EBS is a cloud-based block storage service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). In EBS, your data is saved into blocks, also known as EBS volumes. To protect data, EBS places volumes within an Availability Zone (AZ), where the volume is replicated. Another form of data loss prevention can be achieved with EBS snapshots.
What Are AWS EBS Snapshots?
AWS Elastic Block Storage (EBS) snapshots are point-in-time backups of EBS volumes. EBS volumes are persistent storage volumes used with Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) instances. EBS snapshots enable you to quickly restore or transfer data from EBS volumes. Snapshots also enable you to retain and duplicate data that might otherwise be lost.
When using EBS snapshots, there are a few aspects to keep in mind to optimize your use:
- Data transfer to S3—all EBS snapshots are transferred to Amazon S3. This means you have to account for transfer bandwidth and storage service costs.
- Incremental backups—EBS snapshots are incremental, with each additional snapshot only saving the data that has changed since the last. This reduces the space needed to store snapshots. When you delete old snapshots, data is merged into the next oldest snapshot to ensure you retain a full backup.
- Snapshots are region-specific—snapshots can only be accessed from a single region so you need to be sure that you are storing snapshots in the appropriate region. If you need to access a snapshot from another region, you need to copy it, which creates data transfer and additional storage fees.
- Encrypted volumes don’t offer incremental backups—you can only use incremental backups of un-encrypted volumes. Encrypted volumes require a full backup each time. This means you need to more closely monitor your number of backups to prevent storage overages.
How to Automate AWS EBS Snapshots
Using the Snapshot Lifecycle Manager, you no longer need to stop instances to create snapshots. This enables you to backup volumes without downtime. This tool also enables you to automate the creation, management, and deletion of your snapshots. This management is accomplished through policies applied to volume tags, metadata you assign to volumes for classification.
To use the Lifecycle Manager, you need to first tag your volumes by category or use. For example, you can apply tags specifying projects, departments, or clients using the volumes. If you already have volumes and are now implementing Lifecycle Manager, you can find volumes with missing tags through AWS Config.
To create a snapshot lifecycle policy you should take the following actions:
In your EC2 dashboard and click Lifecycle Manager.
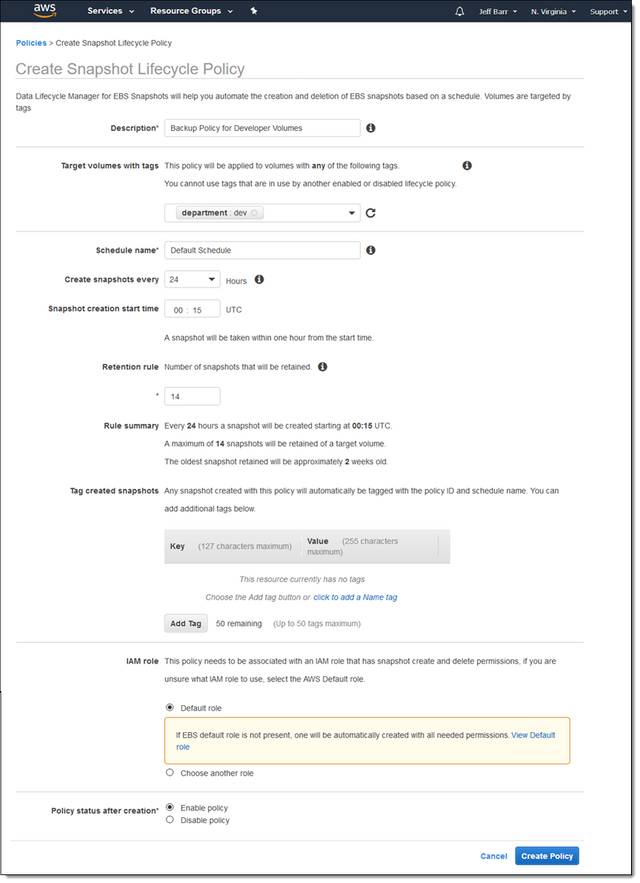
Source:AmazonCreate a new policy, providing a policy name and any tags you wish to include. In this policy, you can determine a backup schedule and a start time. You can also specify how many snapshots to retain.
Source:Amazon
For more detailed guidance, you can see this tutorial.
Benefits of EBS Snapshot Automation
Automating your snapshot creation helps you avoid overlooking snapshots. It can also make it easier to manage your EBS volumes by ensuring that data is duplicated.
Automating the snapshot process has additional benefits, including:
- Automatic backup and maintenance—via the Lifecycle Manager you can automate backups and ensure backups are kept according to policy.
- Low-cost backup option—since snapshots are incremental, storing backups requires less space which reduces cost. Additionally, automation eliminates manual work, reducing staff costs.
- Fast disaster-recovery solution—snapshots allow you to quickly recover data in a disaster. This reduces revenue losses caused by downtime and ensures valuable assets stay available.
Challenges and Limitations of EBS Snapshots
Although EBS snapshots have a number of benefits, these tools are not perfect. When using snapshots, you should keep the following limitations in mind:
- Instances are dynamic—AWS services frequently deploy and terminate instances to ensure availability. This means that automation needs to backup instances frequently and consistently to ensure that no data is lost.
- Reliability—snapshot backups are only as reliable as the policies and systems used to create snapshots. It is up to you to verify that your policies are operating as expected and to ensure that backups are running as scheduled.
- Scalability—it is easy to create a large number of backups without realizing the amount of data you are storing. You need to find a balance point between ensuring that your data is duplicated and that you are not scaling your storage larger than necessary.
There are also a few limitations specific to automation that you should keep in mind:
- Policies aren’t instant—policies only run in the windows you define. If you create a policy on Tuesday to run on Mondays, your volumes won’t be backed up until the following Monday.
- Automation is limited by region—any policy you set needs to be in the same region of the volumes you wish to backup. You cannot set policies from different regions.
- Policies are not tied to snapshots—if you delete a policy, it does not remove any snapshots created by that policy. If you want to delete these snapshots, you must do so manually.
- EBS volumes are not tied to snapshots—like with policies, deleting EBS volumes does not delete snapshots created from those volumes.
- Limited intervals—you can only create backup policies in twelve or twenty-four hour intervals.
Maximum retention period—snapshots can only be kept for 1,000 days. After that, snapshots are automatically deleted. - Snapshots per account are limited—you can only store 10k snapshots per account. Although this number seems large, if you are taking daily snapshots on a large number of volumes, you can quickly hit this limit.
Conclusion
EBS snapshots are an excellent option for data loss prevention. You can use EBS snapshots to create point-in-time backups of data, and then restore the information as needed. To ensure efficiency, you can automate the process. However, keep in mind that there are limitations, including the restriction on the number of snapshots per account. Be sure to experiment and find the workflow that works best for your project.
