FROM EYE TO BRAIN.
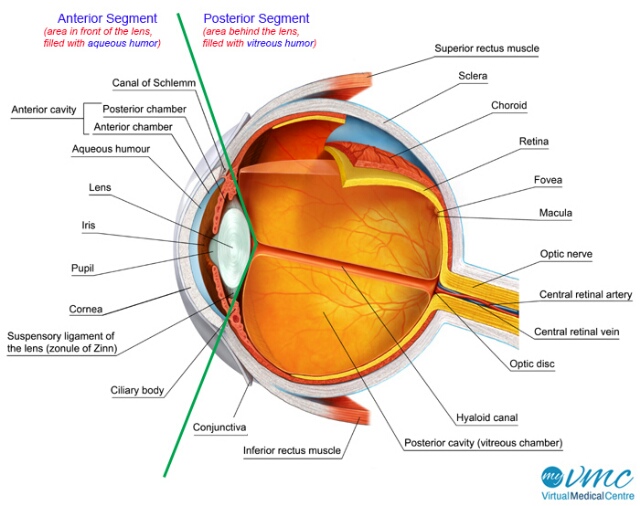
In the previous article, we discussed on different part of the eye, and lay our focus on the Retina, therein we discussed Rods and Cones which are the two receptor cells in the Retina and their functions.
Messages from the eye must travel along multiple pathways to the brain for us to witness visual experience.
[[Rom 1:20]] ASV For the invisible things of him since the creation of the world are clearly seen, being perceived through the things that are made, even his everlasting power and divinity; that they may be without excuse:
Rods and Cones are connected to bipolar cells in different numbers and combinations. A set of neurons called interneurons links receptor cells to one another and bipolar cells to one another. Eventually, these bipolar cells hook up with the ganglion cells, leading out of the eye. The axon of the ganglion cells joins to form the optic nerve, which carries messages from the eye to the brain.
There are about one million ganglion cells in the retina, while we have more than 125 Millions Rods and Cones in the retina, in order for the ganglion cells to receive these huge messages from the Rods and Cones, the information collected by the 125 Millions receptors must be combined and reduced to fit the one million "wires"(ganglion cells)that lead from each eye to the brain.
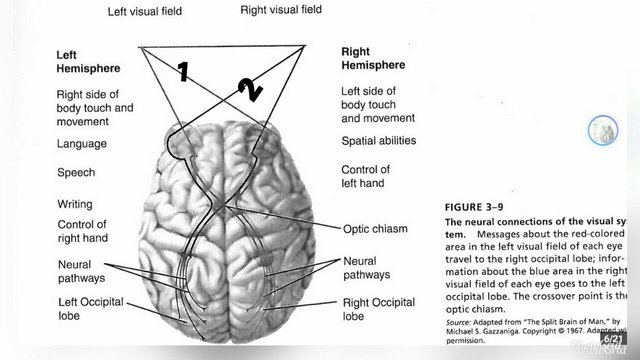
After the nerve fibres that make up the optic nerves leave the eyes, they separate, and some of them cross over to the other side of the head at the optic chiasm.
The nerves fibres from the right side of each eye travel to the right hemisphere of the brain; those from the left side, also travel to the left hemisphere of the brain.
Visual information about any object in the left visual field, will go to the right hemisphere (see figure 1).
Similarly, visual information about any object in the right visual field, will go to the left hemisphere (see figure 2).
The Optic nerves carry their messages to the various parts of the brain, some messages reach the area of the brain that controls the reflex movements that adjust the size of the pupil. Others go to the region that direct the eye muscles to change the shape of the lens. The main destinations for messages from the retina are the visual projection areas of the cerebral cortex, where the complex coded messages are interpreted and registered.
In a research performed by the two Nobel prize winners - David Hubel and Torstea Wiesel- found out that the Brain cells, called FEATURES DETECTOR detect particular elements of the visual field, such as horizontal or vertical lines. Some Feature Detector registers more complex Information, with some being sensitive to movement, depth and colour. All these different types of feature-detector send messages to specific and nearby regions of the cortex. So, our visual experience relies on the brain to combine all the received pieces of information into meaningful images.
Ganglion cells: Neurons that connect the bipolar cells in the eye to the brain
Optic nerve: the bundle of axons of ganglion cells that carry neural messages from each eye to the brain.
Optic chiasm: the point near the base of the brain where some fibres in the optic nerve from each eye cross to the other side of the brain.
Note: there's lots to say about eye, this is a brief explanation of some parts of the human eye. The next article will be on Human ear. Thanks for reading.