Agriculture seems a very simple term, mostly associated with farming. But in fact, it is more than that. agriculture consists of numerous farm-related activities. The history of agriculture dates back thousands of years in time. Agricultural developments are largely dependent on different climates, cultures, and technology. In the civilized world, industrial agriculture based on large scale monoculture is widely practised. monoculture has become the dominant form of agriculture. Over the years, advancements in the field of chemistry, physics and botany have led to rapid mechanization of agricultural activities. Thus resulting in increased agricultural output. This is possible with the help of modern and accurate practices in agriculture.
Chickpeas farm
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE
Deliberate modification of earth surface for the cultivation of plants and rearing of animals and livestock is termed as agriculture. The main purpose of agriculture is to produce food. It includes rearing of animals, plants and other life forms for food, fiber, biofuel, and dairy products to sustain and enhance human life. Agriculture in the past played a key role in the rise and development of sedentary human civilization. Whereas domestication of animals created food in surplus that nurtured the development of the human civilization.
Though agriculture is more than farming, its primary purpose has always been to feed the population. The population of the world has crossed 7 billion. So we have to understand how to feed them. Also, we need to study how we have been able to do it successfully for over 10 thousand years. Domestication of not only animals but also plants are the core subjects here. studying them is necessary to understand the basics of agriculture.
BEFORE AGRICULTURE
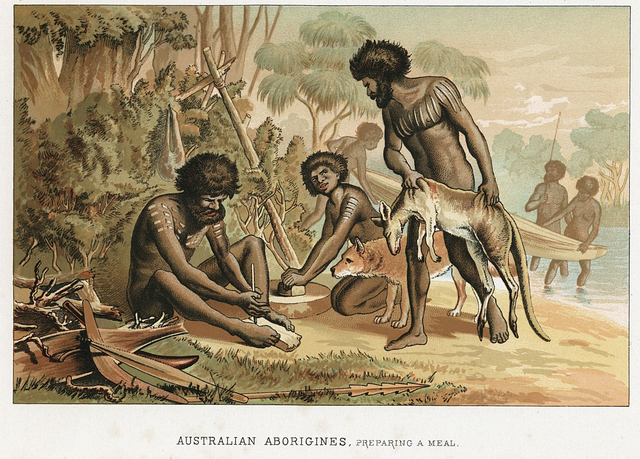
hunters preparing for meal
Humans before agriculture depended on hunting and gathering. This many times led to hunger and starvation. They hunted and fished for animals. also, they gathered plants bearing naturally growing food and moved on. As these groups moved they would consume food to exhaustion. Generally, these groups were of fifty people. These nomad groups moved with their animals to different areas according to what was available at that time for survival. Life was much simpler for them though there was a daily search for food. Hunting and gathering avtivities needed very little time. As a result, ample time was available to socialize as compared to modern times.
WHY SWITCH TO AGRICULTURE
About 10,000 years ago came this big change. Humans started to form their colonies to settle in one place. Geographers, anthropologist, and historians debate over what were the exact causes that led to this change. But generally, they all agree that environmental and cultural factors led to this change. As the last ice age ended, we started seeing environmental changes. There was a shift in available water resources. humans started searching for more stable and sustainable means to survive. Then there was the cultural element. People started to adapt and practice cultural norms. They developed their own belief systems that led to the development of stable societies in one place.
Today we see that the hunting and gathering societies form a very small proportion of the world’s population (0.005%). These are just a few tribes on the outskirts of modern society. They avoid any contact with the rest of the population. We see some of these groups and tribes in the most underdeveloped regions of the world such as Africa, South America, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and in the Amazons. Every once in a while we hear or read stories of these groups from contacts or interactions between the modern societies and these hunting groups.
FACTORS AFFECTING AGRICULTURE PRACTICES
Agriculture practices vary on the basis of the natural landscape, environment, socio-economic status of farms, farm area and main crops. Other factors include production systems, financial support, water reservoirs, animal husbandry, and marketing. Hands-on activity, animals trained to aid the production of food and fertilizers also play a major role in agriculture. Large scale capital and mechanization have come together to do massive industrialized farming. We have taken advanced steps that are incredibly productive, such as modified productive methods, genetically modified seeds, etc.
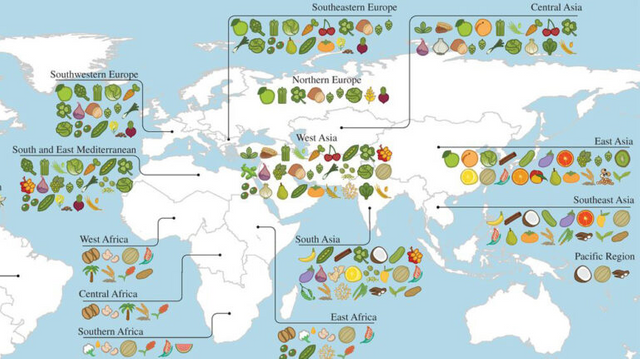
AGRICULTURE IN DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE WORLD
World map of agriculture
Primary regions of diversity of major agricultural crops worldwide.
With the invention of agriculture around 10,000 years, different types of crops were grown globally. This was largely influenced by the geography of the region and what would flourish in this region-specific climatic conditions. Also, it largely depended on what the product did for the actual diet of the people.
Latin and Central America
In Latin and Central America squash, berry, beans, potatoes were grown. Another important crop grown in this region was the maize. Maize is an early ancestor of corn. The inclusion of such food in the diet of people was the primary factor that led to higher calorific intake and more heartier diets for the people.

Africa and south-west Asia
When we move to Africa, we see the emergence of yams and some basic cereals grains such as rice and millets. When we move to South-west Asia we come across heartier cereal grains like wheat, beans, barley, oats, and rye. Presence of Mediterranean culture can also be felt in agriculture.
China
The emergence of rice took place in China. Rice mainly has two types, wet and dry. The interesting thing is that rice and soybean crops that are grown in Minnesota, had their ancestorial roots in East Asia.
South-East Asia
In south-east Asia, we see a little bit of difference in the variety of crops cultivated. We have what is called more vegetative plants and tropical plants that are not based on seed agriculture. But in fact, they are rut based or more tropical based. Mangoes, taros, and coconuts find their roots here. also, it largely depends on what the product did for the actual diet and what they meant for the advancement and development of different societies. farming in India also played a major role in the world of agriculture.
ANIMAL DOMESTICATION IN DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE WORLD
Cow shelter
As we have seen agricultural diversity across the globe, we also need to have a look at the various animals domesticated around the world. Given the incredible variety in the animal kingdom, what is amazing is that there are only a few that can actually be domesticated. Human societies have tried over time to domesticate animals, but only some could be used for food and agricultural activities. Cows, sheep, goats, camels, buffalos, donkeys horses are a few animals that are being domesticated for agricultural activities. We see that the Middle- East and South-West Asia were the center of the domesticated animals.
MAJOR TYPES OF PLANT CULTIVATION IN AGRICULTURE
Previously there were mainly two types of plant cultivation. First was vegetative planting and second was seed agriculture. Vegetative planting is the reproduction by cloning from existing plants. It began in south-west Asia. Whereas seed agriculture is through the intentional act of planting of seeds. Most of the cereal crops are grown by the process of seed agriculture.
FIRST AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION
The First Agricultural Revolution, also known as the Neolithic Revolution, is the transformation of human societies from hunting and gathering to farming. This transition occurred worldwide between 10,000 BC and 2000 BC, with the earliest known developments taking place in the Middle East.
It marks time in history about 10,000 years ago, where human societies changed drastically. Agriculture allowed spare time to develop religions, belief systems, infrastructure for overall development and much more. Farming created a surplus of food that allowed people to explore other aspects of life.
bullock cart used for agriculture
CLASSIFICATION OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS
Agricultural products are classified into food, fibers, fuels, and raw materials. Specific food include cereals, grains, vegetables, fruits, oils, meat, and spices. Fibers include cotton, wood, hemp, jute, bamboo, and flax. Raw materials include bamboo, lumber, resin, dyes, drugs, perfumes, ornamental products such as cut flowers and nursery plants.
CURRENT CHALLENGES FOR AGRICULTURE
Expensive and resource consuming agricultural practices
Intensive use of resources in industrial agriculture has led to rapid increase in the cost of production of agro products. Nowadays, all the developed nations have mechanized their agricultural practices by implementing automated irrigation systems and other agricultural machinery. This has resulted in increased consumption of water, fossil fuels, and tropical resources. Industrialization of agriculture and ever-increasing demand has increased the use of pesticides and fertilizers. Thus resulting in increased cost of productionOver-exploitation of resources
Modern agronomy, plant breeding, agricultural chemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers have sharply increased food production. But at the same time have caused ecological damages. Negative health effects are also a major concern. Selective breeding and modern practices in animal husbandry have increased the output of dairy products, but have raised the concern about animal welfare. Steroids, antibiotics, and growth hormones have increased the meat production, but have drastically reduced the nutritious values associated with them. Impact of agricultural practices on global warming have not been fully understood.Poor land management
Significant degradation of land and water resources have been observed in recent decades. Over exploitation of agricultural land to increase yield has degraded the quality of the soil. It has made soil devoid of the basic nutrients essential for the overall growth of plants. Mono-culture has drastically changed the chemical composition of soil for the worst.Food wastage
As per United Nation, one-third of the total food produced globally becomes useless during different stages of agriculture. Storage, handling, processing, transportation and distribution, all result in food wastage. Supermarket, restaurant and household consumers contribute highest in food wastage. Aesthetic appearance takes over the edibleness of food products resulting in food wastage. This leads to an overall increase in the cost of the food products.Unwillingness to adopt farming as a profession
Agriculture is a billion dollar industry across the globe. Still, the new generation is finding it difficult to accept farming and other agriculture-related activities as a potent means of earning.Poor government policies
Converting farms to commercial land is hurting agriculture. Governments across the globe have failed to understand the importance of agricultural land. The solution to feeding the ever-growing population is only possible in the agricultural sector. Proper inventory management is the need of the hour. Every year Millions of tons of food becomes useless due to poor storage facilities.
MEASURES TO TACKLE AGRICULTURAL CHALLENGES
Farmer at work in maize field in Bihar, India
Farmer at work in maize field in Bihar, India
In order to improve agricultural systems across the globe and raise rural prosperity, we need to take appropriate steps. This is possible with the help of advanced technology and innovative farming techniques.
We need to build a geographic information system to ensure precise and reliable geological data. Also, we have to ensure easy access to this data. Use of satellites for surveying and mapping to get exact demographic data needs to be taken into consideration for precise agricultural practices.
Farm-related knowledge, animal-related expertise and other technical inputs should be made available to the farmers at the appropriate time. This move is necessary to optimize the process of agriculture. Governments at district and rural level need to run awareness campaigns. This is necessary to ensure that farmers are aware of all government schemes. Use of Data analytics, artificial intelligence, geographic-tagging, and satellite monitoring is must to revolutionize agricultural ecosystem.
Upgradation of hospitals for domesticated animals, electricity, water and transportation facilities should be done. While modifying seeds and plant genetically, we have to ensure their resistance to climate change. It is necessary to study the impact of agricultural practices on the environment to strike a balance between mankind and nature. At last, we have to adopt sustainable methods of agriculture to ensure the survival of the human race.
Congratulations @mygadgetshub! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit