
The world of blockchain has now an explosion in the number of active decentralized applications and users engaging with them. However, this surge in usage has also exposed the limitations of legacy blockchain architectures and gave birth to new solutions that better suits our needs.
The three major categories of blockchains that are being used now are Layer 2 rollups, alternative layer1 chains, and appchains.
One of the most important decisions now for dApp developers is to identify the right blockchain platform for their specific application needs. There is no one-size-fits-all solution - factors like scalability requirements, security needs, customizability, composability, developer experience, and costs must be weighed carefully.
The right blockchain choice can empower a dApp with the capabilities needed for long-term success and adoption. This guide explores the key blockchain architectures in-depth, including their unique pros and cons, to provide a framework for making this crucial decision.

Main Factors to Consider
When evaluating blockchain options, dApp developers should begin by outlining their application’s technical and functional requirements today as well as anticipated needs over time as adoption grows. Key factors to consider include:
Scalability Requirements
The blockchain must provide the transaction throughput needed to deliver a smooth user experience as demand increases. Slow speeds or high latency due to congestion will frustrate users.
Having precise scalability requirements will make tradeoff decisions clearer later on.
Security Level Needed
All blockchains aim to provide a decentralized and tamper-proof execution environment, but they employ varying strategies to achieve this. dApps with mission-critical functions may require deeper decentralization and security guarantees. Make sure you have answers to the below questions before you make any choice.
Rolling out custom security measures on a less decentralized chain may be complex, costly and hard to achieve.
Customizability
Some blockchains allow the core protocol and parameters to be customized versus others that take a more fixed, “generic” approach. This allows an app to tailor the platform to its usage needs more closely.
Higher customizability enables tighter blockchain-app integration but may require more ground work.
Composability & Interoperability:
The ability for the blockchain to import dApps from other chains seamlessly, or may be an easy interoperability with other protocols is another key thing to consider. Questions similar to the below might give you answer to this part:
Higher composability unlocks more functionality but may have some architectural constraints.
Developer Experience
The availability of documentation, tools, infrastructure, and community support is crucial for both the core development team and external developers building on top of the platform.
A better dev experience enables moving faster but may limit technology choices sometimes.
Costs
In public blockchains, factors like transactions fees, gas costs for computation, and running validator infrastructure impact operations. The app’s revenue model and user profile influences its sensitivity to costs.
Higher costs may limit adoption and commercial viability of the app.
By keeping these parameters in mind while assessing each blockchain architecture, an informed choice aligned with the app’s needs can be made.
In the next section, we will explore the architectures and their distinguishing pros and cons.
Architecture Deep Dives
Layer 2 Rollups
Layer 2 rollups have emerged as a popular scalability solution for enhancing transaction throughput on Layer 1 chains like Ethereum. They function by handling transaction execution and data processing “off-chain” while inheriting the underlying L1's security guarantees.
Rollups batch hundreds of transfers off-chain and generate a compact cryptographic proof. This proof is periodically posted to the L1 chain along with the new state root, allowing transactions to be verified trustlessly while retaining the L1’s decentralization and security.
Rollups represent a modular approach to scaling, as execution and data availability layers are decoupled from the security layer. This enables independent optimization while reusing battle-tested L1s like Ethereum for security, instead of launching entirely new chains.
Mainly two main categories of Rollups exists today.
Optimistic rollups assume transactions are valid by default but have a withdrawal delay period where invalid state transitions can be challenged. Invalid transactions are reversed while honest transactions are finalized faster. On the other hand, zkRollups use succinct cryptographic proofs called zk-SNARKs to mathematically prove the validity of state transitions. Transactions are instantly finalized with no challenge period.
Here are some of the key advantages rollups offer to dApp developers:
However, rollups also come with downsides also. Like, Rollups rely on the underlying L1’s protocol, limiting customization of core chain mechanics. If you want to get your assets back to L1, it will be through bridges. This can be costly, slow and the bridge UX could be complex for average users. Another concern is obviously, the use of centralized sequencers. Interoperability between different rollup chains is also limited at the moment which could lead to an walled garden ecosystem of thousands of rollups.
Though significant advancements are being made to tackle this issue. Polygon CDK is one of the prominent name here that aims to address this walled garden issues for appRollups.
Talking about its best usages, Rollups are a natural fit for apps already integrated in Ethereum or a similar ecosystem and wanting to retain the network effects. For entirely new apps with complex needs, the lack of customizability and isolation of rollup ecosystems may be limitations.
Alternative Layer 1s
Rather than using rollups to scale existing L1s, another option is to build on entirely new alternative Layer 1 blockchains designed from scratch for higher throughput and better customizability.
Unlike Ethereum which uses a single-chain architecture, these next-gen Alt L1s employ technical innovations like sharding, parallel execution, and optimized consensus algorithms to deliver dramatically higher TPS figures.
Some prominent existing examples include Polygon PoS, Polygon zkEVM, NEAR, Aptos, Coreum, zkSync Era, DCOMM and Tezos. Many other new players are coming up as well.
Here are some advantages of these high-performance Alt L1s:
However, Alt L1s also have some disadvantages like other solutions. There could be a security issue if the validator sets are not sufficiently decentralized. If the ecosystem is not large enough, your dapp could be in an isolated environments with limited cross-chain interoperability. Opting for Rust, Haskell, Move or any new language over the popular ones like solidity requires new developer skill sets.
For many consumer apps like games or social platforms that require high scalability and low costs, building directly on a high-performance Alt L1 may be the best fit. A strong developer community on the chain is helpful, though. Those prioritizing decentralization, composability, and leveraging Ethereum’s network effects may still prefer certain layer 2 rollup solutions however.
Appchains:
Rather than deploying a dApp on a shared “generic” blockchain network, teams can also build their own fully customizable application-specific blockchains, known as appchains.
Appchains function similarly to an independent Alt L1 but are optimized purely for a specific use case rather than being general purpose. Control remains entirely in creators’ hands.
Two common approaches for creating such blockchains:
Here’re some example appchains from different ecosystems:
- dYdX - dYdX became a Cosmos-based appchain with fully decentralized, off-chain order book and matching engine.
- Energy Web Chain - A Polkadot Parachain with a singular focus on energy sector
- RYMEDI Subnet - Healthcare tech giant Rymedi launched 3 Avalanche Subnets
- Plena Finance: This leading DeFi project has launched its own Polygon CdK powered zkChain
Here are some benefits appchains provide:
The main disadvantages of building on an appchain are: finding validators, providing liquidity maintaining an entire network, which is more than just running a few nodes.
Talking about the use cases, for applications that have complex needs and want sovereignty over their blockchain environment, developing a custom appchain can make sense once sufficient scale and product-market fit is achieved.
Shared security and composability with external chains via bridges and protocols like IBC, XCMP, LXLY bridge of Polygon CDK can help mitigate these downsides. Teams can consider appchain strategies as part of a phased roadmap also, after proving core product utility on base L1s first.
Here’s the TLDR:
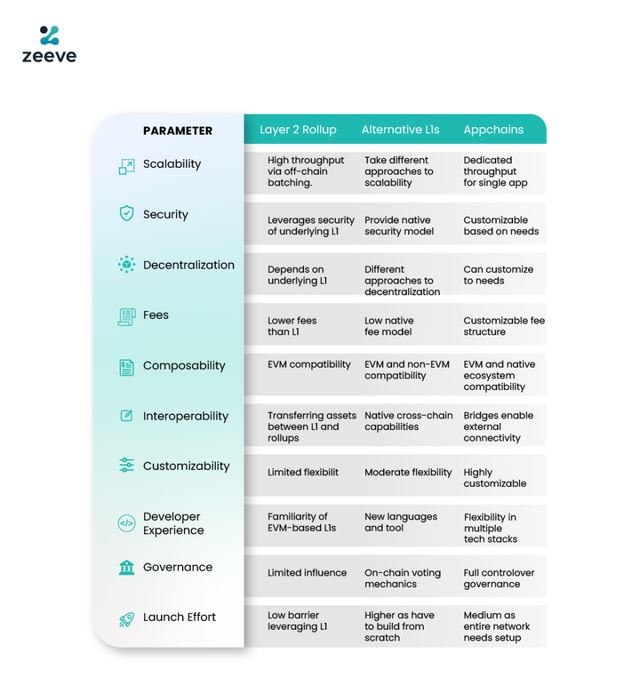
Based on analyzing various real-world projects, we can extract some best practices for aligning architectures with app goals:
By benchmarking options versus core priorities, teams can smartly navigate tradeoffs and engineering costs.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal blockchain to power a dApp is one of the most impactful technology decisions project teams have to make. With new layer 2, alternative L1, and appchain architectures emerging, there are now more scalable options than ever to choose from.
However, there is no universal “best” solution. The right technical design depends completely on the unique goals and needs of the application as we discussed throughout the article.
Teams should thoroughly analyze their technical requirements today and anticipated growth trajectory before evaluating how well each solution can fulfill them given their respective tradeoffs.
In case you are looking for help regarding your right infrastructure choice or may be need the right guidance regarding your migration from existing systems, get in touch with Zeeve experts. We ensure you go to production with minimal turnaround time, a minimum cost and a all managed solution with enterprise-grade security best parctices.
Visit Zeeve today and explore our Rollup-as-a-service solutions, appchain infrastructure, dedicated nodes and hosted subgraphs. We are happy to help you with all your development needs!