Life goes on better with fulfilled promises.
I had made an earlier promise to liberate some folks this year on free information to make money in farming the easy way.
Today, I will be talking on pineapple; cultivation, species and yield per acre.
Pineapple fruits needs no introduction has its one of the best nourished fruit God has given to mankind


Yesterday at the farm, I had a slice and this made Me revert on my promise. I will be provide a well detailed explanation on planting pineapples, the various species best for cultivating and expected planting density on an acre to maximize yield.
Who doesn't love that sweet sugar taste?

It is one of the choicest fruit all over the world because of its pleasant taste and flavour. Pineapple is a good source of vitamin A and B and fairly rich in vitamin C and minerals like calcium, magnesium, potassium and iron.
It is also a source of Bromelain, a digestive enzyme.
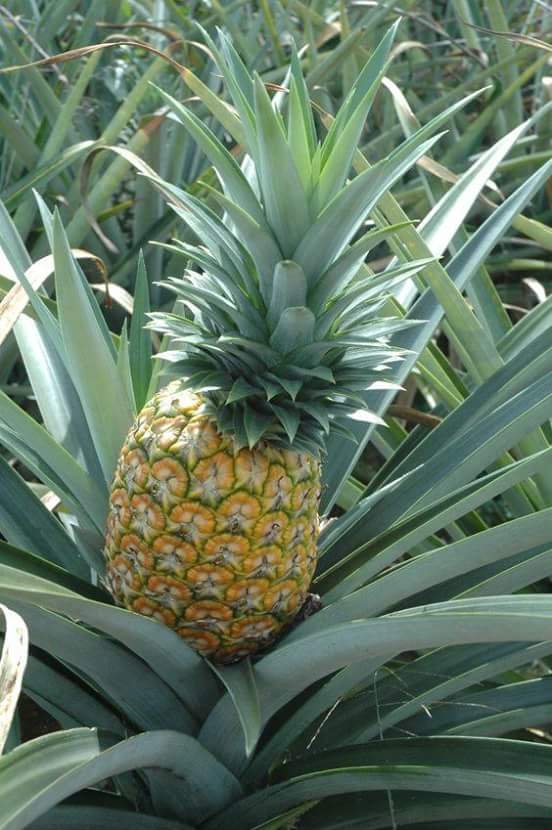

Now let's talk about cultivating pineapple.
General Requirements.
Temperature Range: 65 °F – 95 °F.
Rainfall: 60 cm/year (at regular intervals throughout the growing season).
Soil Type: Well-drained and acidic soil (4.5-5.5 pH).
Propagation: Crown, suckers and slips.
Flowering: Requires cooler temperatures.
PROPAGATION METHOD
The propagation of pineapple plants is mostly carried out by means of crowns. Seeds are not preferred owing to their slow growth. Other parts of the plant such as ‘slips’ and ‘suckers’ are also used for propagation. While preparing the crown for propagation, its lower leaves are peeled off to expose the ‘root primordia’. Crowns are then planted in a potting soil known as ‘Bromeliad Potting Soil’. Then the plants are grown in pots for few days before moving them in fields.
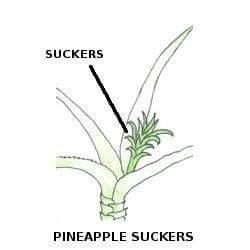
Sucker Propagation:
Planting suckers allow fast growth of pineapples in comparison to the traditional method of planting the crown. For this, you need to first identify them and learn to pick them. Suckers are found between leaves of fully-grown pineapple plants. They can be pulled out with the hand; you just have to twist them at their base. It also prevents the plant (sucker) from getting hurt. Rest of the procedure for growing pineapple plants is same as that used in the traditional method.
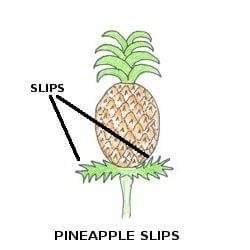
Slip Propagation:
Slips can be found at the base of pineapple fruits. These are tiny plants not found in all varieties of pineapples. The Smooth Cayenne and Rough Cayenne are commonly used for growing pineapples from slips. You can pull and plant the slips just like suckers. The method used for growing pineapples from slips is same as the traditional one.
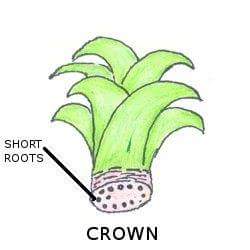
Crown Propagation:
It is the most common method of propagation in pineapples. The crown is pulled or cut off from the fruit and kept for rooting for about 3 weeks after which short roots emerge. The crown can then be used for potting in the house or field cultivation.
FIELD CULTIVATION OF PINEAPPLE
Climate and Soil Requirements of Pineapple
The pineapple plants grow well in a temperature ranging from 65 °F to 95 °F. Although it can tolerate cold temperatures for a short period during nights, the growth gets stunted and fruits become acidic when it is exposed to lower temperatures for a longer time. Well-drained and friable soil, rich in organic matter is considered as best for growing pineapples. The pineapple plants grown at high altitudes bear acidic fruits.
SPECIES (VARIETIES)
Top 5 species advices for planting in commercial scales are
- ND2
- SMOOTH CAYENNE
- SUGAR LOAF
- RED SPANISH
- QUEEN PINEAPPLE
(These selected few are in high demands in Nigeria)
Planting
Before planting, pineapple fields are well-prepared to suit this shallow rooted plant. Crowns prepared for plantation are sown at a depth of 10 cm in double-rows. A distance of 25-30 cm. is maintained between two plants, while two double-rows are kept 0.9-1.8 m apart. Mulching is used in pineapple fields for conserving soil moisture, maintaining the necessary temperature of soil and also for controlling weeds. In the mulching activity, entire field is covered with plastic sheets or bagasse (sugarcane pulp) is used.
Fertilizer Application
Nutrient requirements of the pineapple plant change across different regions. Like any other crops, pineapples too require nitrogen in greater quantities than any other soil nutrient. In Kenya, 472 kg nitrogen per hectare is used in the first year in 4 equal parts. For acidic soils, the application of magnesium sulfate proves to be beneficial. It is applied at a rate of 327 kg/ha in sandy-clay soils of Puerto Rico. Chelate is actually a chemical compound in which a metal atom is bound by other atoms. Iron, when applied with nitrogen in a chelated form, increases the crop yield as well as the fruit size.
Irrigation and Weed Control
For the cultivation of pineapple plant, irrigation is required only in the dry months of summer. Manual weeding is not recommended in pineapple fields, since it proves to be expensive and can also lead to soil erosion. Practice of mulching is the best option for controlling weeds.
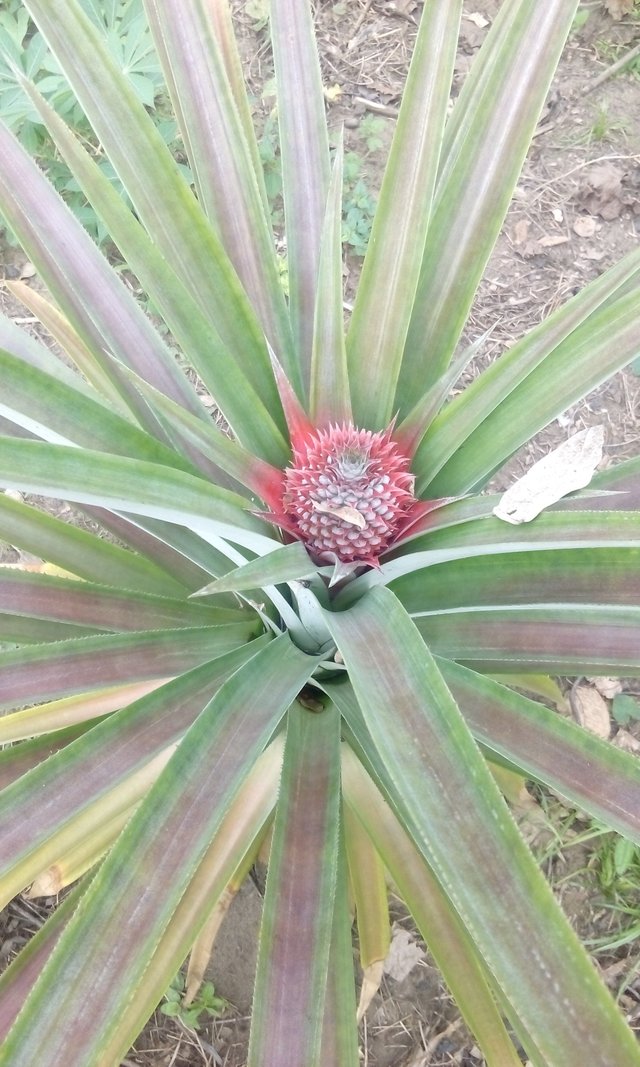

Flowering
Induction of flowering is undertaken to control the time of harvest and maturity in pineapples. Use of chemicals to control the natural and ‘organic’ growth of any plant is artificial and unnatural; however, cultivators tend to practice it to avoid excessive fruit production during peak periods. Earlier, ethylene gas was commonly used to control the fruiting process. Today, hormones such as a-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) are used. When a pineapple plant is 6 months old, it is treated with hormones to induce flowering.

Pests and Diseases
Care of pineapple plants becomes important in order to protect them from pests and diseases. Controlling the nematodes is necessary because they stunt pineapple growth. 1,3-dichloropropene or 1,3-D is efficient in controlling the nematodes and is applied using the fumigation process. In this process, the soil is smoked. Mealy bugs which cause the wilting of pineapple leaves are controlled by spraying pesticides. The fire ants which carry mealy bugs from one plant to another need to be controlled in this case. Root rot disease is controlled by improving soil drainage and fungicide application.

Harvesting
Summer fruits of pineapple mature early as compared to the winter ones. To know if the summer fruits are ready for harvesting, check whether the pineapple’s ‘eye’ is pale green. In the winter season, fruits turn light yellow at the base and are considered as ready for harvesting. For pineapple fruits to be ‘canned’, it is necessary to harvest them when fully ripe.
The activity of pineapple cultivation requires in-depth knowledge of different stages of growth of this plant. With proper care and maintenance you can grow pineapple in fields as well as in the indoor environment.
Thank you for the audience. I will be doing more of these for people to learn and get involved.
Great men are farmers.
Nb: some pictures are taken online.
Interesting read
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yes, indeed. I love pineapples :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Nice write up, widely researched. Can we have a private to talk more about this.thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yes, anytime you are ready. Reach me on +2349060259999 and on whatsapp +2347082876856. Will be glad to be of help
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Helpful write up, didn't know this much about pineapples
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
More info still coming.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Fine apple is not a single but also collection of fruits.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit