Orang utan (Or Orangutan, another name is mawas) is a kind of great apes with long arms and hairy reddish or brown, which live in the tropical forests of Indonesia and Malaysia, particularly on the island of Borneo and Sumatra.
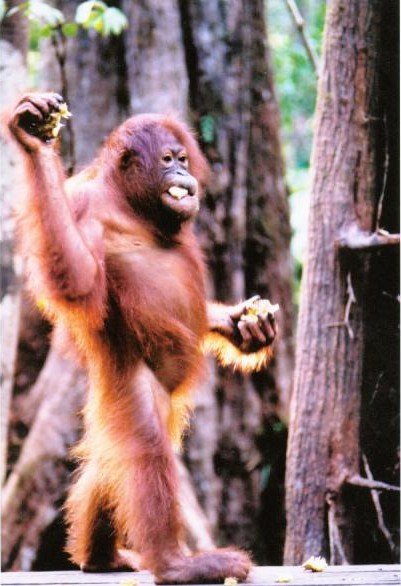

Characteristic features :
They have a fat body and a large, thick-necked, long and strong arms, short legs and bowed, and did not have a tail.
Orangutan has a height of about 1.25-1.5 meters.
Orangutan body covered with red-brown hair. They have a large head with a mouth high position.
When it reaches the level of sexual maturity, have a male Orangutan skulls fat on both sides, the crown of a large, and growing long hair becomes a beard around the face. They have the same senses as humans, ie hearing, sight, smell, taste, and touch.
Male Orangutan weight around 50-90 kg, while the female Orangutan weighs about 30-50 kg.
Palms they have four long fingers plus one mother jari.Telapak their feet also has an arrangement fingers are very similar to humans.
Orangutan still belong to the species of great apes such as gorillas and chimpanzees. Group of great apes are classified mammals, have large brains, eyes that leads forward, and hands that can grip.
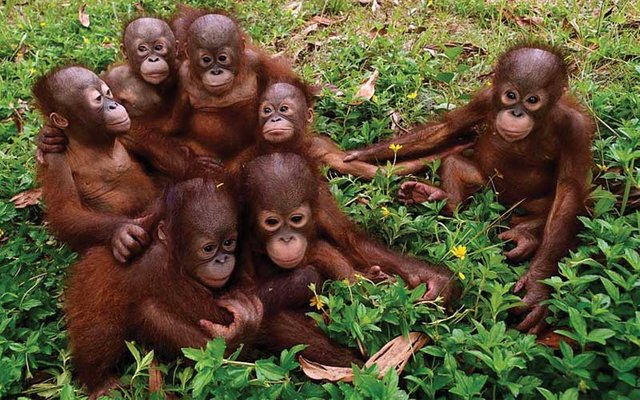


Classification :
Orangutan including vertebrate animals, which means that they have a spine. Orangutans also includes mammals and primates.
Species and Subspecies
1. There are two species of orangutan, the Borneo Orangutan / Borneo (Pongo pygmaeus) and the Sumatran Orangutan (Pongo abelii).
2. Descendants of Sumatra and Borneo Orangutan different from 1.1 to 2.3 million years ago.
3. Subspecies

Genetic Learning has identified three subspecies of Bornean Orangutan: P.p.pygmaeus, P.p.wurmbii, P.p.morio. Each subspecies differentiated according to regional geographical distribution and include the size of the body.
Central Kalimantan Orangutan (P.p.wurmbii) inhabit the West Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan. They are the largest subspecies of Borneo.
Borneo Orangutan the Northeast (P.p.morio) inhabit areas of Sabah and East Kalimantan. They are the smallest subspecies. Currently there are no successful Bornean Orangutan subspecies recognized.


Location and habitat :
Orangutans are found in the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, which is on the island of Borneo and Sumatra in the region of Indonesia and Malaysia. They used to live in dense trees and made a nest of leaves. Orangutans can live in a variety of forest types, ranging from keruing forests, hills and plains, watersheds, freshwater swamp forests, peat bogs, dry soil above the mangrove swamps and palm, to the mountain forests.
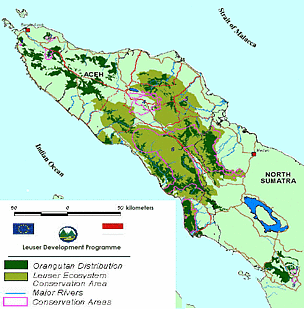
In Borneo, Orangutans can be found at an altitude of 500 m above sea level (asl), while her relatives in Sumatra reportedly can reach the mountain forests at an altitude of 1,000 m above sea level. The Sumatran Orangutans is one of the endemic animals that exist only in Sumatra. Orangutans in Sumatra only occupies the northern part of the island, ranging from Timang Gajah, Central Aceh until Sitinjak in South Tapanuli. The existence of these protected mammals Act 5 of 1990 on Conservation of Natural Resources and Ecosystems and classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
In Sumatra, one of the Orangutans population found in watersheds (DAS) Batang Toru, North Sumatra. The population of wild orangutans in Sumatra is estimated to number 7,300. In DAS Batang Toru pupulasi 380 tail with a density of about 0.47 to 0.82 individuals per square kilometer. The population of Sumatran Orangutan (Pongo abelii lesson) is now estimated 7,500 birds. Whereas in the 1990's, an estimated 200,000 heads, their population contained in 13 separate geographical areas. These conditions led to their survival is increasingly threatened with extinction.
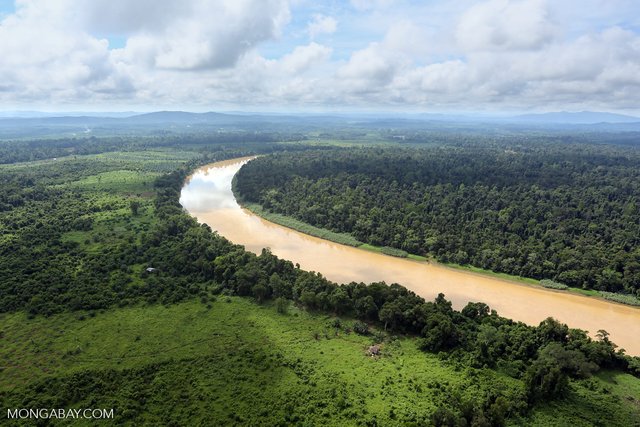

Today almost all of Sumatran Orangutans are only found in the province of North Sumatra and Aceh province, the Lake Toba as the southernmost limit of its distribution. Only two relatively small population located in the southwest of the lake, the Sarulla East and forests in Batang Toru West. The Sumatran Orangutans population found in the West Leuser (2,508 people) and East Leuser (1,052 people), and Rawa Singkil (1,500 people). Another potential population estimated to survive in the long term (viable) contained in Batang Toru, North Sumatra, with a size of about 400 individuals.
Orangutans in Borneo are categorized as endangered by IUCN divided into three subspecies: Orangutans in Borneo are grouped into three types, namely Pongo pygmaeus pygmaeus located in the northern part of the Kapuas River to the northeast of Sarawak; Pongo pygmaeus wurmbii were found from the south of the Kapuas River to the western part of the Barito River; and Pongo pygmaeus morio. In Borneo, Orangutans found in Sabah, Sarawak, and almost all the lowland forests of Borneo, except South Kalimantan and Brunei Darussalam.
Food :
Although orangutans including omnivorous animals, most of them only eat plants. 90% of food in the form of fruits. Food include tree bark, leaves, flowers, some types of insects, and about 300 types of fruits
In addition they also feed on nectar, honey and mushrooms. They also like to eat durian, although the sharp aroma, but they loved it.

Orangutans do not even need to leave their tree if you want to drink. They usually drink the water that has accumulated in the holes between tree branches.
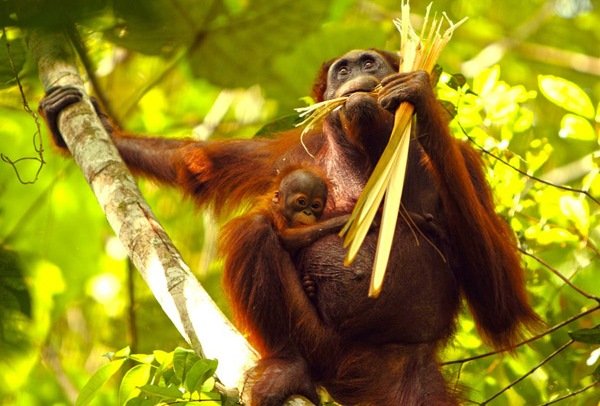

Usually orangutan mother taught them how to get food, how to get a drink, and various types of trees in different seasons. Through this, it can be seen that the orangutan turns out to have a map of the location of the forest complex in their brains, so they are not wasting power when searching for food. And children can also find a variety of trees and plants, which can be eaten and how to process the food that is protected by a shell and sharp thorns.
Orangutans Conservation Status :
The Sumatran Orangutans has been included in the classification as Critically Endangered by IUCN. Its population plummeted where in 1994 the number reached more than 12,000, but in 2003 to approximately 7,300 individuals. Data in 2008 reported that the estimated number of Sumatran Orangutans in the wild only about 6,500 birds.
Historically, Orangutans found in forests across Sumatra, but is now confined to the area of North Sumatra and Aceh provinces. Suitable habitat for Orangutans currently only about less than 900,000 hectares in Sumatra island.
Currently estimated Orangutans will be the first great ape species that became extinct in the wild. The main cause is habitat loss and the wildlife trade.
Orangutans is the basis for the conservation of species. Orangutans plays an important role for forest regeneration through fruits and grains that they eat. Orangutans loss reflects the loss of hundreds of species of plants and animals in the rain forest ecosystem.
The world's remaining primary forest is the basis of human well-being, and the key to a healthy planet is biodiversity, contribute to help save Orangutans mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, insects, plants, and berbagain sorts of other species that live in the rain forests of Indonesia..
"Help save the orangutan from extinction and illegal trade or poaching .."
Please Upvote and share..
See you...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit