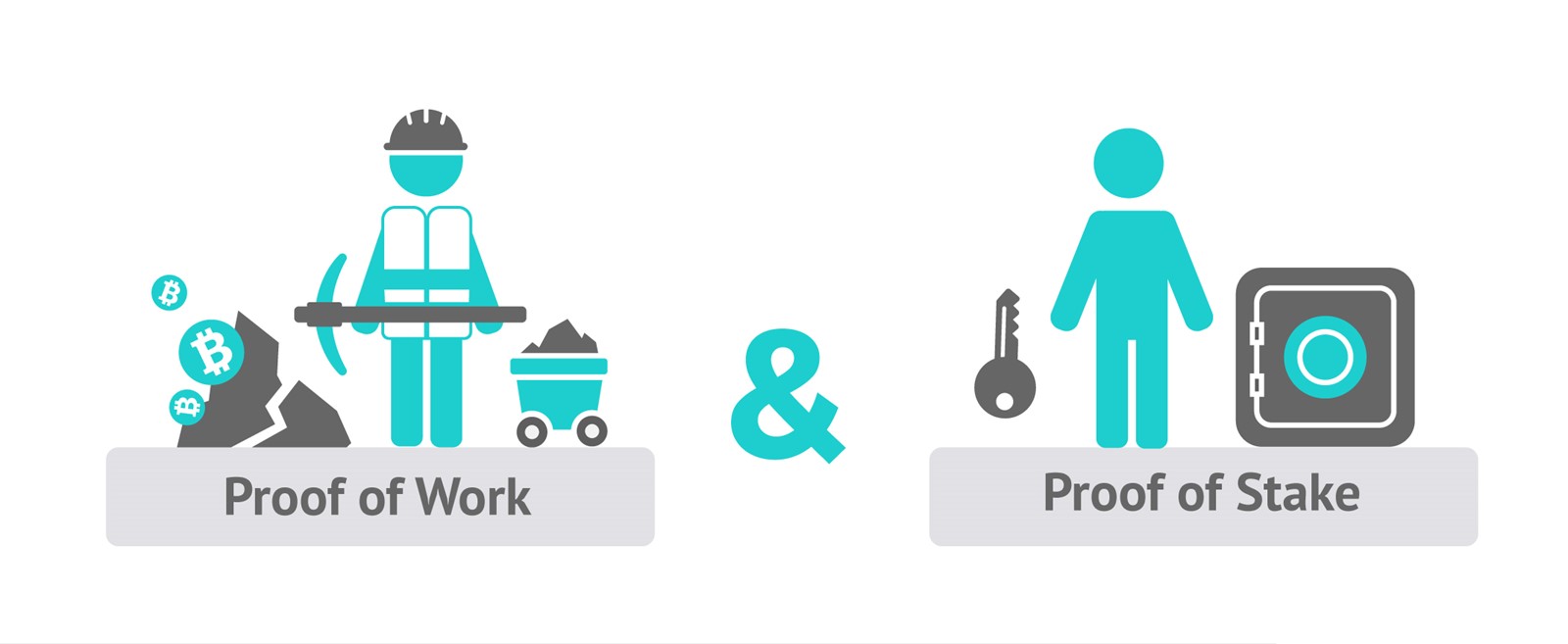
The two basic principles underlying transaction verification in the blockchain network are Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW is the original principle that has created Satoshi Nakamoto and solves the problem of the credibility of the distributed book of records. The disadvantage of the PoW system is that it uses a lot of energy and resources because the points inside the network compete in the speed of solving cryptological puzzles. The goal is to solve the puzzle faster than others, resulting in the creation of new cryptoes belonging to the owner and the fastest point. The Bitcoin network is particularly famous for its PoW system, because the algorithm used favors the use of highly specialized hardware - devices made from a large number of ASIC chips that are specifically designed for mining. Some other blockchains are designed to hinder the development of specialized ASICs, but mining is used by all hardware-graphics cards.
On the other hand, PoS works on the principle of investing the existing cryptoseconds, allowing the user to take part in the verification of the transaction. Coated coins can not be used for anything else, and behave as classic cash coins in the bank. Users who invest in cryptocons and thus participate in maintaining a network earn from the basis of collecting a transaction fee paid by users who initiate transfer coins to another user. Yes, of course, it has its own list of challenges - primarily the possibility for miners to verify multiple blockchains at the same time, because there is no extra cost of calculation that discourages them as in the PoW system.
#steemit
Authors get paid when people like you upvote their post.
If you enjoyed what you read here, create your account today and start earning FREE STEEM!
If you enjoyed what you read here, create your account today and start earning FREE STEEM!