
Read this in German or Spanish
Philosophy
Orbs is among the next generation of blockchain technology, with a governing philosophy that no one blockchain system can be sufficient for everyone. Orbs is designed for B2C or B2B2C companies reaching large numbers of consumers, adding practical changes that give those businesses more utility than infrastructure provided by previous generations like Bitcoin or Ethereum or other new forms of blockchain. In particular, the Orbs infrastructure is fundamentally devised with large-scale consumer apps like Kik Messenger in mind.
Decentralized Business

The Orbs blockchain infrastructure is designed especially for established brands. The prime use of blockchain - decentralized consensus - allows everyone to check for compliance and validate transactions in place of a single authority. Decentralization allows smaller businesses to band together, creating combined ecosystems that can challenge the major tech giants.
Consumer apps decentralize for many reasons. They can craft their own economy conditions within the app, utilizing branded tokens as a means of exchange. That distributes economic value among users, letting smaller players to have more control within these ecosystems and to facilitate a virtual economy.
Tokens also allow for easier transactions within a private network than traditional currencies. They come with neither the burden of fees and middlemen, nor are they limited by cross-border complications and separate payment apps.
A 'requirement-driven' chain constructed with our design partners
As a requirement-driven company, Orbs is designing its blockchain based on the needs of its design partners, its first customers. Rather than launching a new blockchain and then seeking out the right market, Orbs is working with clients to address their needs inherently in the design of the blockchain.
We find that, while years of academic research and groundbreaking tweaks in newer forms of blockchain are impressive, they might not address practical needs. Sometimes, these new blockchains only address a narrow aspect of a given problem.
The Orbs approach, identifying real problems and implanting direct solutions within our core product, is more pragmatic. This shifts the focus of blockchain innovation from theory to praxis, with emphasis on real-world business and practical application.
Architecture and Virtual Blockchains
Orbs shards different tenant companies on the network by default. Within that architecture is the support of multiple, parallel “virtual blockchains” (a.k.a. "sidechains") providing independent ledgers over a shared “physical node environment.”
These chains enable easier scaling and predictable levels of service while simultaneously benefiting from a shared network.
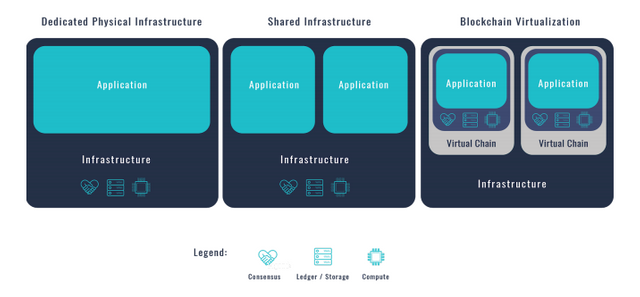
The development of Orbs was inspired by other technologies, such as cloud computing. Just as websites once universally ran on shared hosting but shifted to dedicated hosting or virtual machines on top of a physical server, Orbs’ virtual chains will protect individual blockchains from overcapacity on the infrastructure’s general network.
That independence lets different applications running on the Orbs platform apply different computing and storage capacities depending on their needs.
Consensus: 'Reputation,' not just stake or work
Orbs has introduced its own proprietary consensus algorithm, Helix, something more suited for mass-market applications and a large volume of transactions than PoW, and something more efficient than PoS.
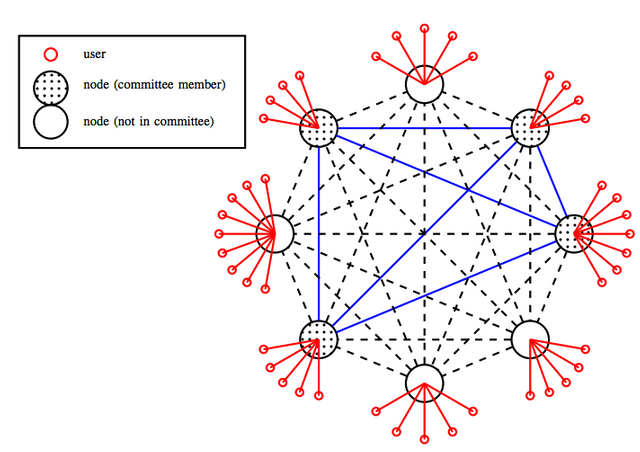
Illustration of a Helix network with n = 8 nodes, serving various numbers of users.
To reach consensus in a given ledger, Orbs uses a permission-consensus model as opposed to a the Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) models, which are generally less suitable for B2C apps.
The algorithm provides fast consensus and immediate transaction finality. Algorithmic, randomly selected committees of users assigned to block validation makes the process more efficient. That focus allows the state database to be under constant consensus, reducing wait time for block validation.
The use of committees to delegate reaching consensus also reduces costs by making the underlying infrastructure more economical, limiting the impact of heavy network traffic by using only a couple dozen nodes instead of 20,000, as is the case with Ethereum. Using the committee-based consensus strategy discussed above, Orbs reduces fees to negligible costs.
Rolling consensus allows Orbs to define expiration on previous blockchain data, essentially pre-programming data for deletion once it is obsolete.
Blockchain 3.0
Orbs represents a new generation of Blockchain 3.0 systems. Orbs embodies the future of blockchain specialization by focusing on decentralized apps that reach millions of users. Blockchains are not one size fits all.
✅ @gedalyahreback, I gave you an upvote on your first post! Please give me a follow and I will give you a follow in return!
Please also take a moment to read this post regarding bad behavior on Steemit.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit