
INTRODUCTION
The rapid effect of technological change on the global economic structure are creating immense transformations in the way individuals, companies and nations organize production, trade goods, invest capital, and develop new products, services and processes. Sophisticated information technologies permit instantaneous communication among the far-flung operations of global enterprises. New materials are revolutionizing sectors as diverse as finance and communications. Advanced financial technologies have altered long-standing patterns of productivity and work patterns. All this has both created and mandated greater interdependence among individuals, firms and nations. The rapid rate of innovation and the dynamics of technology flows mean that comparative advantage is short-lived. This permits both developed and developing countries to harness technology more efficiently, with the expectation of creating higher standards of living for all involved. This rapid technological change brought about the new economy.
The New Economy of the Internet produced hundreds of companies each worth billions of dollars, and thousands of companies each worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Given that the New Economy of decentralized applications is starting on top of the now massively deployed Internet and mobile devices, and it appears to have as much ability to ripple throughout our economy and society as the Internet did, the (financial) wealth created by the Decentralized Economy appears to be on scale with the Internet, if not much greater. This new economony would not have been possible without the massive help of the blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology can be said to be the backbone or bloodline on which every cryptocurrency operation is structured. Blockchain technology combines three concepts and their technological incarnation, to create a system with functionality and reliability — a system that in particular is decentralized. Those concepts and associated technologies are crypto-encoding, a ledger of cryptographically-linked transactions, and an incentive mechanism for dozens or even millions of independent actors to execute the cryptographic processing that perpetuates the blockchain.
In order to make the system reliable, blockchains employ a cryptographic technology that both irrefutably links each transaction to the previous one, and assures a consensus (in lieu of a single centralized third party) of trust. This combination assures that each successive transaction (or so-called “block”) in the chain of transactions is correct, trustable and irrefutable.
Under the blockchain technology they are a good number of cryptocurrencies which are already taking over the market. The most notable of the cryptocurrencies powered by blockchain is the Bitcoin which was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrent ever produced, and it was endowed with numerous features but had some challenges such as scalability, auditability, security, to mention a few. These challenges in recent years has threaten to stunt the growth of the whole network.
In recent years other alternate coins have been springing up to solve this issue but to no avail, bringing a huge question mark to the whole credibility of the crypto-network, until recently.
WHAT IS PROXIMAX?
ProximaX is a blockchain project founded by Lon Wong and Alvin Reyes. The project aims to establish a sustainable and fast network protocol that will improve upon modern blockchain structure. Main focus of the project’s work is making a number of comfortable services for decentralized applications developers.
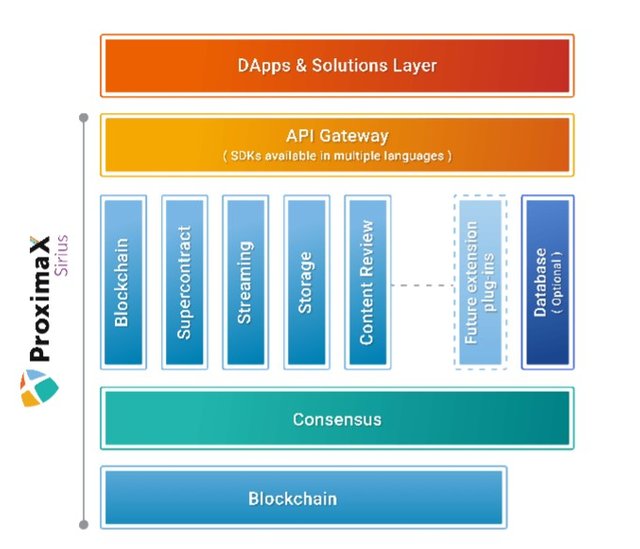
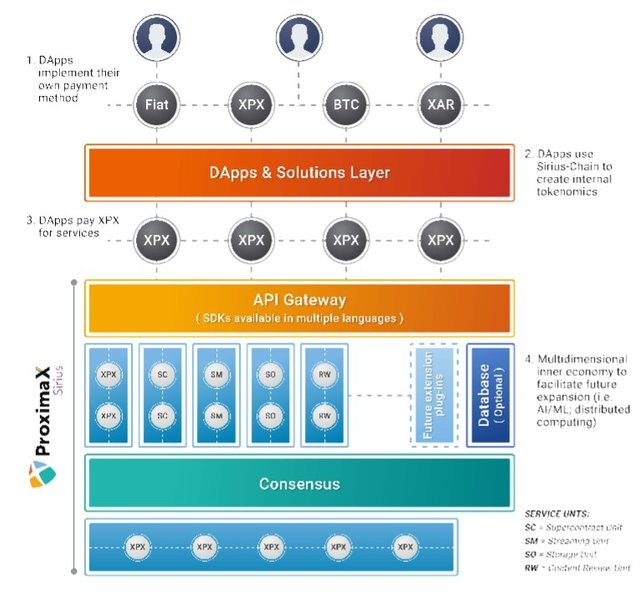
ProximaX also known as ProximaX Sirius is a next-generation Integrated and Distributed Ledger Technology development platform made up of proven distributed and decentralised layers: blockchain, storage, streaming, and database. All of this components are held together by the blockchain protocol (Sirius Chain), which acts as the platform’s backbone. Bundled as one, it is a superior technology that shines best with its security, speed, cost-efficiency, immutability, auditability, scalability, flexibility and easy usage.
Source: High-level Technical Whitepaper
ProximaX provides the world with a scalable and secure blockchain system that is able to support the emerging decentralized economy. ProximaX strives to scale trust for billions of people and create a radically fair economy. Since its existence ProximaX has helped curb the existing problems in the crypto world. It has helped solve the problem of scalability, security, and easy way of working, which has been the major challenge in the cryptosphere for the past 12 years.
The consensus algorithm is a key component of any blockchain. It determines how securely and quickly blockchain validators reach consensus on the next block. The first blockchain consensus protocol which powers Bitcoin is Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus or Chain Based consensus. This consensus mechanism was not scalable for a blockchain system with hundreds or thousands of nodes due to its low communication complexity. Due to this, the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus was invented to replace the Proof-of-Work consensus.
ProximaX Sirius Chain uses the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Greed (PoG) consensus algorithm which is arguably the most effective and performant algorithm scheme. It is the best fit for this platform as it is economically efficient, and has minimal hardware resource requirements, making it easier to invite blockchain participants, and balance the network. This consensus algorithm has also helped ProximaX to process transactions securely, quickly and efficiently, at a rate of thousands per second or more, offer a range of basic transaction types that launch cryptocurrencies past their core use of a payment system alone, and the creation and deployment of advanced applications.
The Proof-of-Greed (PoG) is a consensus mechanism created by ProximaX, it is a mechanism that decentralizes the block forging process even further. It is an extended reputation input that ensures no node can be too “greedy” when accepting transactions with large fees while still considering the block generation time. PoG also solves another major problem found in other blockchain networks, this being that there is no fee adjustment framework. With PoG, the fee size is adjustable for both consumers and Validators.
Sirius Chain is based on the latest version of NEM’s blockchain called “Catapult” (Dragon version). Catapult provides a predefined set of features that are applicable to most if not all business use cases. This makes Sirius Chain extremely attractive for building any type of service either as an extension or as an application vertically on top. ProximaX Sirius relies on Sirius Chain to facilitate transactions for the platform’s core services. Given that Sirius Chain will perform some “heavy-lifting”, ProximaX developers further enhanced some of Catapult’s core elements, in turn improving its performance.
P a g e 2 | 4 4 High-level Technical Whitepaper
Sirius chain is the backbone of ProximaX which holds together all the activities (core services) that occurs in the ProximaX platform. Sirius chain provides an agile architecture that facilitates the addition of new core services, and the creation and deployment of advanced applications.
Sirius Chain has the following in-built features:
Account: An account is a key pair, which consists of two types: private and public key. It is associated with a mutable state stored on the Sirius Chain. In other words, you have a “deposit box” in the blockchain, which only you can modify with your key pair. As the name suggests, the private key has to be kept secret. Anyone with access to the private key ultimately has control over the account.
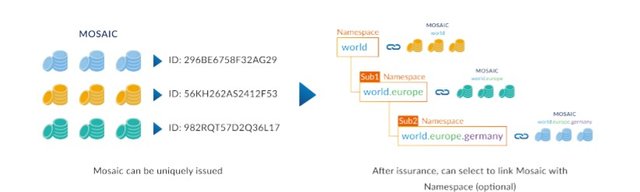
Namespaces: Namespaces allows you to create an on-chain unique place for your business and your assets on Sirius Chain. A namespace starts with a name that you choose, similar to an internet domain name. If one account creates a namespace, that will appear as unique in the Sirius Chain ecosystem.
Mosaics: Mosaics are part of what makes the platform unique and flexible. They are fixed assets on Sirius Chain that can represent a set of multiple identical assets that do not change.
A mosaic can be a token, but it can also be a collection of more specialized assets such as reward points, shares, bonds, warrants, signatures, status flags, votes, or even other currencies.
Metadata:* Data stored on Sirius Chain such as accounts, namespaces and mosaics are all immutable by default, which limits the flexibility of storing additional data that needs to be associated to these state objects.
Metadata solves this by creating a data attachment to the predefined objects on Sirius Chain, therefore creating a level of flexibility to storing data.
Multi-level multisignature: Multilevel multisignature is used for creating multilevel agreements on Sirius Chain. In a typical blockchain implementation, multisignature is an agreement between multiple parties having custodian to a specific account (mostly called sub-account, and child account).
Aggregated transactions: Aggregate Transactions merge multiple transactions into one batch of transactions, allowing trustless swaps, and other advanced logic. Sirius Chain does this by generating a one-time disposable contract. When all involved accounts have cosigned the aggregate transaction, all the inner transactions (i.e., transactions aggregated in the batch) are executed simultaneously.
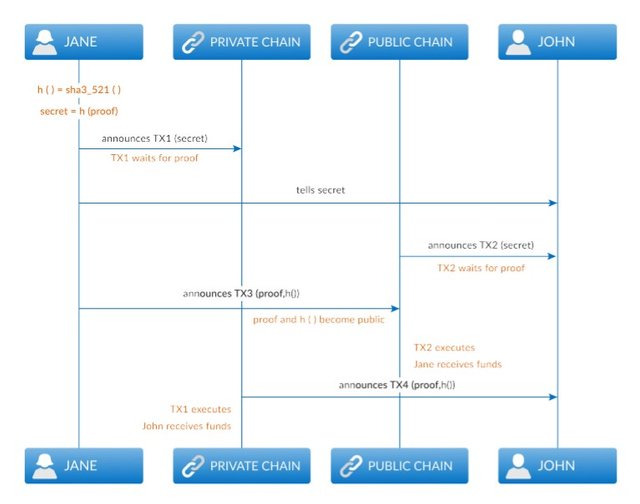
Cross-chain transactions: Cross-chain transactions are transactions between two Sirius chains, be they private or public chains. It is a very useful transaction mechanism to exchange assets between two parties residing in different chains. Also called “atomic swap”, it involves locking up funds in the chain of the sending party (ies) and then issuance of such assets in the receiving party’s chain.
Cross-chain in the Sirius platform uses the lock fund concept, where the fund is locked upon crossing chains and then unlocked in the reverse.
High-level Technical Whitepaper
BENEFIT OF DEVELOPING A PROJECT IN ONE PLACE
Sirius chain acts as the IOT (Internet of Things) platform which was developed in a form of IOT middleware, which purpose was to function as a mediator between the hardware and application layers. Its primary tasks includes data collection, remote device configuration and control, device management, and over-the-air firmware update.
Sirius chain is the middleware which all activities going on in ProximaX rely upon to survive. For example when using ProximaX for database management which involves data collection, device management, messaging and OTA software update. You can sit at the comfort of your home and get data from anywhere through the help of IOT, all you have to do is setup when you want the activity to take place. The features in which this platform obtain are; scalability, customizable, and highly secured. What your business can do let’s say if you were running an online chatting business.
CORE SERVICES OF PROXIMAX
ProximaX core services are predefined plug-ins. Whilst Sirius Chain provides for each service node a decentralized immutable ledger for statistics and reporting using transactions, core services also use Sirius Chain as a source of robust logic for performing services with economic incentives. Building services on top of a blockchain is quite challenging, as it requires developers to have a comprehensive understanding of the distributed nature of blockchain technology. In order to make developing on blockchain more accessible to a wider developer community, ProximaX integrated a universal set of core services with Sirius Chain; which include;
i. Sirius Storage:
Most applications and system solutions require storage. To make ProximaX Sirius a holistic development platform, it was imperative that storage be added as one of its core services. Sirius Storage is able to store all types of binary data, be it graphic, video, or just text. Sirius Storage can provide reliable storage of files of arbitrary nature. The level of reliability is determined by the user of the storage drive and is significantly related to the level of payment made.
Sirius Storage has some core services such as; storage preparation, new storage replicator, upload, delete, modify, rename, copy, directory, and synchronize.
ProximaX as an amazing feature when it comes to its Sirius storage. This feature is known as Proof of Storage in which is used in a distributed storage network to perform replication process and to ensure that the data is intact and can be retrieved at any time. Sirius Storage comes with two predefined Proof of Storage schemes, which are; Enhanced Proof of Storage and Simplified Proof of Storage.
The ProximaX Sirius Storage can be used by large companies to store vital information’s which will be needed in future. With its efficient scalability it will be easy to stored thousands of information which their present archives might not be able to store. And also with its ability to retrieve data through the help of the Proof of Storage it will be a boost in the company’s efficiency.
ii. Sirius Streaming: The Sirius Streaming shows that the blockchain is really expanding into different sectors, before this innovation it was all clear to us that the real focus of blockchain was on finance. But now exploring other sectors is something great. The Sirius Streaming platform is divided into two (2) parts. Which includes;
Storage Streaming: These is where data is pre-recorded or persisted on Sirius Storage and streamed to different viewers. The storage streaming service is tightly connected with the storage service, as Sirius Storage provides data loading. The ability to download is available not only for the content owners of the streamed data, but also for the end-consumers of the streamed data. This opens up the ability for creating a variety of applications with content distribution functions for different domains and service policies. The goal of the storage streaming service is to provide an autonomous and economically fair way of streaming pre-recorded or persisted data from a persistent device such as a Replicator. This type of streaming process helps the masses to get access to pass information like videos of past events. One of such company who is into this streaming process is YouTube. The storage streaming node actors are; The Acceptors (the Pre-load files to be streamed), Replicators (the Replicate the files and stream file data to end-consumers), and Storage Verifiers (the Verify the replicated data across different Replicators). The protocol which backs up this streaming exercise is the Fair Streaming Protocol which allows streaming between nodes that do not know each other yet trust each other through a common cryptographically signed data.
Live Streaming: This is where data is recorded live, transmitted and immediately distributed to viewers. The main aim of live streaming is to create a platform for streaming live data from a single sender source fanning out to multiple distribution points to one or more receivers in an autonomous and economically fair way.
ProximaX also has an amazing feature when it comes to its Sirius Streaming. This feature is known as Proof of Bandwidth which is a crucial element in any streaming service. In the streaming network, bandwidth and reputation are necessary to ensure that the consumer is serviced with the best available nodes that will deliver the data stream from one point to another. In ProximaX Sirius’ streaming service, nodes are expected to provide bandwidth statistics via an in deterministic process that returns a set of data (time tags) that will be used to determine reputation with respect to their bandwidth. They are various nodes actors that run the affairs of live streaming such as; the stream discovery node (which maintains a list of authenticated streaming nodes), Stream Landing node (which receives content from a Stream Sender and broadcasts it to one or more stream distributor nodes), Stream Distributor node (which multiplies content (fan-out) and distributes it to one or more stream receivers, Stream Sender (which broadcasts live streaming data (sender, start point), and Stream Receiver (which receives streaming data (recipient, end point).
ProximaX Sirius Streaming provides a highly secured message passing based on Tor routing techniques. The corresponding SDK allows a consumer to announce their “presence” in the system, extend multiple onion routes between any network nodes, look up other consumers, and request secure encrypted connections with any other consumer that is active in the network.
ProximaX Sirius Streaming can be used to create an application such as Netflix and Youtube in which people can access videos both live and stored videos. This is very easy and possible to implement with the Proof of Bandwidth which is a crucial element in the streaming service and also because of how it is highly secured.
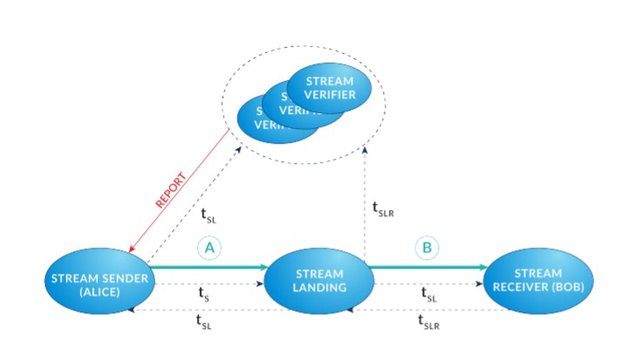
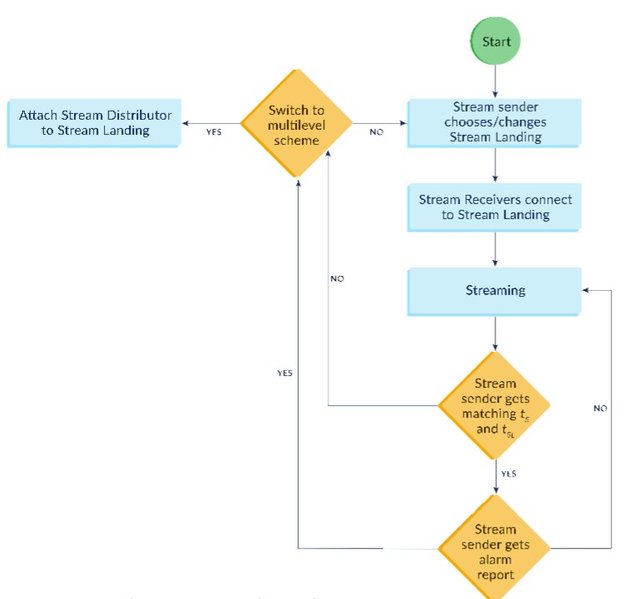
Live Streaming Protocol is the method used for peer-to-peer live streaming within the ecosystem. During a streaming session, reward transactions via the blockchain are avoided because it could cause unpredictable delays that would detriment streaming performance. Instead, the solution uses time tags to determine the reputation based on the node’s bandwidth. The steps on how the live streaming process works are outlined below.
Live Streaming Protocol (1 Stream Sender to N Stream Receivers):
The Stream Sender (Alice), or a sponsor willing to pay for the live streaming session, creates a stream contract with a user-defined SM amount and metadata.
Motivated Stream Verifier nodes check their connection between the Stream Sender and Stream Receivers. Depending on the latency and bandwidth capability result, the
Stream Verifier nodes stake their deposits in SM units accordingly.
Stream Sender performs an initial check of the Stream Verifier nodes’ jitter latency and bandwidth.
Stream Sender chooses one of the Stream Verifier nodes to be the initial Stream Landing node, taking into account deposits and the result of the initial jitter latency and bandwidth check.
The communication from Stream Sender to Stream Receiver is established through the chosen Stream Landing node.
The Stream Sender inserts a unique signed time tag tS with metadata (e.g. block volume) into the stream content and sends it to the Stream Landing node.
Each time a Stream Landing node receives a time tag tS, it confirms it by signing the time tag tSL and sends it immediately back to the Stream Sender. If the Stream Sender does not receive the time tag tSL on time, implicating a faulty Stream Landing node, then the Stream Sender may replace the Stream Landing node from one of the Stream
Verifier nodes.
Stream Sender sends the time tag tSL to all Stream Verifier nodes.
Stream landing node transmits the time tag tSL along with stream content to the Stream
Receiver (Bob).
Stream Receiver receives the content from the Stream Landing node, it confirms receipt of the stream content by signing the time tag tSLR. The signed time tag tSLR with added metadata about stream quality (e.g. received volume) is sent back to the Stream
Landing node as proof that the Stream Receiver has received the stream content.
Stream Landing node asserts the Stream Receiver’s proof in order to gain a reward.
The time tag tSLR is considered as proof of successful block streaming since it has to be signed by both Stream Sender and Stream Landing nodes.
If the selected Stream Landing node exhibits poor performance, the Stream Verifier nodes sends a report to the Stream Sender of the current stream status. The Stream
Sender accumulates reports from all Stream Verifier nodes and makes the analysis of the Stream Landing node’s performance by comparing the matching tSL and tSLR tags received. If the number of tSL tags are significantly lower than tSLR , then it implies there are lost tags caused by a faulty Stream Landing node. The Stream Sender can switch streaming to a new Stream Landing node by selecting one from the list of Stream Verifier nodes.
on completion, all worker nodes, which includes Stream Verifiers and Stream Landing
Nodes, are rewarded based on their contribution during the streaming session.
P a g e 35 | 4 4 High-level Technical Whitepaper
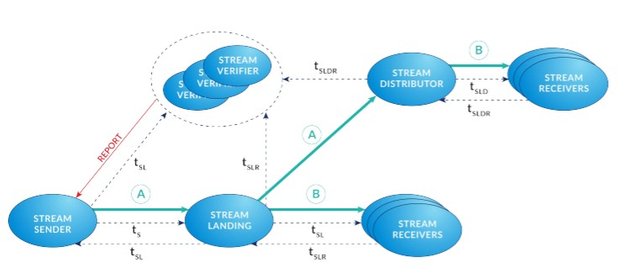
Live Streaming Protocol (1 Stream Sender to N Stream Distributors to N Stream Receivers):
In the case when a single Stream Landing node cannot support a sufficiently large bandwidth for multiple Stream Receivers resulting in a continuous Stream Landing node re-election, then a Stream Distributor node is needed to distribute the traffic in order to provide better streaming service.
The Stream Distributor node interacts with the Stream Landing node and Stream Receivers in the same manner similar to the previous section (1 Stream Sender to N Stream Receivers). Both Stream Landing and Stream Distributor nodes share the same set of Stream Verifier nodes.
iii. ** Sirius Supercontracts:** This has to do with the storing of codes in the Sirius Storage in other for them to be easily executed, stopped, or modified upon obtaining consensus from preestablished authorized parties. This great cryptocuurency has helped curb the problem of immutability in the blockchain caused by traditional digital contracts. The objective of the supercontract function is to build an executable code that directly represents a digital contract that can be custom built to run a specific business use case. Supercontracts can be written in a wide variety of computer languages such as; Java, C++, Python, C#, etc. in order to provide the Sirius supercontract service certain process must take place. This can be seen below;
A new supercontract is uploaded into Sirius Storage.
A hash is generated that references the supercontract.
To approve the supercontract, consensus needs to be reached by pre-established authorised parties via a multisignature transaction.
Once approved, the application developer uses a SDK to call the supercontract.
The announcement triggers the execution of the supercontract.
The execution output will result in triggering transactions in Sirius Chain.
iv. Sirius Database: Is a private or hybrid offering platform that provides document-based storage with added blockchain properties using Tendermint as its consensus algorithm. This platform service is a database with blockchain properties that has simple transfer transaction contracts, its own asset management, and metadata storage. Bigchaindatabase (IPBD) writing takes less than a second because validation is based on the consensus of voting nodes. It has its own querying feature on top that leverages on the underlying documentbased database query functionality. With it being a decentralized database, it can either stand on its own as part of a backbone solution or complementary to ProximaX Sirius’ other core services. Sirius Database is a technology agnostic component as it can also work with technologies outside of ProximaX Sirius, including Ethereum Virtual Machine. With Sirius Database, applications on top can perform operations that yield the same result/response as any other decentralized processing technologies via REST APIs.
Bigchaindatabase (IPBD) is powered by a traditional distributed database in Mongo database which implicitly has the characteristic of scale (throughput, capacity, and low latency) and is querriable.
PROXIMAX: TOKENOMICS
This tokens serves as the lifewire of the ProximaX ecosystem, by playing a big role in serving as the payment vehicle for various activities on the network such as; payment of various fees, it is also used as a stake in the consensus model used with ProximaX, and also it serves as a voting right to the holders of the token. In the token ecosystem the tokens are divided into two parts; (i.e internal and external). The internal includes;
ProximaX’s Native Token (XPX): The blockchain protocol dictates the native currency that will be in circulation. For Sirius Chain it will be XPX. The platform's multiple services are tied to the blockchain protocol. Therefore, consumers that want to utilize the platform’s services need to pay in XPX.
Custom tokens (mosaics): Custom token are in-built contracts pre-defined on the blockchain protocol to enable consumers to create digital asset representations on the platform. For example, custom token can represent a currency, a consumption measurement, a means of exchange, or any physical real world assets. They can be used to power a DApp’s inner economy. Custom token as its unique qualities such as; divisibility, duration, initial supply, mutability, and transferability.
Service units:
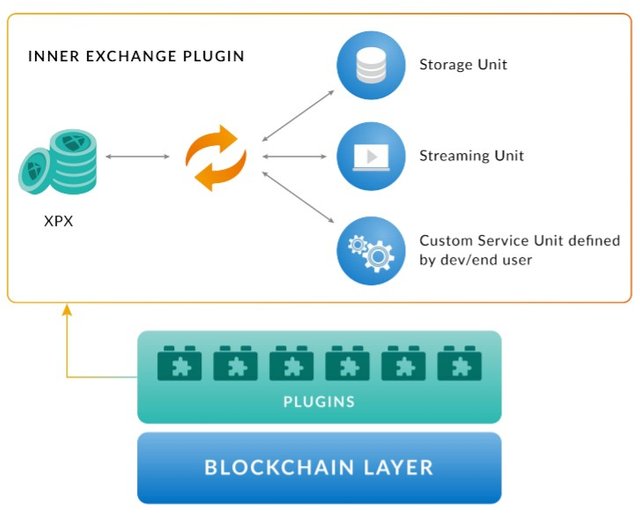
XPX is used to subscribe to the ProximaX Sirius public network in exchange for service units through an Automated Inner Exchange between the platform’s native token (XPX) and the defined service units. With Sirius Chain’s capability of creating custom and pre-defined plug-ins using a common framework. Service units can be compared to Harmony One token, which is consumed by the Harmony network to execute smart contracts. In ProximaX Sirius, the presence of several integrated services benefit from the use of several types of “Gas”, called service units. This units are used to pay for platform services, incentivize nodes for running a service. There are numerous types of service unit such as; storage unit (i.e 1 SO is equivalent to 1 GB of space per month), streaming unit (i.e 1 SM is equivalent to 1 streamed GB), supercontract unit (i.e 1 SC is equivalent to 1 supercontract instruction code), and review unit (i.e 1 RW is equivalent to 1 XPX worth of paid content).
This approach enables ProximaX Sirius to have a multidimensional inner economy where service units are used to power services rendered by different node actors. This approach helps facilitate the future expansion of the platform’s services by enabling the creation of new types of service units (i.e. AI/ML unit; Distributed Computing unit).
Initial proposed service unit rates in equivalent XPX (subject to change):
● 1 SO = USD 0.004
● 1 SM = USD 0.02
● 1 SC = USD 0.000005
● 1 RW = USD 0.005
While the external;
Automated Inner Exchange
The Automated Inner Exchange is a two layer solution built on top of Sirius Chain to facilitate the exchange between the platform’s native token (XPX) and the defined service units. With Sirius Chain’s capability of creating custom and pre-defined plug-ins using a common framework, ProximaX developed an inner exchange to wrap the complexity behind exchanging multiple internal tokens into a simple and functional process, so that consumers can easily utilize the platform’s core services.
P a g e 7 | 4 4 High-level Technical Whitepaper
This shows that ProximaX has gone out of its way to make sure its users get the best kind of services (i.e providing everything in one place); such as the ability to create new service applications, create new core services, etc. the picture below explains it all;
PROXIMAX USE CASE
( ![blog-post-sample-2.png]
![blog-post-sample-2.png]
Jakun Enterprises want to develop and build an online chatting platform on the top of blockchain. It wants a platform which is highly scalable, easy to use, large database, and storage and live streaming.
In this use case “Jakun Enterprise” wants an online chatting platform which is scalable, easy to use, storage and live streaming, and a large database.
There are features which will help this project to be successful and the only cryptocurrency platform which will be able to make this possible is ProximaX.
ProximaX uses the Proof of Stake which is very efficient in this line of business. Because of how fast it can be in processing thousands of transactions in a second or more. Past events shows that PoS is highly scalable and cost effective which means transaction fees will definitely be low.
ProximaX is highly secured so therefore, ProximaX will develop an End-to-End encryption system of communication in which communicating users can read the messages. However the system is developed to beat the attempt of surveillance since no third party can break or decode the data.
ProximaX although highly secured is easily accessible and this will help Jakun Enterprise because it uses the AI-based programs. ProximaX can help the enterprise to create a chat bots which human users can communicate through via text messaging by using natural voice to simplify the tasks. The only online chatting company that owns its own chatting bot is Telegram. Because of ProximaX vast endowment (cloud synchronization) the company will be able to store large files and other files like images, docs, audios, and videos in different places. Talking about the messenger app, messages, chat histories, and files are stored in the cloud, and these can be accessed anytime and anywhere where internet connection is available. Through this users will be able to stream both live and stored videos.
After doing and in depth examination on the platform Jakun Enterprise finally decided to join the proximax network to build its online chatting platform.
CONCLUSION
Nowadays, speed and ease is needed, cryptocurriencies have become a constant of the internet and people around the world, with all the advances available, it was a matter of time to get to this, ProximaX was ahead of the future and came to offer a service of storage, supercontract, streaming, and database. This is what ProximaX has been able to achieve, developing a cryptocurrency that is highly scalable, secured, flexible, and auditable. It has its own blockchain which is known as Sirius chain in which all activities can occur in one place. And it also uses the Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Greed (PoG) consensus mechanism. proximaX can be said to be the best innovation the best innovation the cryptoworld has seen for decades.
Congratulations @mindsfest! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit