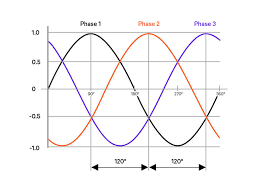
Three-phase AC supply consists of three alternating currents (or voltages) that are sinusoidal in nature and separated by a phase angle of 120° (one-third of a cycle). These three voltages or currents are typically denoted as Phase A, Phase B, and Phase C.
Sinusoidal Waveform: The voltage in each phase rises and falls in a sinusoidal pattern.
Phase Separation: Each phase reaches its peak and crosses zero at a 120° offset compared to the others.
Components of a Three-Phase System
Three Conductors (Lines):
Each carries an alternating voltage signal for one phase.
Commonly labeled L1, L2, and L3.
Neutral Conductor (Optional):
Provides a return path for current in some configurations.
Used in a "star" connection for distributing single-phase loads.
Ground:
A safety connection for fault conditions.
Types of Three-Phase Connections
Star (Wye, Y) Connection:
One end of each winding is connected to a common neutral point.
The other ends are connected to the line conductors.
Offers two voltage levels: phase voltage (voltage between line and neutral) and line voltage (voltage between any two lines).
Line voltage is √3 times the phase voltage.
Delta (Δ) Connection:
Each winding is connected end-to-end to form a closed loop.
No neutral point is present.
Only one voltage level exists, equal to the line voltage.
Advantages of Three-Phase Supply
Efficiency:
Three-phase power systems are more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances compared to single-phase systems.
Constant Power:
The power delivered is relatively constant compared to single-phase systems, which have pulsating power.
Reduced Conductor Size:
For the same amount of power, three-phase systems require smaller conductors compared to single-phase systems.
Suitable for Heavy Loads:
Ideal for operating heavy machinery, motors, and industrial equipment due to higher power capacity.
Applications
Industrial Use:
Drives heavy machinery, electric motors, and industrial processes.
Commercial Buildings:
Supplies HVAC systems, elevators, and lighting.
Power Transmission:
Preferred for distributing electricity over long distances due to its efficiency.
Key Characteristics
Frequency:
Typically 50 Hz (Europe, Asia, etc.) or 60 Hz (USA and some other countries).
Voltage Levels:
Transmission lines: High voltages (e.g., 11 kV, 33 kV, 132 kV).
Distribution: Reduced to safer levels (e.g., 230/400 V).
Balanced Load:
Ideally, the loads across all three phases are balanced, minimizing losses and improving efficiency.
Mathematical Relations in a Three-Phase System
Why Use Three-Phase Supply?
Three-phase AC is preferred over single-phase for most industrial and commercial applications because it provides:
Smoother and more efficient operation of motors.
Greater power density.
Improved voltage regulation.
Flexibility in load distribution.