From the science of biology, we have learned about the evolution of humanity that has been running for millions, but it does not want to dwell on how humans evolved from apes but wanted to state that science can provide scientific answers about how long this lifespan has lasted.

The Milky Way's Galactic Center in the night sky above the Paranal Observatory (the laser creates a guide-star for the telescope).wikipedia
The development of science has also given an ever-deeper picture of human existence in the universe. For thousands of years human beings have formulated their existence on the surface of a land which is then defined as a planet earth, and that the planet earth is very old; Thus, there has been considerable evidence gathered to explain the origin and age of planet Earth. How long human existence on earth and how old planet earth can be determined is because so much evidence is available and the ideas underlying the existing theory can (and have) tested various experiments.
Then we move the center of attention, that it turns out that the earth can be expressed as a small member of the solar system centered in the sun, that the sun is just a dwarf member of billions of stars in a cluster (galaxy), that there are so many galaxies in the universe. The question is, how can man explain this, and how old is this universe? How do we know the age of the universe?

The universe is astronomically everything that can be observed. Observable means that a 'part' of the universe can be seen, obtained by its information, and learned messages from that information. Apart itself may be very far out of human reach, for example, the moon as a 'close' sky object, even though humans once landed on the moon, but attempts to understand the moon will not be enough with two or three landing times; thus, inevitably to understand the information of such distant objects we can only rely on the information that reaches us. The form of information that reaches us universally is light, either visible light or energy in another form to us from different angles of the universe. We can understand the moon from the sunlight reflected by the moon's surface, we can tell a lot about stars from the stars at night, the sun at noon, or tell about the galaxy through the radio waves that reach us.
The task of later astronomers is to examine the available information and to construct a picture of our universe. How to arrange it? First, take careful observation and measurement; secondly, using valid laws of physics to build models and theories that are expected to explain observed phenomena, then, let go of all the prejudices and things that affect our judgment of explanations so that they become the result the objective. Then how the picture?
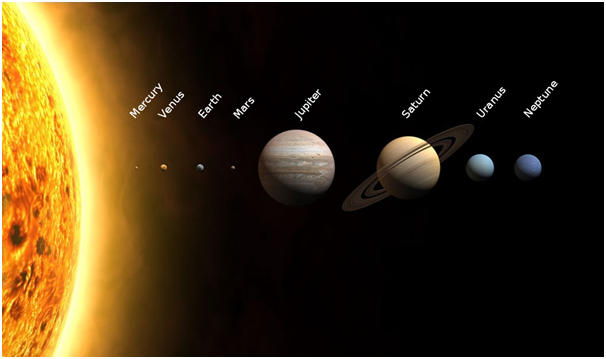
We start from our own Earth, Earth is the third planet, from the eight planets recorded around a star called the Sun, complete with many dwarf planets. Thus, the Earth family is named as the Solar System. In the family of the Solar System, there are dozens of moons and countless pieces of rock and ice chunks left over from the formation of the Solar System. Evidence for this has been widely accumulated, ranging from stones carried from the moon, broken rocks falling from the sky (meteorites), and space dust has taken away outside the atmosphere.
Then, turning to the Sun, the Sun is just one of the billions of stars forming a cluster of stars we call Milky Way galaxies, among the hundreds of stars that have been learned to have planets, just as the Sun. There are stars that prove to be older than the Sun, some are newly formed from galactic raw materials.
So how far is the distance we have traveled based on the picture earlier? If all the information is carried by light, while the light moves at a rate of 300,000 km per second. With this knowledge, it is found that for the star closest to the Sun takes 4.3 years for its light to the observer on Earth; and it takes 100,000 years to light across the Milky Way galaxy. Thus it introduced a unit of distance called the unit of light years, so that the distance of the star closest to Earth is 4.3 light years, and one light year is 9500 billion kilometers.
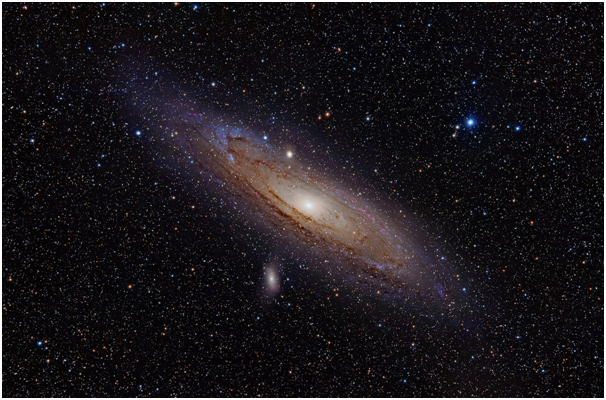

Away from outside the Milky Way galaxy, there are other galaxies. Observations with the largest telescopes in the world show that billions of galaxies in each direction we look at the sky. Around our galaxy, there is one greater than our galaxy in the Andromeda constellation, 2.4 million light-years away. So if we look at the Andromeda galaxy tonight, we have seen the light that came from there after 2.4 million years ago, (was it human then?). That's just one galaxy close to our galaxy, while there are still many more distant galaxies. So how old is the universe? Is it as far as the eye sees?
Astronomers also formulate a similar scale for time. The measurements that have been made show that the universe formed about 14 billion years ago in a very tight and hot state, known as the Big Bang. The sun and the Earth are formed from the raw materials of gas and dust from the Milky Way, about 4.5 to 4.6 billion years ago. The earliest evidence of life on Earth has existed about 3.7 billion years ago. With such a scale, if the record of human civilization was about 5000 years ago, how much human life is so much younger than the age of the universe, but how can we calculate the aging of the universe? We'll get there. thanks!

Best regard @ aneuktulot
references and related reading :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galaxy
https://www.space.com/52-the-expanding-universe-from-the-big-bang-to-today.html
https://www.quora.com/What-is-a-three-word-description-of-the-universe
https://www.descriptionari.com/quotes/universe/
https://www.britannica.com/science/universe
https://www.space.com/39815-hubble-suggests-universe-expanding-faster-study.html
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/universe/origins-of-the-universe/
Hi, I found some acronyms/abbreviations in this post. This is how they expand:
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit