My translation of an interview with Artem Abaev, a co-founder of Soundchain project
Smart-contracts can help us to build new business models and fully autonomous digital economies almost in every niche. Music business is one of the areas that needs it the most: To say the least, this field of intellectual rights is totally in chaos. For example, in some cases it is quite difficult to understand who exactly owns music rights. There's a tangled skein behind every track: Musician rights that appear according to law, label, producer and sponsor requirements, who invested the money and waiting for their ROI, sometimes it also includes claims of people who contributed in track creation on freelance basis. Even home-made hit remixers start to claim intellectual rights on remixes, which is actually wrong.
" The problem of intellectual rights is that there's no 100% trusted database of music compositions. That is why no musical service in our country is fully covered with intellectual rights catalogs provided by right holders. There's no authority that can define reliability of contracts, intellectual right has a declarative character. There's a plenty of arguments when a number of declarants claim to be right holders in order to gain profit. "The situation must be changed, it is necessary to find comprehensive and extensive solutions as huge amount of money is just "Hanging around wrong accounts", as founder of consulting agency Insimple.ru Aleksey Nikolaev says about the music scene.
One more problem is that it is not clear who and for what must pay. There are more or less standard plans for income generating: Sales of physical media, subscriptions and services like Apple music. However, monetization of music commercial use (by cafes, restaurants, film studios et c.) is a big problem. As a matter or fact, right holders have 2 choices: whether to make a license agreements with commercial user (it happens individually, therefore, it is inconvenient) or hand it over to other companies on the basis of non-contractual management hoping to have their award collected and transferred.
"In the following years the work of composers, artists, producers and music creators on the whole will be changed in two system aspects", expects Igor Kraev, founder of music-in-media distribution project Tophit.ru. - First of all, the technology of accessing mass market and promoting new products must be replaced. Second of all, we speak about direct content monetization, i.e. sales of digital copies and revenue collection for a particular artist or track/video directly from mass users. Radio and TV will lose musicians and industries, the role of RAS (Russian Authors Society) and same organizations will drop as far as royalty share in musicians' income will go down while direct monetization income will be on the rise. Setting of rules will be prerogative for online-platforms, especially for those who can provide access to the mass market and direct labor monetization of entertainment media creators.
The blockchain technology will help to reach the whole new level, as founder of mastercash.org project Artem Abaev believes. Now he offers soundchain.org to the market - it is a music platform based on smart contracts and the blockchain technology.
Artem, could you tell us how application of smart contracts together with the blockchain technology can solve existing problems of music business?
Blockchain solutions are created as a virtual layer to ease rights flow pattern, one for every type out of five - proprietary, obligation, corporate, intellectual and personal non-proprietary. In the proprietary right field there are property ledgers created, obligation rights are adopted to smart contracts (e. g. Escrow), personal non-proprietary rights are also recorded in ledgers. A sample attempt to "thread" corporate rights into the blockchain is well known with respect to theDAO story. It is obvious that in the field of intellectual rights that is basic for music industry the blockchain can be used to set up a right holder ledger and transfer license agreements to smart contracts. From the legal point of view the blockchain is something bigger than automation and elimination of middlemen. In the corporate right there's a good way to regulate relations among group of people concerning their common rights - a legal entity. Private individuals put together their property, say a "registration spell" and create a front party. The relations with it and between participants are regulated with corporate law, otherwise they had to make contracts with each other and their partners about each asset flow that would be too complicated and expensive. Nowadays we can see the same outgrowth of necessary contracts in the field of intellectual rights and the difficulty of an individual agreement for intellectual property items is constantly increasing. It seems reasonable to apply corporate mechanisms in order to manage intellectual rights. However, apart from a legal entity that is backed with property and big amounts of money, a certain music composition might have no particular material value. Moreover, the group of right holders varies for different compositions. SPV can be created for joint management of expensive patents, but a legal entity for one composition is quite an expensive decision.
So what is the way out?
That is where smart contracts can give a helping hand. Automation helps to multiply entities almost for free: Once we create a voting and value distribution mechanism, we can copy it and adjust it precisely for every asset, no matter how small it is. I. e. we can "Steal" the idea of corporate law and apply it in music. Moreover, we're much less connected with the current regulation: There is no need to oblige participants to execute decisions, enforcement is not required as far as execution is included by design. It means that we don't need to resort to corporate law - behind the network of smart-contracts we can install a legal layer that will fit to our purposes at best and look for "sleeping" legal mechanisms that can be awaken.
How does particular implementation of these ideas look like?
We have been trying to apply these technologies in the Soundchain project. Here we use a mechanism called divisibility of copyright - divisibility of the sole right to intellectual property item. The sole right can be handed over, that is called alienation; or it can be handed over for use, that is called licensing. But it is also possible to pick a piece of it that keeps all the legal power and hand over that piece, in this case both partners will be right holders and the relations between them about the intellectual property item will be regulated with an agreement. Nowadays this mechanism is used quite rarely as far as making contract is an expensive and long process, the more participants it comprises, the more expensive and complicated it becomes. However, smart contracts can help us to reduce the price, divide the copyright to as many pieces as we need and provide complicated contract mechanisms to manage it.
How does the Soundchain project work and what does it take to start using the platform?
Track creator uploads a music composition to the decentralized network, and here we can draw an analogy with a joint-stock company: The right holder sets up the regulations and joint management rules, determines the number of tokens (crypto-shares) issued for the track and opens the license for it using smart contracts for different types of commercial use. If necessary, it is possible to make a division between co-authors, musicians, producers, labels and managers– i. e. between everyone possessing the composition rights. To make it more obvious, let's reflect this process in the following diagram:
Tell us about the business-model of Soundchain, how is it monetized?
The model is described in the following infographic:
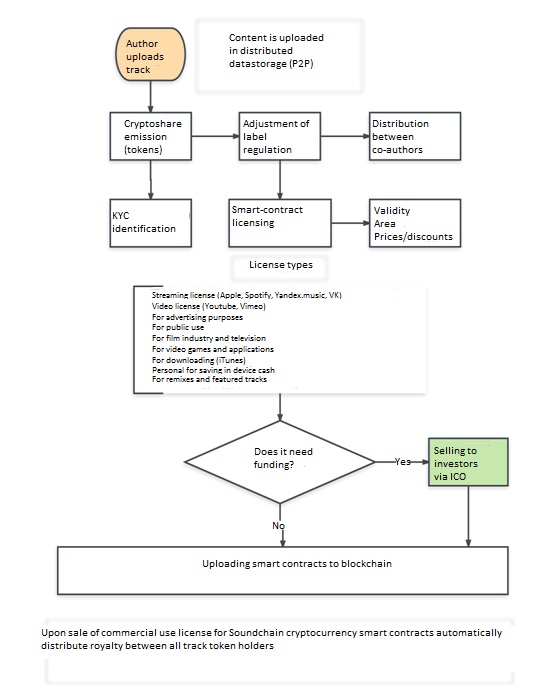
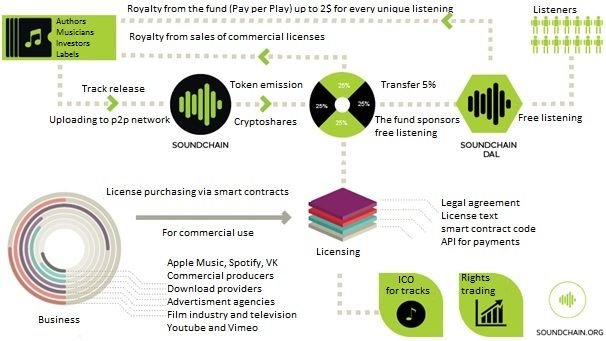
This pattern gives us huge opportunities unattainable in the frame of conventional legal mechanisms. First of all, we can organize a coordinated management of music rights and licenses for any number of right holders by means of voting. Second of all, the process of issuing commercial licenses and distributing income becomes automated. Third of all, it is possible to make microtransactions using the Pay Per Play model that leaves out middlemen like labels and authors communities. It is allowed to trade author's rights to a track like common shares using an exchange. Labels in its turn can take the responsibility for asset management and administration for a share in the track. To sum it up – it is full discretion, authors/right holders take their own decisions about what to do with their creative product using a convenient design tool. Musicians are people of art that is why sometimes it is quite difficult for them to understand how things work – it is much easier to hand over the management of their intellectual rights to a label or a music manager. Actually we're talking about new types of companies that work autonomously in digital environment on the basis of the distributed ledger technology and smart contracts – decentralzed autonomous labels (DAL).
You have mentioned Pay Per Play monetization model – why is it considered to be an effective business solution?
Besides royalty from commercial license sales, track shareholders will also receive rewards from a non-commercial fund for every unique listening via Soundchain player. As far as the main beneficiaries on the platform are right holders (not miners like it is in the original chain of Ethereum platform), the major part of emission will be directed to the fund for payments per play. In order to implement this pattern, we have developed a special protocol Proof-of-Listen that will function autonomously via smart contracts. In order to move to the new model Pay Per Play, we have designed an incentive mechanism to promote musicians/authors to migrate from a traditional dollar based model to our model: by this, they can multiply their income and give up the previous creativity monetization patterns or agreements without any misgivings.
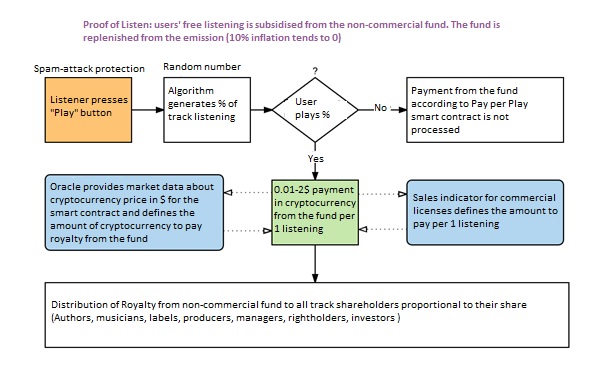
Still there are quite specific genres of music with a narrow group of lovers, therefore, they probably will not get a great number of listenings. Is this technology suitable for them?
We do understand that not every track will bу commercially interesting from the license selling point of view, that is why we have developed so called POS-deposit of tracks in order to have an alternative reward increase from the fund for every listening. Track Authors (shareholders) can buy cryptocurrency in the open market or attract funds using ICO and freeze it for a certain period of time using a special smart contract in order to increase the reward from the fund. Probably we will burn part of cryptocurrency using the ICO mechanism in order to balance emission and turn on the deflation lever on the platform that will fully depend on the market.
What happens if the number of burnt tokens overcomes the value of emission?
Then we will get natural economic growth due to market factors, not only by means of market speculations. Moreover, cryptocurrency will be used for its primary purpose – acquiring of commercial licenses. Soundchain can attract funds or even participate in IPO that is strictly regulated, or in ICO (before it's regulated in the same manner). Together with us, a musician can make an ICO for every song without breaking any laws, which is quite the opposite: People's love of music can become an investment: Fans will be shareholders of their favorite artist's track but part of attracted funds will be destroyed on the platform. That is how our cryptoeconomy works.
*What method will be used for Soundchain? *
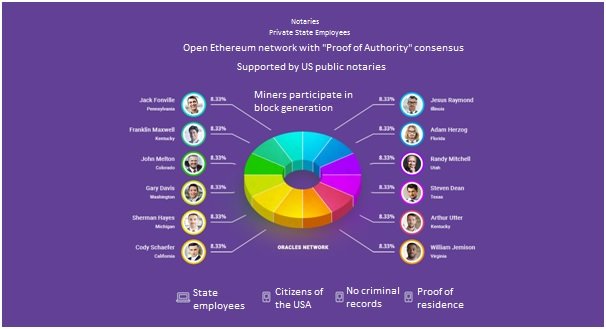
We integrate a hybrid protocol PoA Notary (Proof of Authority), licensed notaries from the USA are authorized and secured with a strict corporate agreement right down to the description of technical fork (changing of code core) and work flow chart development. We have reached a compromise between public and private blockchains that is suitable for implementation of the distributed ledger technology in real business right now. Vitalik Buterin says that his technology is experimental, by this he's trying to secure himself from the society and business in case of coding errors. That is why we cannot be confident that transition to PoS will be smooth, considering Ethereum Foundation errors in what seems to be a simple fork.
Reference: Proof-of-Stake(PoS): The security method in cryptocurrency based on the necessity to prove the possession of stake amount on the account. When using this method, cryptocurrency pattern will more likely choose the next block for approval with bigger amount of funds on account. This method is used as an alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW) where probability of block approval is bigger for the account with higher computation capacity.
How are you planning to develop your project in the nearest future?
We're launching our own blockchain based on Ethereum code with similar emission timetable, the inflation will be about 10% and it will tend toward zero. This network will be used to develop Dapp-apps exclusively for music industry: Starting with marketplaces and finishing with games like "Guess the song" and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges for music assets. Exchanges will help to trade intellectual rights as common shares, but the earning capacity will be based on smart contracts and royalty payments.
There are two vectors of project development. The first one is based on transition to a fully stable and tested PoS (Proof-of-Stake), the second is based on modification of consensus method PoA (Proof-of-Authority) to PoAI where human participation is not required at all and nodes will be managed by Artificial intelligence. But at the moment it's just a concept that is being studied in parallel.
Apart from validators, we're planning to introduce two additional groups of participants – Keepers and Registrars, in this case our "ecosystem" will look like this:
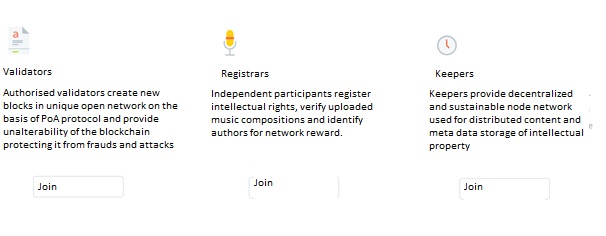
The team must be extended, it is necessary to draw skilled professionals from Evrone to develop some platform components, we also need to complete an alpha-version, present the platform on the Western market and start the first period of funding via ICO. ЯWe're creating a new website where we will introduce the new team and publish White Paper for the blockchain launch, we also need to rework and finalise the economic model as soon as we have changed the concept a few times already.
Why did you choose ICO to atrract funds?
We have refused to use venture investments for our project: The principal asset and value of a blockchain startup is its token or cryptocurrency. The important thing is the way it is used in the economy and in the product, not the growth of company shares. We can use technology investments but ICO pattern is easier and more convenient for everyone. In Decenter Telegram channel we receive proposals for a closed round of pre-ICO. A number of funds have announced their readiness to invest at the early stage, we have appointed talks with cryptocurrency fund thetoken.io by Vladimir Smerkis and Viktor Shpakovskiy that focuses on blockchain investments.
Artem, what do you think about further way of music industry along with the blockchain in general, can you give any forecast?
We are not the only team dealing with the integration of distributed ledger technology into the music market and I'm absolutely confident that the industry transformation by means of the blockchain technology is just the matter of time. It is highly likely that the Soundchain release will be a stress for Spotify investors and managers prior to their IPO, even if it sounds dramatic. Recently they have acquired startup mediachain.io that is calling itself a blockchain platform for some reason, although they don't use any consensus mechanisms. Based on their logic we can also call Tor a blockchain. On the whole the situation is as follows: either you integrate decentralized computing in your platform or you're doomed to extinction. It can take 5-10 years for big companies to acknowledge that their model is essentially dead. The blockchain is something that can move tectonic plates in crusty business as the changes are long awaited already. I suppose in the nearest future we will see a lot of theme articles based on the blockchain technology with hybrid protocols PoA Notary as they are more reliable, faster and less exposed to attacks. After implementation of the crosschain technology PolkaDot (developed by Parity.io) such hybrid networks will be able to make transactions to other networks and fix the result of executed transactions in fully public networks.
Special thanks to Daniil Reitman, a lawyer, for assistance in preparing the article.
Congratulations @brasilianboyar! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit