
The Internet of Things has created a reliance on technology that has changed the way in which information is collected, transferred, assimilated and stored. The explosion of technology use has materially changed business intelligence and strategy as well as creating new revenue streams. Technological progress has however, exposed vulnerabilities where data has become a valuable commodity.
Cyber criminals have found increasingly sophisticated ways in which to intercept data and use it for social engineering and profit. In parallel, data regulation and privacy policy is changing and at the forefront of this is the incoming European GDPR mandate.
GDPR is the acronym for General Data Protection Regulation. It is the biggest shake up to data regulation since the creation of the internet. It is a piece of legislation that passed in EU law in 2016 and comes into effect on 25th May 2018.
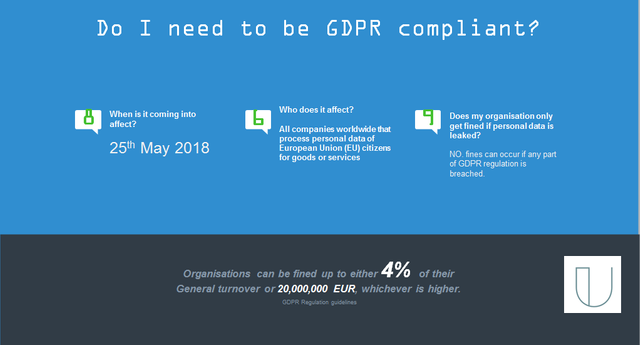
The aim of the legislation is to protect the rights of the individual. It affects the way in which data requests are made, accepted or denied and how data is processed, used, stored, archived and deleted. Any data breach, accidental or deliberate, must be notified to authorities within 72 hours and there is a strict framework for both remediation and fines.
Fines are levied at a high rate specifically to encourage best practice and make the consequence of a breach palpable. The legislation affects all companies engaging with citizens in the EU and relates to data personal to the person e.g. name/address/contact details/profiling.
The recent news about the alleged misuse of social media data used by interested parties to affect political outcomes has played out on the world stage, making a European data privacy initiative a global issue.
In parallel, the exponential growth in the use of blockchain technology for technology, finance and all Socio-economic markets has created a groundswell of counter activity. The blockchain is a shared distributed ledger technology. It works at both a public and private level and stores data in validated blocks. Fundamentally it relies on blocks linking and working together, as opposed to emanating from a central infrastructure that relies on spotlight protection.
Think of it as a honeycomb where new transactions or interactions result in a new and additional block. The blockchain can’t be replicated; it can only be added to so that the state of the blockchain is constantly validated by its users who take responsibility for an element of a block. Each new iteration is identified as the nation state but each previous iteration is recorded. An immutable record of what has gone before.
For GDPR and cyber security this has a transformative advantage. Each piece of data is irrevocably recorded e.g. akin to the traditional handwritten entries in a ledger. This assists the protection of data as defined by GDPR. As the blockchain is in a perpetual state of use and replenish, the data entry points shift and this makes it considerably harder for cyber criminals to falsify access. Traditional password protected systems can be scammed with fake passwords or identification certificates, the blockchain moves so quickly and is geographically and device agnostic that it makes it difficult for cyber criminals to be effective.
Blockchain operates on an algorithm based consensus principle whereby it is the computing power that validates if an entry is authentic and therefore accepted or denied. It can track assets from entry across an end to end transactional journey, supply chain etc.
UNCLOAK™ is the first blockchain service to detect cyber threats and put businesses and individuals at an advantage. It works with blockchain 3.0 EOS which enables a geographical placement of distribution; alongside AI technology which scrapes the global web to identify potential keyword driven cyber threats. Uncloak provides a bug bounty solution rewarding screened hackers for spotting and validating potential hacks. Like the AI and robotic step change from technology driven learning complemented by human nuanced intelligence, Uncloak seamlessly blends this with best in breed in terms of blockchain, and AI.
The survey link below highlights how far behind the curve businesses are about the challenge and opportunity of GDPR.
In a keynote address at The Block Chain Conference in San Francisco in February 2018, IBM’s Global Blockchain Offering Director John Wolpert says, “You need a fabric that allows for lots of competition on platforms and huge competition on solutions. We need to evolve the Internet to become economically aware and this Internet is not going to be an application, it will be a fabric.”
Uncloak pulls back the fabric to reveal real world opportunities that both GDPR and blockchain can proffer. Uncloak is at the forefront of a cultural data shift and is perfectly aligned to the need to both protect and evidence the data stream.
Tayo Dada Founder of Uncloak said ‘it has been reported by business groups that companies will have to spend £1.2 million each on average to prepare for the complex rules on data processing. Uncloak offers an affordable business solution and will take zero-day threats down to zero hour, in the context of the GDPR ruling on readiness and responsiveness to breaches, there has never been a better time to embrace the new technological led landscape.’
As we say at Uncloak, “prevention is better than cure” when it comes to information data management and in the case of GDPR compliance the ability to recognise immediately where your company computer systems are vulnerable to potential data breaches is just one of the problems we aim to solve.