Amino acids are the building blocks from which your body makes proteins, certain hormones, neurotransmitters and other important molecules that keep you healthy. Some amino acids are manufactured by your body, and several others, referred to as essential amino acids, must be obtained from your diet. Amino acids play a pivotal role in certain aspects of nervous system function.
GLUTAMINE
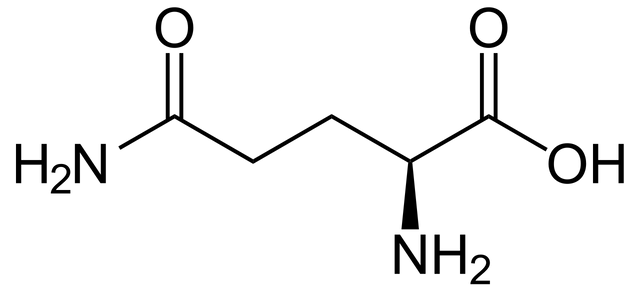
The amino acid glutamine serves an important role as an activating neurotransmitter in your central nervous system. Glutamine also transmits many of the touch- and pain-related messages in your peripheral nervous system, the part of your nervous system that lies outside your brain and spinal cord, according to R.A. Webster Ph.D., author of the book "Neurotransmitters, Drugs, and Brain Function." The neurotransmitter gamma amino butyric acid, or GABA, one of the primary inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, is made from glutamine.
source
GABA
GABA reduces nerve activity in the brain and inhibits the activity of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is responsible for motivation and drive. GABA is widely distributed throughout the brain and is used by a large number of neurons, indicating a the need for the brain to be able to quiet activity and manage over-stimulation. Deficiency of GABA has been shown to induce seizures. GABA also shapes brain activity in ways that may lead to excitation of some areas and serves an important activating function during the development of the nervous system.
ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE
Amino acids may improve athletic performance by altering certain moods, behaviors and physiological functions, explains Mauro G. Di Pasquale in his book "Amino Acids and Proteins for the Athlete: the Anabolic Edge." Supplementing with tyrosine and phenlyalanine might increase your levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine and the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, which are made from these amino acids. Dopamine's motivational boost, together with adrenaline's energy-promoting effects can provide a significant boost to athletic endeavors and may alleviate symptoms of depression in some people.
TRYPTOPHAN
Tryptophan, obtained in the diet by eating turkey and other poultry foods, is a precursor to serotonin and can have relaxing or sedative effects as well as relieve anxiety-related depression. Your brain also uses tryptophan to produce the hormone melatonin, which regulates your day/night cycles. Increasing levels of tryptophan can improve sleep, reduce carbohydrate cravings and soothe frazzled nerves, according to Barbara Wexler, M.P.H., author of the book "Tryptophan: Powerful Serotonin Booster." This amino acid also contributes to spinal cord development and deficiencies can lead to scoliosis.
Congratulations @cheretta! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit