning, and understand the thresholds that must not override corrective motives. It turns out that stimulating the tonsils does not lead to emotional reactions, increasing heart rate or other excitement signs at current levels of up to 0.5 mA. The participants reported that they did not notice any external interference in the work of their bodies during electrical stimulation of the brain.
Neurosurgery said they did not directly affect the hippocampus, responsible for memory, believing that this could lead to undesirable consequences, and that it worked through the "interface" - tonsils. This option is due to long-term initial experiments with rodents, which revealed the function of almond-shaped bodies as control areas of all memory. It chooses which events and images are more important and "directs" attention to certain areas of the brain where "important" is stored.
Studies on humans almost exactly those experiments on rodents and the results obtained were quite similar. The material examined 160 images of neutral objects filmed in different places and asked them to say whether these objects were located inside or on the street. At the same time, after viewing 80 of them, participants received the experiment of electrical stimulation within one second after such a picture disappeared from the screen.
Then, almost immediately the survey was conducted and half of the original subjects (40 catalysts and 40 conventional). Patients did not recognize one group better than the other - all the estimates were statistically the same. But when the brain was re-energized in a day, the recognition of the 40+ 40 remaining objects brought the coveted result - those images that were stimulated the day before and remembered much more effectively.
In 79% of participants (11 out of 14) there was a general improvement in recognition after 24 hours compared with the test immediately after presentation. Showed greater effectiveness by patients with deep memory impairment due to disease, one of them forgot almost all unstimulated images, but showed good results for subjects with stimulation.
Experiments have also made it possible to better understand the electrical interactions within the human brain - valuable practical data have been obtained for experiments and techniques in the future. The next step will be a more accurate adjustment of the electrical stimulation parameters of the amygdala to pass tests for other types of memory - not only imagination, but also spatial and auditory. Studies must address events in the brain that will replicate situations that occur with a person in the real world.
Yes, the electrocroent treatment of stuttering is the age of the cave, and now the science moves forward with leaps and bounds and devices and sensors implanted soon in the brain will stop to cause a surprise. And it's amazing .

Photography, because, the definition, tonsillitis, (Blue), Hipcampos, (Yellow), Barihinal, cortex, (Pink), too, electrician, signals, from, all, the land, at the time of, the definition, workout, B, Rakognetyon. Author: Corey Inman. Source:
The brain is amazing. I study psychology and yes I am amaze by all the complexity of the brain. Thanks for your post !
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thank you my friend =)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
:)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by ahmed abu jabal from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews/crimsonclad, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows and creating a social network. Please find us in the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP. Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
شكرا للمشاركة
نشجعك على استخدام تاغ
#arab
في مقالاتك
كما و وضع روابط لمصادر الصور التي تستخدمها و مصدر المعلومات
حصلت على تصويت من
@arabsteem curation trail !
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit