Abacas Exchange Overview
The Abacas Exchange exists to provide a medium for the exchange of marketable assets (base assets) that can be placed into custody and represented via a digital asset token.
Assets that can be tokenized include traditional assets (Currency, Stocks, Precious Metals), crypto-currencies (BTC, ETH) and many non-traditional assets.
The Abacas Exchange is unique in that only digital asset tokens may be traded. The tokenized asset is held in custody outside of the exchange and the custodial account is managed by an independent trust.

Investor Trading Diagram
Any two Abacas Asset tokens may be traded on the exchange. When orders are matched, the transactions are recorded and the Abacas ledger balance updated to reflect the change in ownership.
The base asset held in custody is unaffected by the exchange of Abacas Asset Tokens as depicted below.

Abacas Tokenized Asset
An Abacas tokenized asset is identified by a unique Abacas Token ID within the exchange (Example: @BTC for Bitcoin, @AAPL for Apple common stock).
The Abacas Token ID links to meta-data defining the specifics about the base asset on account with the custodian, custodial information including provenance, and the specific rules of the Abacas Protocol that apply to this token and the underlying asset.

Abacas Protocol
The Abacas Protocol is comprised Meta-Data, Rules and Procedures.
Meta-Data is captured on each party (Investor, Custodian, etc.), each base asset (Asset Type, Denomination, Identity, Provenance, etc.) and the corresponding Abacas Token.
The rules govern what procedures must be applied to each entity (party, base asset, token), and the orchestration of those procedures in a logical order.
Example: New Investor Registration Protocol

Fulfilled by Abacas / 3rd Party
An Abacas Tokenized Asset that is held in custody of a registered trust of the Abacas Exchange and fully supports all aspects of the Abacas Protocol is identified as “Fulfilled by Abacas”.
The Abacas Exchange provides the option for 3rd parties to manage the trust/custodial relationship outside of the Abacas Exchange. When this occurs, the asset being traded is identified as “Fulfilled by Party”. In the diagram below, the @AAPL token is fulfilled by Abacas as the Trust and Custodian are registered with the exchange.
Alternatively, Investor 2 has purchased dapAAPL tokens which are also tokens on Apple shares, but the trust management and custody of the apple shares are outside of the Abacas Exchange.

Liquidity / Market Rates
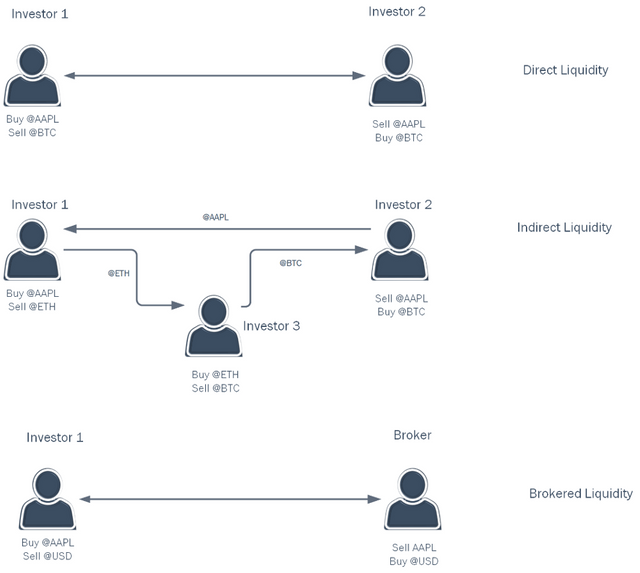
There are three types of liquidity in the Abacas Exchange:
Direct Liquidity occurs when two investors wish to exchange the same two asset pairs at a mutually agreeable price.
Indirect Liquidity occurs when three or more investors who’s orders when linked form a liquidity chain that fulfills part or all of each order at a mutually agreed price.
Broker Liquidity is essentially a market maker providing the ability to exchange fiat (@USD for example) for an asset that must be acquired external to the Abacas Exchange and then deposited into custody and the asset tokenized into the investor’s account.
External Market Rates are utilized in the Abacas Exchange for a sanity check on market orders. A market protected order will not fill unless the liquidity in the Abacas Exchange is within a specific spread tolerance from the market feed.
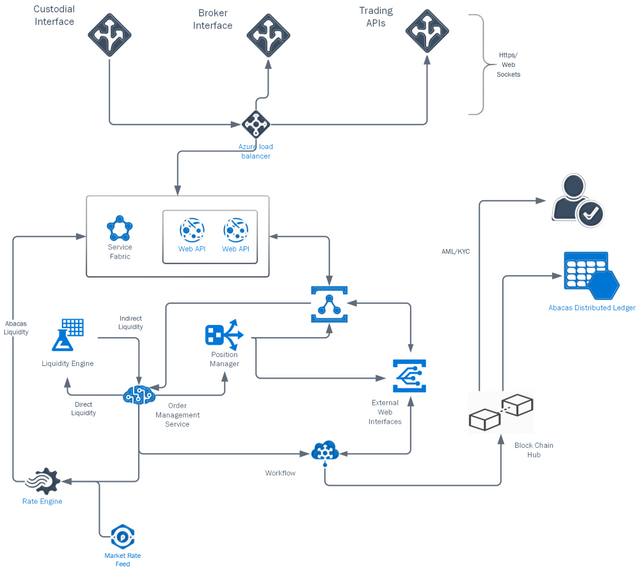
System Architecture
The Abacas Exchange is a cloud-based system providing access via web browsers and mobile applications. There are three primary users of the Exchange (Client/Investor, Trust/Oversight, Operations/Admin)

The services of the exchange are either scalable micro-services or distributed services in a cluster all of which are load balanced for scalability.
The Order Manager is the key service running the exchange and manages and monitors each asset pair order book of the exchange.
The Liquidity Engine monitors the Order Books and forms liquidity chains based around the most liquid asset pairs in the exchange (The Liquidity Core) and Machine Learning Pattern recognition of those liquidity links most relevant based on investor demand.
The Rate Engine receives market rates for the base assets in custody which is utilized for determining whether the bid/offer spread of the exchange is competitive, and to protect market/limit orders from manipulation based on the depth of the Abacas Order Book.
The Position Manager receives all activity from the Order Manager including changes in order status and those orders that are partially or fully matches. The activity creates the account position, transaction history and open order book which is then published through Web APIs to the client browser/mobile app.
The Web Applications are the forms and screens that a user sees in the web browser. These applications communicate with back end services through Web APIs that in turn connect with the services of the Abacas Exchange.
The Workflow Services include processes such as Accounting, Regulatory and Custodial interfaces as well as any workflows (data interchange) with 3rd party providers including AML/KYC, and Transactions/Ledger changes to the cloud-based repository and block chain ledger.
System Interfaces / APIs
The Abacas Exchange provides APIs over Https/Web Sockets as well as integration with blockchains both for value transfer, record keeping (Abacas Distributed Ledger) and blockchain service providers (AML/KYC).