
“green and black rope” by Clint Adair on Unsplash
Over the last 300 years, there has been significant development in technology. The rate of adoption of new technologies has accelerated dramatically over the years. It took around 75 years for telephone, 13 years for television and only 3.5 years for Facebook to connect 50 million people.
But the adoption and evolution of technology has not been easy. Like back in the days of horse-carting, if you asked a person “What will be the next innovation in the transportation?”, the person would have replied “A faster horse”.
Invention of the internet had also initially met with critical skepticism. Paul Krugman, a renowned economist, said: “By 2005 or so, it will become clear that the Internet’s impact on the economy has been no greater than the fax machines’”. Today, the horses are sleeping peacefully and fax machines are kept in antique museums.
Impact of any technology is known and accepted when it delivers its promises and provides better results than its predecessors.
Similarly, Blockchain is certain to have a profound impact if it delivers to its promises. Of course, Blockchain technology is still in its nascent stage but therein lies the opportunities. Let me introduce the concept in its most basic form in this blog.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a software code, any blockchain consist of multiple blocks. Each block stores data digitally similar to how each page of a book holds small part of the information.
This technology was originally developed in 1991 by a group of researchers called “Timestamp”. It timestamps digital documents wherein it can’t be tampered or backdated. Suppose, a person’s property paper is timestamp, it means the exact date and time is recorded digitally and can be verified by higher authority. The problem with timestamp was, a similar fake timestamp can also be created with exact date and time, proving to be as good as the original. Thus, it was important that the system should have verification mechanism of its own to deem it as a real one.

“gold-colored Bitcoin” by Andre Francois on Unsplash
With the help of cryptography, a digital currency named Bitcoin solved this problem. Bitcoin, created by Satoshi Nakamoto (pseudonym) published a whitepaper in 2009 after the financial meltdown. Bitcoin is a network of distributed ledger. A distributed ledger contains multiple blocks and each block is linked to all other blocks through nodes to verify that the block is part of its network. Let’s see with an example, how a Blockchain network is created, each block has three major components:
Data — Information to be stored in blocks. Example: Company can store its public or private data. In case of Bitcoin block, number of bitcoins, transaction details.
Hash- Digital Identity of the block itself. Similar, to the identity of the individual in the identification system (ex: Aadhaar) in the national database.
Hash of the previous block — To verify the consensus. Suppose, a new block of different network(B) is trying to penetrate the original network(A), it should verify the previous block hash of A.
Blockchain has various benefits, some of the key ones are:
Enhanced Security- Information is recorded on the block and it is stored across the network of servers, rather than single server. Making the chain decentralized and network as peer-to-peer. It is very difficult for anyone to hack the network since large networks require massive computing power.
Accountability- Each network server would function as one node. If information of block A is passed to block B, then it is registered as an activity 1 in each block. Later, Block B is passing an additional set of information to Block C, it will verify activity 1 before that. This creates accountability of every activity within the blockchain network thus avoiding duplication.
In order to understand the benefits in detail, it is important to know the types of Blockchain and how they are different with respect to each other. Blockchain has two major types: public and private. Let’s look at the key differences between the two types:
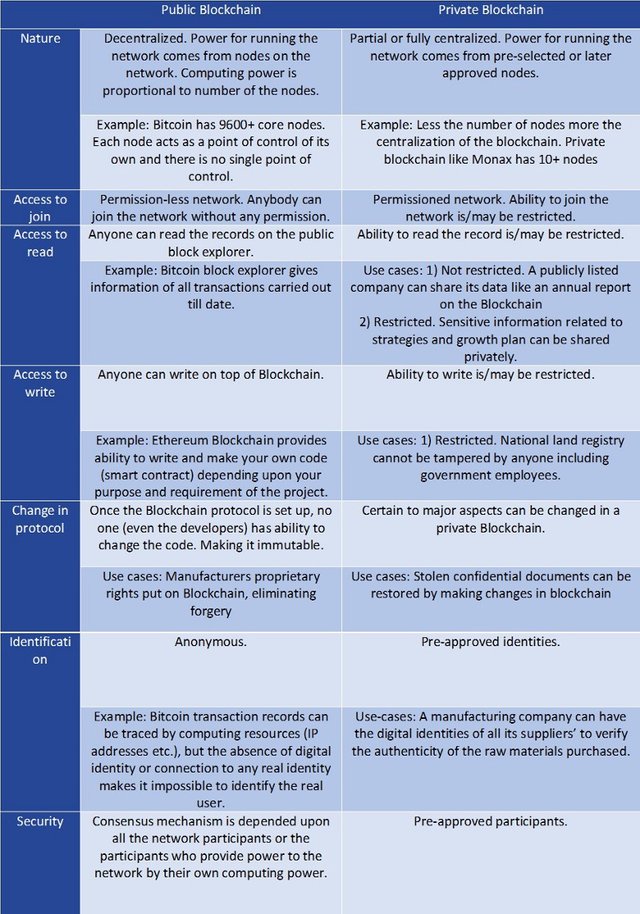
Of course with the understanding of public and private Blockchain, there is no linear argument that one is better than the other. It depends upon the purpose and the requirement.
Conclusion
There is also a greater side of argument that private blockchain is not blockchain at all, as the fundamentals of blockchain mainly such as decentralization, accountability, change in protocol etc. are altered. Those are the foundations of a private blockchain.
The public and private blockchain debate could be related to internet and intranet in 90s.
As internet adoption went leaps and bound ahead from intranet and today internet functions as foundation of majority of systems. Public blockchain can have relatively similar adoption process and reach a scale of mass adoption if it delivers to its promises. On the other side, private blockchain aren’t going to fade out. There are certain blockchain prototypes wherein the hybrid blockchain- merging of public and private blockchain is tested upon. Overall, blockchain will survive and thrive, further changing the way we live and do things.
One of the pioneer venture capitalist investor, Tim Draper quoted “I think it’s going to have such a transformative effect on industries that we never even imagined would be transformable. Blockchain will go after trillion dollar markets — these are finance, healthcare, insurance, banking and governments”.
In my next blog (Part II of this series), I will cover more about public & private blockchain with their past and recent developments.
(This blog series is co-written with inputs from Mr. Adith Podhar, who is the Managing Partner at Gemba Capital. You can reach him on [email protected])
References
https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
https://blockchainhub.net/blockchains-and-distributed-ledger-technologies-in-general/
https://blog.ethereum.org/2015/08/07/on-public-and-private-blockchains/
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://medium.com/@kunal.shivalkar93/why-blockchain-is-the-next-big-revolution-part-i-of-ii-1df23c24ec6f
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @kunalshivalkar! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board of Honor
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @kunalshivalkar! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit