What is Deep Learning?
You might have heard the term, and if you haven't, you most certainly will as Deep Learning is currently pushing the limits of AI.
To put it simple: Deep Learning is a fancy term for a Neural Network with many hidden layers. A Neural Network is basically a mathematical model, inspired by the human brain, that can be used to discover patterns in data. The input (your data, for example a spoken sentence "I like apples") goes into the Neural Network, gets processed through the nodes in the hidden layer(s) and output comes out (for example, a prediction for the sounds/words the model estimates were said before, based on the earlier data it has seen). The difference between a Neural Network and Deep Learning is simply that most Neural Networks only have a couple hidden layers, and in Deep Learning there are many more, allowing for much more complex patterns.
What's the difference between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning?
As we know, Artificial Intelligence is the future. You might think of it as science fiction, but part of it is already part of our everyday lives!
The easiest way to think of their relationship is to visualize them as concentric circles with AI - the idea that came first - the largest, then Machine Learning - which blossomed later, and finally Deep Learning - which is driving today's AI explosion - fitting inside both.
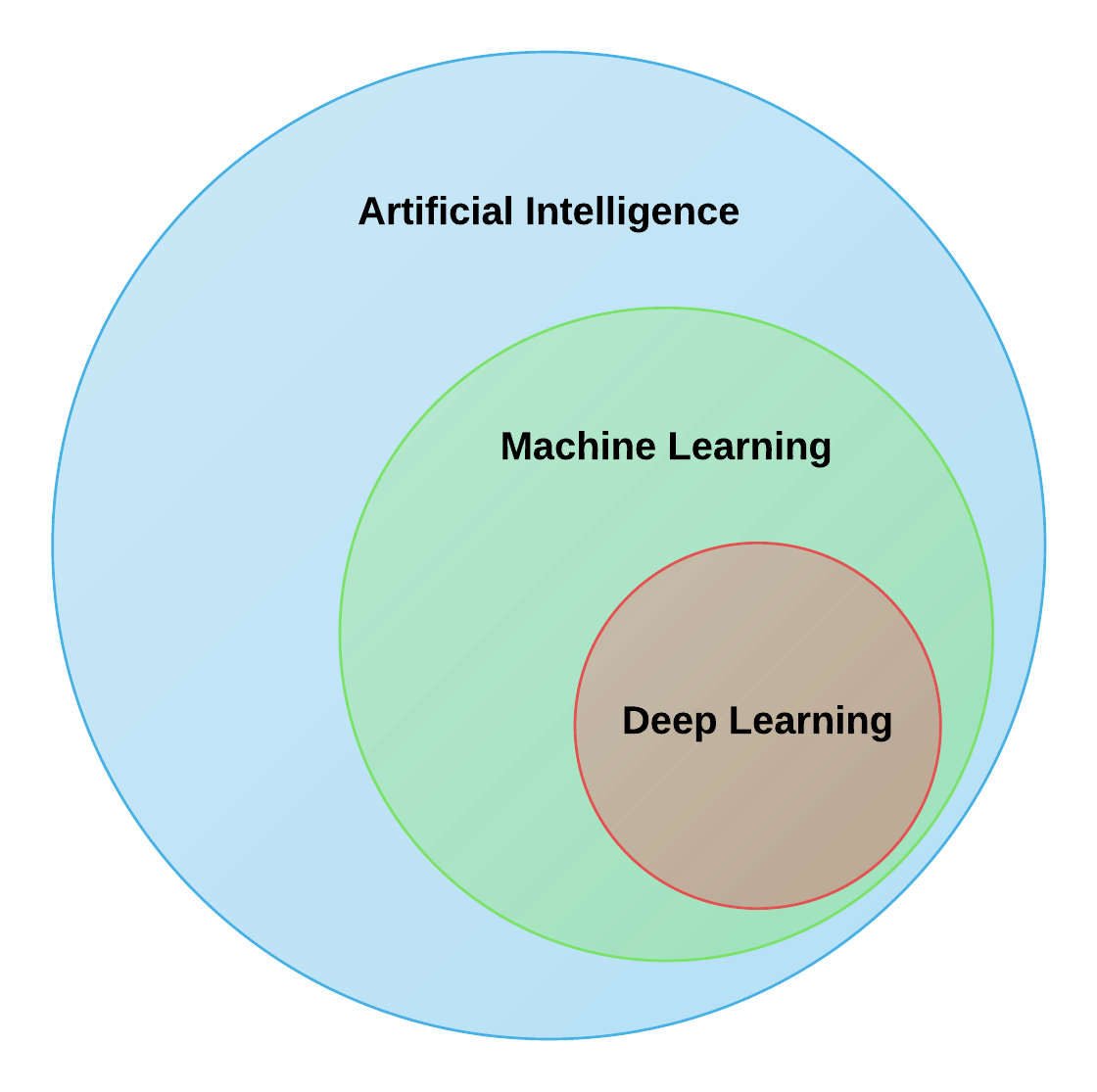
When we say AI we refer to human intelligence exhibited by machines. Machine Learning is an approach to achieve AI, and Deep Learning is a technique for implementing Machine Learning.
As mentioned earlier, Deep Learning is in turn achieved using Deep Neural Networks. Those are inspired by our understanding of the biology of our brains - all those interconnections between the neurons. But, unlike a biological brain where any neuron can connect to any other neuron within a certain physical distance, these artificial neural networks have discrete layers, connections and directions of data propagation.
You might, for example, take an image, chop it up into a bunch of tiles that are inputted into the first layer of the Neural Network. In the first layer individual neurons, then passes the data to a second layer. The second layer of neurons does its task, and so on, until the final layer and the final output is produced.
Each neuron assigns a weighting to its input - how correct or incorrect it is relative to the task being performed. The final output is then determined by the total of those weightings. So think of the following example: the attributes of a stop sign image are chopped up and "examined" by the neurons - its octogonal shape, its fire-engine red color, its distinctive letters, its traffic-sign size and its motion or lack thereof. The neural network's task is to conclude whether this is a stop sign or not. It comes up with a "probability vector", really a highly educated guess, based on the weighting. In our example the system might be 86% confident the image is a stop sign, 7% confident it's a speed limit sign and 5% it's a kite stuck in a tree, and so on - and the network architecture then tells the Neural Network whether it is right or not.
Today, image recognition by machines trained via Deep Learning in some scenarios is better than humans, and that ranges from cats to identifying indicators for cancer in blood and tumors in MRI scans. Google's AlphaGo learned the game, and trained for its Go match - it tuned its Neural Network - by playing against itself over and over and over.
Thanks to Deep Learning, AI has a bright future
Deep Learning has enabled many practical applications of Machine Learning and by extension the overall field of AI. Deep Learning breaks down tasks in ways that makes all kinds of machine assists seem possible, even likely. Driveless cars, better preventive healthcare, even better movie recommendations, are all here today or on the horizon. AI is the present and the future. With Deep Learning's help, AI may even get to that science fiction state we've so long imagined.
What's next?
If you want to find out about a sub-part of Deep Learning, which is Deep Convolutional Neural Networks, check my post.
Thank you for reading.
Congratulations @quantum-cyborg! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @quantum-cyborg! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
AI is so lit af , that can do wonders in real Life. Seriously :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2016/07/29/whats-difference-artificial-intelligence-machine-learning-deep-learning-ai/
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit