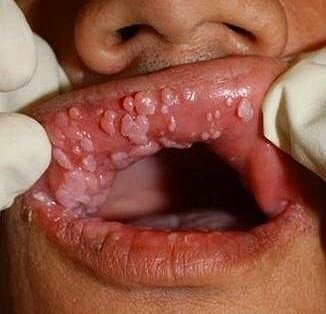
This photo shows a bunch of warts grouped together on the mucosal surface of this patient’s oral cavity.
Warts (verrucae vulgaris) are common, benign epidermal lesions caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. They can appear anywhere on the body in a variety of morphologies.
HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers, and is currently on the rise; primarily the tonsils, the base of the tongue, and a very small number of front of the mouth, oral cavity cancers. HPV16 is the high-risk type most responsible, and affects both males and females.
In women, there’s a link between cervical HPV infection and cervical cancer.
The diagnosis of most cutaneous and external genital warts can be made through clinical examination or with application of acetic acid and biopsy.
Surgical intervention is considered when a large number of warts are present, a large area is affected, or the patient has refractory disease. Overall, physical destruction or excision has been more effective in eradicating genital warts than medical therapy, but oral warts are a little tricky due to the fact that the medications used topically to treat oral HPV should not be applied to mucosal surfaces.
These medications are typically Immune response modifiers (eg, imiquimod and interferon alfa) or cytotoxic agents which includes antiproliferative drugs (eg, 5-fluorouracil) and chemodestructive or keratolytic agents (eg, salicylic acid).
Foto ini menunjukkan sekelompok kutil yang dikelompokkan bersama di permukaan mukosa rongga mulut pasien ini.
Kutil (verrucae vulgaris) adalah umum, lesi epidermal jinak yang disebabkan oleh infeksi human papillomavirus (HPV). Mereka bisa muncul di manapun di tubuh dalam berbagai morfologi.
HPV adalah penyebab utama kanker oropharyngeal, dan saat ini sedang meningkat; terutama amandel, dasar lidah, dan jumlah yang sangat kecil di depan mulut, kanker rongga mulut. HPV16 adalah tipe berisiko tinggi yang paling bertanggung jawab, dan mempengaruhi pria dan wanita.
Pada wanita, ada kaitan antara infeksi HPV serviks dan kanker serviks.
Diagnosis kutil kelamin kutaneous dan eksternal paling banyak dapat dilakukan melalui pemeriksaan klinis atau dengan penerapan asam asetat dan biopsi.
Intervensi bedah dipertimbangkan saat sejumlah besar kutil hadir, area yang luas terkena, atau pasien memiliki penyakit refrakter. Secara keseluruhan, kerusakan fisik atau eksisi lebih efektif dalam memberantas genital warts daripada terapi medis, namun kutil oral sedikit rumit karena obat yang digunakan secara topikal untuk mengobati HPV oral sebaiknya tidak diterapkan pada permukaan mukosa.
Obat-obatan ini biasanya adalah pengubah respons kekebalan (misalnya imiquimod dan interferon alfa) atau agen sitotoksik yang mencakup obat antiproliferatif (misalnya 5-fluorourasil) dan agen kemodestruktif atau keratolitik (misalnya asam salisilat).