



The Blockchain technology has changed the way the business was being done and now the business can be trustless and without a third party. The conduct of business can be fair & transparent now with blockchain technology. The potential use-cases are many and it can really add more value to the economy & the business can be cost-effective. It can offer new opportunities and people can value & monetize different asset class. Even after having such a wonderful technology, it is having a very limited application in the real world. The reasons are many such as- scaling capacity, its capability to serve millions or billion users seamlessly, keeping the state of decentralization, security issues, network overload, transaction cost, etc.
So unless the underlying blockchain infrastructure is scalable, resource-efficient, easy, wide open and being able to fit to the requirement and suitability of all types entities in a generalized sense it can not truly become public blockchain & mass adoption of Blockchain technology will be far from reality.
This article will introduce and detail about Harmony, a state-sharded blockchain which uses a unique approach to make it "linear & scalable" & optimize the consensus & transaction layer to solve the generic bottleneck of scalability. The state of decentralization and security remains intact with the state sharding technology. The block propagation is faster than ever and the speed of the network is greatly enhanced in this approach. Harmony aims to offer an infrastructure which anyone can use & grow on the top of blockchain technology.

(1) The choice of a consensus mechanism as a scaling solution
The consensus mechanism is very fundamental to any blockchain and the choice of a particular consensus further impact the scaling capacity of the blockchain. There are different types of consensus mechanism out of which some improves security and state of decentralization but lacks in scalability while some other improves scalability but compromise with the state of decentralization to some extent.
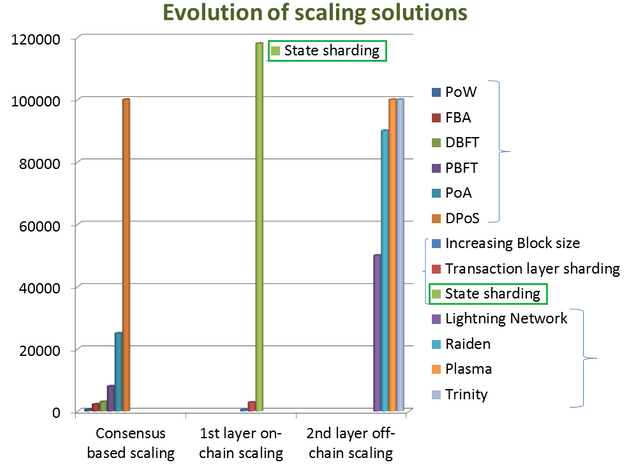
There various consensus mechanism are- PoW, PoS, DPoS, PBFT, FBA, DBFT, PoA, etc. Out of this, PoW preserves security and decentralization but lacks in scalability. DPoS improves speed significantly but partially centralized. PoA also improves scalability but it is suited for permissioned private blockchain.
(2) First layer on-chain solution
The first layer solution involves making some changes to the code base but the fundamental parameters can not be changed which may otherwise require a hardfork.
Scaling capacity can be improved by increasing the block size or by reducing the block creation time. But it may not significantly improve the scaling capacity.
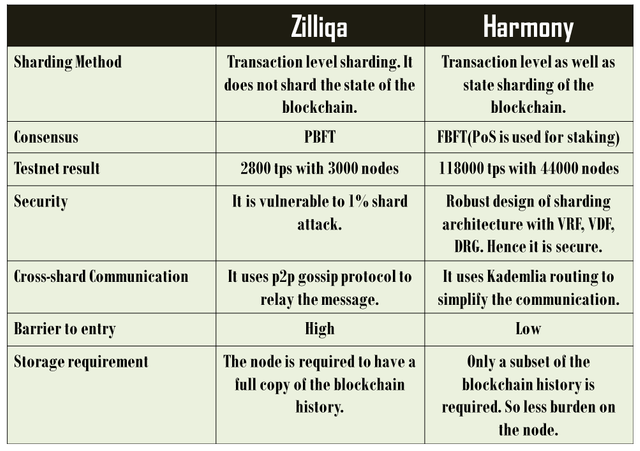
By sharding the network, scaling capacity can be significantly improved. Zilliqa uses transaction layer sharding-the reported scaling capacity is 2800 tps. Harmony uses state sharding and the reported scaling capacity is 118000 tps.
(3) Second layer off-chain solution
In second layer off-chain solutions, the transactions from the main chain are off-loaded from the main chain to a secondary protocol to reduce the network load and congestion on the main chain and improve the scalability. The side chain and side channels are generally used.
The transactions happen between two parties through state channel off-chain and the transaction is not broadcasted until the parties decide the close the state channel.
The lightning network of Bitcoin, Raiden network of Etherum, Plasma of Etherum, Trinity of NEO blockchain are the perfect examples of the second layer off-chain scaling solution. It significantly improves the scaling capacity.

Harmony is a public blockchain which has a full-stack approach to optimize at every layer in consensus algorithm and aims to offer a scalable blockchain infrastructure where the next generation decentralized economies can thrive. It focuses on high transaction throughput, low latency, security, state of decentralization, etc. The major selling of Harmony is state sharding technology which was never done before. Apart from that, it has brought very minute improvement on various attributes of existing blockchains to make the Harmony network linear, scalable, efficient than ever. Some of the various improvements include- using BLS signature, relying on FBFT instead of PBFT to make it linear, using Kademlia protocol to make the cross-shard communication faster and effective, using erasure code for efficient message broadcasting, etc. The major attributes of Harmony network are- using DRG for assigning nodes into the shards, using effective PoS to maintain the state of decentralization, making the network firm & secure against any kind of attack.

(1)Energy-intensive consensus
The consensus is key to any blockchain network and it is used to verify the information that is added to the ledger. The major networks like BTC, ETH use PoW based consensus, even the first sharded based blockchain Zilliqa use PoW based consensus. In PoW it is required to solve a cryptographic puzzle and it is basically a chain-based consensus. But the computation power required to operate in a PoW based consensus is highly energy-intensive.
Harmony network uses PoS that relies on a linearly scalable BFT algorithm. PoS does not require energy-intensive computation power like PoW, hence it is a green alternative to PoW. For the validators to participate in the network, they need to stake a certain amount of tokens. Therefore it is energy-efficient.
(2) Dilemma between scalability & decentralization
There has been a generic struggle between scalability and decentralization since the inception of blockchain technology. While decentralization is fundamental to blockchain technology, scalability is essential to enhance the performance of the decentralized application, enterprise implementation, gaming, etc. The major network like BTC or ETH still scales at a lower rate(BTC at 7tps and ETH at 20 tps) which does not stand or even comparable with the scaling capacity of VISA and these are PoW based blockchains. On the other hand EOS scales at a better rate and that is a DPoS based blockchain. In most of the blockchains, scaling solutions require to compromise with the decentralization of the network. So scalability is coming at the cost decentralization.
Harmony solves this dilemma and it preserves both scalability and decentralization and one aspect need not have to be compromised to achieve the other. It uses state sharding technology in its architecture which neither compromises security nor decentralization. It makes the network scalable to an extent which can be at par or even better than the centralized payment solutions like VISA. The reported scaling capacity Harmony in testnet is 118000 tps with 44000 nodes.
(3) Resource efficiency
In PoW based blockchains, one has to go with a mining rig and has to establish a physical arrangement to take part in the network. In other types of blockchain which uses PoS or DPoS, one does not need any major physical arrangement like PoW based network. But conventionally in all blockchains(with any consensus), in order to become a node, it has to store the entire state of the blockchain. With the ever-growing ledger size, this is getting more restrictive from the view point of resource utilization with each passing day. In general, simple resources may not be able to participate in this type of network.

Harmony solves the issue by its state sharding technology where the node joining the network does not have to store the entire state of blockchain, rather only a subset of the blockchain state is required to be stored. As Harmony shards the state of the blockchain, the different shards possess different state which is a subset of the entire state of the blockchain. That means any new node can quickly sync with the network. Therefore any simple computer can participate in the network. Hence Harmony is resource-efficient as compared to other public blockchains.
(4) 1% shard attack(security)
In a PoW blockchain without sharding, the attacker needs 51% of the network's hash power to gain control of it. In a blockchain that uses sharding technology & PoW based consensus, all the shards(as the network is split into a number of shards) have certain hashing power. For example, if the network has 100 shards then each will have 1% hash power. So the attackers will start concentrating their hash power on the single shard and ultimately take control of it. Hence an attacker can easily control a shard with 1% of the network hash rate. Simply put, the security challenge in an unsharded PoW is 51% of the hash power, but in a sharded PoW, the security challenge is 1% of the network hash power.

Harmony uses PoS to eliminate the attacker's ability to concentrate hash power & Harmony is firmly secure against 1% shard attack. In its sharding structure, it uses DRG(Distributed Randomness Generation), VRF & VDF to assign nodes into the shards. Further, the sharding structure varies in every epoch. An epoch is a predetermined time interval in Harmony. So it is not possible for the attacker to crack the random number and gain control of a shard in the network. The combination of beacon chain and shard chain makes it difficult for the attacker.
(5) Network overload & complex communication within the network
In the existing PBFT algorithm, network overload is not linear. It incurs a network overload of O(n*n) as all the nodes rebroadcast to all other nodes to count the votes. Further, the cross-communication also follows the normal gossip protocol. Therefore the existing mechanism is neither linear nor scalable.
Harmony makes the network linear and scalable by reducing complexity in PBFT(Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) from O(n*n) to O(n) and makes it FBFT(Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerance). Here the counting of votes is done by multi-signature signing(using BLS signature) instead of rebroadcasting. The cross-communication in the sharded network uses Kademlia protocol which simplifies the complexity from O(n) to O(log(n)). It does not use the traditional gossip protocol for message broadcasting. It uses erasure code for message broadcast which further reduces the network overload and makes it efficient.

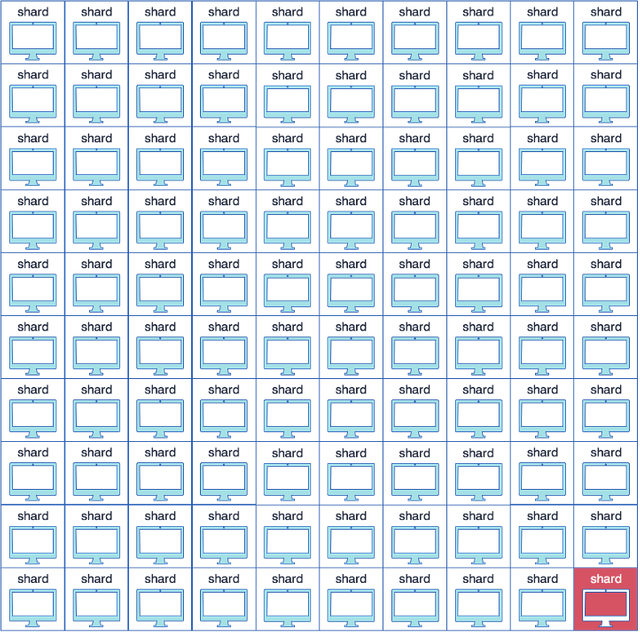
State sharding
Harmony uses state sharding technology, so the network is divided into a number of shards and the nodes are assigned into the shards for a predetermined time interval known as epoch. In each epoch, the nodes are reshuffled and assigned to the different shards again. The reshuffling is done using DRG to create a random number and based on that the nodes are assigned to the shards. It also uses VRF(Verifiable Random Function) and VDF(Verifiable Delay Function) to make it robust.
Each shard chain holds its own account state and that varies from other shards. The user account and the smart contract operates differently in a state-sharded blockchain like Harmony. A user account can have different balances in different shards and the user will be able to move the balance from one shard to the other through cross-shard transaction. A smart contract is also limited to a particular shard. But again multiple instances of the smart contract can communicate with each other through cross-shard communication.
Epoch
It is a fixed time interval during which a sharding structure is fixed and the shards run the consensus process. The sharding structure varies from one epoch to the other. In each epoch, a random number is generated using DRG and based on that random number new sharding structure is determined.
Consensus
Harmony is a PoS based network which runs with a linearly scalable BFT algorithm which is also known as Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerant(FBFT). FBFT is an improvement over PBFT because of the complexity getting reduced from O(n*n) in case of PBFT to O(n) in case of FBFT.
Traditionally in PBFT the consensus is carried out in two phases, i.e. "prepare" and "commit" phase. The nodes are categorized as "leader node" & "validator nodes". A proposal is initiated by the leader to all the validators and the validators further broadcast that to all other validators. The same process is repeated in both "prepare" & "commit" phase. Both the phase finishes when more than "2f+1" votes are seen, where f is the number of malicious validators. Due to the fact that the validators rebroadcast the message to other validators, it incurs a communication complexity of O(n*n). Harmony solves this complexity by making an improvement over PBFT which is known as FBFT and the complexity reduced to O(n) in FBFT. In FBFT it is not required to rebroadcast the message to other validators, rather the leader collects the vote by multi-signature signing. So it becomes linear. This is important for a scalable blockchain with hundreds or thousands of nodes.
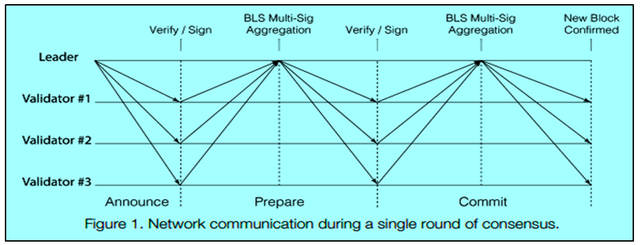
In order to further make it effective & to improvise the network, Harmony uses BLS multi-signature(which requires only one-round trip) instead of schnorr multi-signature( requires two round-trips). So Harmony with FBFT & BLS multi-signature is much faster and linearly scalable than BFT algorithm.
FBFT consensus is reached in the following ways:-
There are two phases in this consensus, i.e. "prepare" and "commit" phase.
Prepare phase
- The leader broadcasts the block header to all the validators.
- The validators verify it, sign it using BLS signature and send it back to the leader.
- After receiving at least "2f+1" valid signatures, the leader broadcasts the aggregated multi-signatures with a bitmap.
Commit phase
- The validators check the multi-signatures which has at least "2f+1" signers, verify it, then sign it and finally send it back to the leader.
- After receiving at least "2f+1" valid signatures, the leader aggregates them into the BLS signatures, creates a bitmap and finally commit the new block with all multi-signatures and bitmap attached & broadcast the new block to all validators.
DRG
DRG(Distributed Random Generation) is used to generate mutually agreed random number so as to assign nodes into the shards. This random number has the following properties:-
- No one can predict this random number.
- The random number generation is not biased.
- It is verifiable by any observer.
- It is scalable to a number of participants.
Further, it uses VRF(Verifiable Random Function) to cryptographically select the nodes and VDF(Verifiable Delay Function) to counter the last revealer-attack. The DRG with VRF ad VDF is key to the security of Harmony sharding architecture.
- The leader sends "init" message with the hash of the last block to all the validators.
- After receiving the "init" message, VRF is computed to generate a random number & a proof for each validator. Then each validator sends the random number and the proof to the leader.
- The leader collects all the random numbers(which should be at least "f+1") & then generate the final randomness "pRnd".
- The leader runs BFT among the validators to reach consensus and commit "pRnd" in the block.
- VDF delays the randomness and the leader starts computing the actual randomness "Rnd".
- Once "Rnd" is computed, the leader runs BFT among the validators to reach consensus and finally commit the randomness in the blockchain.
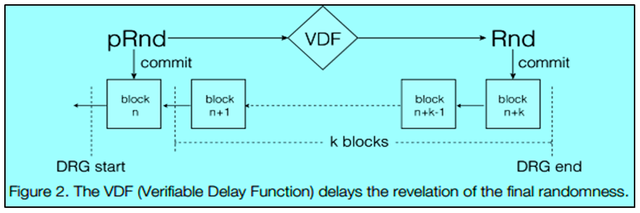
No one can manipulate the above protocol because:-
- By the time "Rnd" is computed, "pRnd" already committed in the previous block.
- Even if a dishonest leader tries to stall the protocol, the timeout mechanism in BFT will trigger and that will eventually switch the leader and restart the protocol.
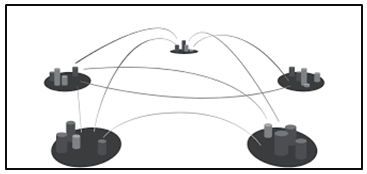
Beacon chain & Shard chain
A shard chain in Harmony is identified as a chain which stores its own state and validates its own transactions which are relevant to itself. The sharded blockchain of Harmony consists of a number of independent shard chain which communicates with each other using Kademlia protocol and reaches consensus.
A Beacon chain is also a shard chain. It also processes transaction like a shard chain but it has two distinct responsibilities:-
- It generates a random number based on which the validators are assigned to the shards.
- It is the chain where the validators stake their deposit.
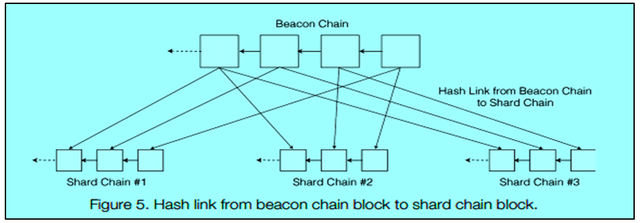
Beacon chain is a key entity for the security of the state of the blockchain. The beacon chain includes the block header & checks its validity by verifying the hash of the previous block and multi-signature log. The beacon chain acts as a relay between the shards and hence lowers the computational burden. It also makes it difficult for the attackers to include a fake block as the attackers have to corrupt both beacon chain and shard chain.
Resharding
Resharding in Harmony is important from security point of view. It is obvious that in a decentralized network like Harmony after an epoch ends, nodes may unstake & go, some new ones may come and some may stay, so the rearrangement of voting share in each epoch should be such that the network runs optimally and in a balanced state. Harmony's resharding approach adopts cuckoo rule.
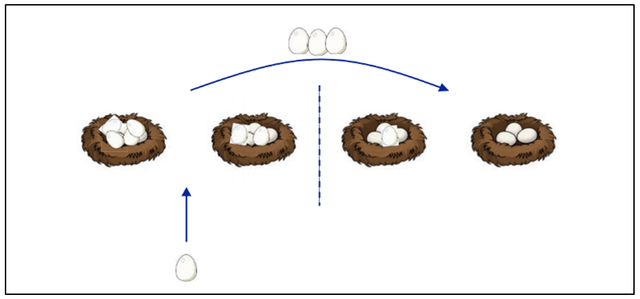
- The nodes which unstake are expelled from the network.
- The new node who wants to join the network is assigned with a cuckoo random number and the position of the random number indicates the shard number of the new node. The existing node close to the cuckoo random number is moved to a new shard.
- The existing nodes who want to stay, receive new voting shares for the next epoch.
- The new shares are randomly assigned to the shards which have more than median of voting shares of the entire network.
- A constant number of the voting shares are redistributed and assigned to those shards which have less than median of voting shares of the entire network.
Adaptive threshold PoS
The price of voting share is calculated as:-
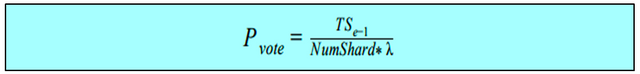
λ= security parameter(extremely important from security point of view)
NumShard= Number of shards
TS( e−1)= Total amount of tokens staked during epoch "e-1"
It is important to note that λ is the denominator in the above equation and Harmony in its research has established that when the value of λ>600, the probability of a single shard having more than one third voting shares is negligible(probability P=0.99997). That further establishes that the probability of a shard failure as "once in 1000 years", if the epoch is considered as 24 hrs each and λ is greater than 600. Hence Harmony sets λ=600 to ensure high security for the shards.
Stake-based sharding
The validators who want to participate in the Harmony network needs to stake a certain amount of tokens and the number of tokens will further determine the number of voting shares assigned to the validator. In each epoch, the voting shares are re-shuffled and randomly assigned to the validators. Each voting share corresponds to one vote in BFT consensus. The price of voting share is calculated algorithmically(as described in Adaptive threshold PoS).
Harmony adopts "shard by shares"(one voting share to one shard) instead of "shard by validators"(one validator to one shard) in order to counter an attack scenario known as "large-stake attack", in which the malicious actors possess more than one-third voting shares. In Harmony, a random permutation is done on all the voting shares and the permuted list of voting shares are divided by the number of shards and then the voting shares are assigned. This improves security against large-stake attack.
Fast state Synchronization
In the traditional blockchains, the new validators joining the network need to download the full state of blockchain and that consumes a significant amount of time to sync with the blockchain. Further, in order to check the validity, the cryptographic traces(signatures) from the current state to the genesis block is verified and that again consumes a lot of time. Harmony solves both the issue and the new node joining the network can quickly sync with the blockchain.
It is to be noted that, in Harmony, a node joining the network need not require to download the full state of the blockchain, rather the new node has to download the block header(which is very small in size as compared to the whole blockchain state). Hence the new node can quickly synchronize with the network within the epoch.
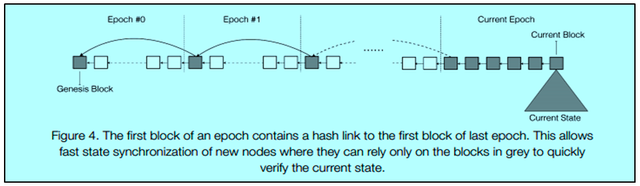
In order to speed up the verification of the current state which is downloaded, the first block of each epoch will include an additional hash pointer to the first block of the last epoch. Hence any new node joining the network can jump across the blocks within an epoch by tracing hash pointers to the genesis block. That eventually speeds up the verification of the current state.
Cross-shard communication
Cross-shard communication is generally viewed as a complicated aspect in a sharded network. It is also key for achieving consensus and in order to achieve fast consensus, the communication has to be leaner.
Harmony adopts shard-driven approach and uses Kademlia protocol to make the complexity of cross-shard communication leaner and simpler. Kademlia protocol is a distributed hash table which is used to improve the exchange of information via an overlay network. Kademlia protocol does not require overhead like a gossip protocol and messages can travel explicit distance before reaching the destination. So using Kademlia protocol the overhead gets simplified from O(N) to O(logN)). Simpler cross-shard communication further helps to reach fast consensus.
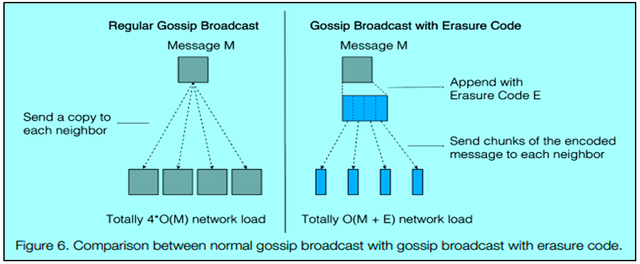
Efficient broadcasting
Conventionally in a blockchain, the communication happens through gossip protocol and the relay of the message happens in a p2p way. Therefore in a p2p broadcasting, if a node has 5 neighbors, then the node has to send a copy to each neighbor and the overall network load will be 4 * O(M). If there are "n" number of neighbors, then the overall network load will be n * O(M).
M= message size
Harmony adopts a different approach, first it encodes the message with an erasure code and then it sends the chunks of encoded messages to each neighbor. So in Harmony, the overall network load will be O(M+e), which is much smaller in comparison to the conventional blockchains. Hence the message broadcasting mechanism in Harmony is much more efficient.
M= Message size
e= Size of the erasure code
Effective PoS & Consensus rewards
Harmony adopts Effective-Proof-of-Stake mechanism in its design which prevents stake centralization & allows even stake distribution among the validators, which supports stake compounding & delegation. The design principle of state sharding blockchain(in Harmony) is such that each shard contains a large number of validators with an equal or similar stake so as to prevent 1% shard attack.
So while the criteria to choose validators is stake based, it does not usually follow the common approaches of PoS blockchains as it is well known that in most of the PoS blockchains, there are cases of stake centralization and "rich getting richer" approach. Hence Harmony adopts effective PoS approach so that the degree of decentralization remains intact.
It also supports the compounding of block rewards and delegations, as delegation will allow the general token holders to stake without being a validator.
The highest-ranked validators are elected based on stake as the committee. The rank of stakes determine the validators in an epoch and in the new epoch, the rank of stakes will change. The "block reward" & the "voting power" are in proportion to the effective stake of a validator.
The effective stake is calculated as per the following formula:-
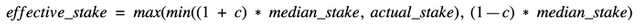
The effective stake of a validator is generally bounded between the "upper limit" & the "lower limit".
Upper limit= (1 + c) * median_stake
Lower limit= (1 — c) * median_stake
c= protocol parameter
Actual stake Vs Effective stake

Analysis of "Actual stake Vs Effective stake" curve
- It acts as an equalizer to ensure even distribution of stakes.
- It makes the staking pool decentralized.
- The highest-ranked validator benefit less (economically) as compared to the lower-ranked validators.
- For compounding, the validators in yellow area are incentivized & the nodes in blue and green area can re-stake their rewards in the same validators.
- For delegation, it is relatively better to delegate to the validators in the green area as the return to stake ratio is higher in the green region and hence better rewards.
Rewards & stake slashing
The protocol-defined new tokens are rewarded to all the validators who signs the block. Similarly, the transaction fees are rewarded to the validators. A slashing mechanism is in place to discourage any malicious or dishonest act.
In case of double signing, there is a minimum of 2% slashing on the stake and it further increases linearly as the number of validators being slashed at the same time.
In case of unavailability, there is also penalty such as- voting power depletes by 25% for 3hrs of unavailability continuously, voting power depletes by 100%(no voting power) for 12 hrs of unavailability continuously.
In case of "no voting power", the validator is considered as inactive and in such a case, the validator can not participate in the consensus process and the validator has to send "rejoin transaction" in order to be considered for validator election again.

Merits
It simplifies the network complexity by using BLS signature for multi-signature signing to collect votes.
It makes the network linear and scalable. It can achieve scalability which is never realized before. The testnet scalability reports 118000 tps with 44000 nodes.
DRG, VRF, VDF for assigning nodes to shards makes the network firm & secure against attackers.
It is resistant against 1% shard attack.
It lowers the barrier to entry.
State sharding is very unique and it optimizes the blockchain network and makes the network resource-efficient.
It can support large economies, gaming industry, decentralized financial services, enterprises and many other types of projects.
It does not compromise with the security or decentralization of the network by offering scalability. It preserves all of them simultaneously.
Beacon and shard chain makes the attacker ineffective.
It reduces the overall network load.
It uses Kademlia protocol for cross-shard communication which enables direct & faster sending of message between the shards.
It can effectively counter large-stake attack as it adopts "shard by shares" approach.
New nodes can easily join and quickly sync with the network as they don't have to store the entire state of blockchain.
Demerits
- There is no doubt that the blockchain solution offered by Harmony is genuine and can really become a blockchain for billions but the structure is little complex to understand and for the general enterprises it may not be that easy. Therefore extended support is needed.

Zenex is a company which has 5000 employees. As regulatory compliance, it generally asks its employees to submit the ID and Address proof to update its database every 6 months. The employees are generally asked to share their bank statement for address proof.
In last 6 months, the employees have started complaining to Zenex that, they are not comfortable by sharing their sensitive & private information in the name of regulatory compliance, as the sensitive data like bank transactions, account balance are also getting revealed. They have also requested to the Director of the company to find an alternative solution so that their privacy can be respected.
The Director acknowledges this issue and asked the concerned department to look for an alternative solution using which both "compliance check can be done quickly" and "privacy can also be respected". The advisor to director has suggested using Harmony blockchain network to solve the issue. Explain how Harmony blockchain can be a viable solution to this issue.
Sharing a document can be a fundamental obligation to regulatory compliance, so is the case here with "Zenex". The employees are submitting their bank statement as a document of address proof, but in that process, they are also revealing other sensitive information such as bank transaction details of their account. It may be unnecessary on the part of verifier who checks the address proof. It is also the breach of private data.
Harmony is a secure and highly scalable state sharding blockchain. The users generate a set of predefined rules using zero-knowledge proof and based on that rules, they can make up their private data in an efficient manner. In this use-case, they need to submit the bank statement as an address proof, but using zero-knowledge proof they can reveal only those information that is essential for the compliance. The other private and sensitive informations need not require to be revealed. That can be set with ZK proof.
Further, Harmony is a very fast & scalable network. The communication protocol of Haromy network is also linear, simple and fast as it uses Kademlia protocol. So the users can send their data hassle-free. The verifier can get its compliance check done very quickly.
Simply put, if Zenext will use Harmony blockchain network, then not only it can address the issues of its employees in the context of the breach of private & sensitive data, but also can get the compliance check done in a synchronous manner.
Zenex is fully satisfied with the attributes of the Harmony network and decides to use this network for its compliance check



Many types of blockchain projects exist in this domain which offers to address a particular problem interface. What I observed and analyzed about Harmony is that it has gone deep into the micro bottleneck of various existing blockchains and tried to offer a solution which can make the network better and efficient than ever. Scalability is a very open and broad issue of blockchain since its inception and what Harmony has offered is not going to compromise the other fundamental attributes such as security and decentralization. Its sharding structure may be little complex, but this structure & the mechanism makes the Harmony network secure. The project really reflects extensive research and hard work in the backend. I can see a bright foundation of blockchain infrastructure in the form of Harmony where varieties of decentralized economies, large scale infrastructures can thrive and prosper.
More Information & Resources
- Harmony website
- Harmony OnePage
- Harmony Whitepaper
- Harmony Medium
- Harmony Twitter
- Harmony LinkedIn
- Harmony Instagram
Hello @milaan this is an interesting perspective and a very extensive review of the Harmony blockchain, it is no doubt that the team at Harmony has gone deep into research and implemented cutting edge procedures to ensure the blockchain is capable of meeting industry demands and blocking off the loopholes left open by existing technology.
Indeed State sharding is very unique and it optimizes the blockchain network and makes the network resource-efficient.
Thank you for using the Realityhubs tag, your effort is appreciated and we look forward to more of your reviews.
Realityhubs Mod
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you, sir.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I really enjoyed your review information with a neat paragraph layout.
Keep up your great work.
Regards,
@anggreklestari
[Realityhubs Curator]
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you, sir.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hey Garlam - Head of Marketing at Harmony here - really love the article and was wondering if you'd be open to more work as one of our writers!
Message me on telegram - @garlamw (and yes it is the real me - check my twitter to verify my telegram id - https://twitter.com/GarlamWon)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit