Tejvan Pettinger October 18, 2017 economics
A look at the economics reasons for high youth unemployment (16-25) in the UK.
youth-unemployment
During the recession, youth unemployment rose at a faster rate than the main unemployment rate. After peaking at 20% (1 million) in early 2012, youth unemployment has recently fallen to 12 % (2017)
The reasons for youth unemployment are fairly similar to other causes of unemployment. They include:
Lack of qualifications. Young people without any skills are much more likely to be unemployed (structural unemployment) A report by Centre for Cities suggest there is a correlation between youth unemployment and poor GCSE results in Maths and English. To some extent, the service sector has offered more unskilled jobs such as bar work, supermarket checkout and waiters. However, the nature of the labour market is that many young people lack the necessary skills and training to impress employers.
Geographical Unemployment. Youth unemployment is often focused in certain areas – often inner cities where there is a cycle of low achievement and low expectations. For example, the employment rate for 16-24 year olds is only 64% in the North East compared to a national average of 70%
Real Wage Unemployment. You could argue unemployment is caused by labour market rigidities and wages being above the equilibrium rate.Traditionally young workers have been paid lower ‘apprentice wages.’ In the UK, there is a minimum wage of £5.60 – for those aged 18-20 (2017). For those aged 21-24, the minimum wage is £7.05 – Age 21-24. (2017) – just below full minimum wage of £7.50. However, nominal wage growth has been muted leading to falls in real wages. This has increased potential for real wage unemployment – especially amongst younger workers.
Lack of graduate jobs. Many young people leave college with a degree but then find graduate jobs are in short-supply. Some find they can be over-qualified for the job market they enter.
Cyclical Unemployment. The biggest cause of unemployment in the UK is often cyclical/demand-deficient unemployment. This is unemployment caused by the falling output which occurs during the recession. During the 2008 recession, youth unemployment increased at a faster rate than the actual unemployment rate. It is often young workers who are more likely to experience unemployment; this is because with the least experience they are the easiest to remove from the labour market. Also, firms often don’t sack workers, but they do stop taking on new (young) workers.
Frictional unemployment. School leavers may just take time to find the right work.
Cultural/social factors. Youth unemployment is often highest amongst deprived areas where there is pessimism over job prospects. Youth unemployment is often higher among people who have a history of broken families, drug use or criminal record. Youth unemployment is also higher amongst ethnic minority groups. In 2016, the unemployment rate for young Bangladeshi and Pakistani people aged 16-24 was 28%. This compared to youth unemployment rates of 12% for the White ethnic group (the lowest) and 25% for people from a Black ethnic background (the second highest) (link)
Underground economy. Official unemployment may occur in areas where there is a thriving black economy. i.e. there are unofficial jobs for people to take. These jobs may be illegal such as dealing in soft drugs. However, it is hard to ascertain the extent of these unofficial jobs and it is easy to make sweeping generalisations about deprived areas.
Hysteresis. Hysteresis is the idea that past unemployment trends are likely to cause future unemployment. If young people have been unemployed in the past, it becomes increasingly difficult to get a job. This is because
Lack of jobs may cause young workers to become demotivated
A lack of past employment may cause firms to be unwilling to hire in the first place.
Unemployment means workers don’t have the opportunity to learn skills and on the job training.
A note on youth unemployment rates
The official unemployment rate for youths is influenced by the high number in education. When we say the youth unemployment rate is 18% – it doesn’t mean 18% of people 16-25 are unemployed.
It means 18% of those 16-25 year olds who are looking for work are unemployed.
The graph below shows many young people are in education/higher studies.
Inactivity rates amongst the young
youth-unemployment-inactivity
Inactivity rates include people who are classed as unemployed, but also includes people who are not economically active, people in education or not actively seeking work. Thus inactivity includes people in education and training, but also those discouraged to leave the labour market.
Why is youth unemployment rate higher than average?
Youth unemployment rate statistics skewed by relatively higher numbers in education.
Young workers least qualified with lowest levels of relevant skills. Therefore, less employable.
Some young workers leave university with degrees but find graduate jobs are in short supply.
Young workers may be perceived as less reliable by employers.
Young people who are unemployed – find it hard to break the cycle of no job – therefore no experience – therefore hard to get a job.
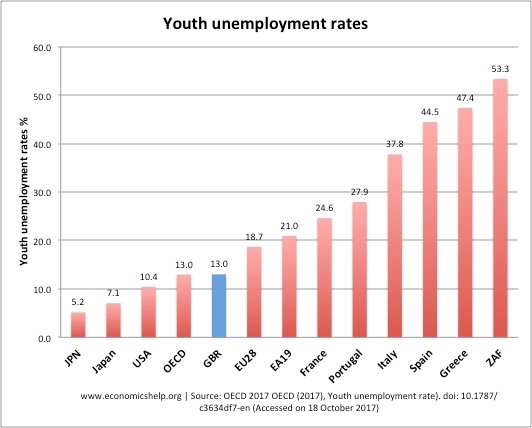
Global youth unemployment
youth-unemployment-global
Source: OECD
worth sharing article dear. Thanks for this information.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thanks for reading this
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
that is real problem all over the world
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
So glad that Steem is putting a dent in unemployment.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
yes steemit is a good platform for us
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Very informative article and great analysis.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thank u jnb
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
piece of advice .. do use some informative pictures
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
i will try to provide some thing better
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Wooo good job bro
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thanks for the points i will try to consider them in life for better future
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit