
Soource
Processor
The device which performs the process of data and data processing is the processor of computer. We can call it a computer brain cause the processor is the most important part of a computer. Actually, Computer performance depends on it. So many important tasks, such as data processing, logic and decision-making work, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc are organized here. Usually the power of the computer depends on the power of the processor.
Source
Genesis of Processor
British scientist Charles Babbage introduced the memory and input / output card in his "Analyzed Engine". Todays this modern processor has resulted in the continuation of his device. The previous day's computer processors were very big. But in 1971, the invention of microprocessors started with the introduction of small processor. At present the processor we mean actually indicate the microprocessor.
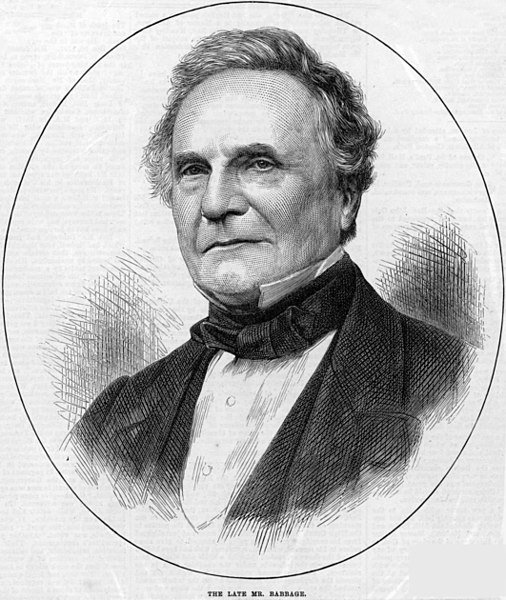

Charles Babbage
source
Although there was the ability to work very limited in the beginning, but todays microprocessors can execute more than billions of seconds per second. A microprocessor is created by putting all the Functionality of a Central Processing Unit (CPU) on a single Integrated circuit (IC).
Microprocessor
Microprocessor is one type of semiconductor chip that is located on a computer's CPU. Its main task is to provide instructions on how to transmit data sent to the computer as input, mathematical identification or memory depositing. Actually, a microprocessor is a self-contained and programmable mathematical engine that controls and performs all operations of the computer through instruction. In other word, this microprocessor is the source of all the work of a computer. Therefore, it is called the brain of a computer. The speed of a computer depends on the speed of the microprocessor. This integrated chip is a small, thin silicon with a few hundred million transmitters in a few square millimeters.Short History of Microprocessor:
Between the late 1960s and early decades of the 1970s the microprocessor was invented from 3 projects which was Garrett Aire search’s Central Air Data Computer (CADC), Texas Instruments' TMS 1000 (September 1971) and Intel's 4004. Arguably, Four-Phase Systems AL1 microprocessor was also delivered in 1969.
Source
In 1968, the Garrett AiResearch (who employed designers Ray Holt and Steve Geller) was given the task of creating a flying controller for the US Navy's new combat aircraft F-14 Tomcat. Its design was completed in 1970, using a MOSFET-based chip. At the beginning this design was used on all the Tomcat aircraft. This system contained a " 20-bit, pipelined, parallel multi-microprocessor". But it was not allowed to publish details due to classified issue of the navy until 1997. For this reason, the MP 944 chip-sets were remained very unknown to the people. On 17th September, 1971, Texas Instruments made 4-bit TMS 1000 and initially created a calculator using the one chip.


The 'Intel 4004 chip' a significant 8-bit microprocessor was built on November 15, 1971, under the supervision of Italian engineer Federico Faggin.
Classification of Micro-processor:
According to the type there are two types of microprocessors. Such as
| 1.General Purpose microprocessor | 2. Dedicated microprocessor |
|---|
General Purpose microprocessor:
The processor we use 'Pentium Central processing unit’ is the General-Purpose microprocessor. According to the software Instruction It performs differently. For example, we use various types of software to do on operating systems. It can be said about 'Google Chrome browser' , 'IDM' etc. From these we can browse any site, download files, document etc. The process of getting these are controlled by General Purpose microprocessor. So
Source
“a general-purpose microprocessor is capable of performing many different functions under the direction of instructions. Given a different instruction set or program, the general-purpose microprocessor will perform a different function.” source
Dedicated microprocessor:
Dedicated microprocessor is also known as 'Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC)’. These are made for specific tasks.For example: Nokia 1100 phone is controlled by one of the specific models Dedicated Microprocessor.

Source
When Nokia 1100 controls the phone, the Dedicated microprocessor of this phone created to control it. The microprocessor can’t have the ability to show video song, because it is only made for the 1100 model. So,
“a dedicated or custom microprocessor that is capable of performing only one function”. source
depending on working procedure microprocessor divided into two parts:
| Datapath | Control Unit |
|---|
Datapath:
Any data related operation, microprocessor execute it by its datapath. It contains registers that store data inputs for a period of time. For example, to add two numbers to the algorithmic logic unit, it's executed by datapath.
Control Unit
Another name of the control unit is the controller. It’s work is to controlling all the operations of datapath. The control unit is the Finite State Machine (FSM). The reason for it is that the system from one stage to another stage is specified for this control unit. What is the amount of work should be done in which state, also fixed, for the control unit. That's why Finite State Machine (FSM).
The control unit has three parts. Such as
| 1.Next-state logic | 2.State memory | 3.Output logic |
|---|---|---|
| A circuit whose work is to explain the machine what would be the next step. | Such a circuit whose work is to Send electronic signal to make sure Finite State Machine (FSM ) is onloaded and ready. | A circuit that generates control signals for data control. |
First Generation Microprocessors(1971-73)
The first-generation microprocessors was published in 1971-1972, which was processed in sequence, they fetched the instruction, decode the command and then execute it. After finishing the instruction microprocessors updated the instruction pointer & fetched to the next, performing this sequential drill for each instruction in turn. For Example:Intel 4004, Texas Instruments TMS 1000.
Second Generation Microprocessors(1974-78)
In second generation microprocessors, more transistors were added on the integrated circuit. But amount was little. The second generation of the microprocessor were faster than first generation because of overlapped fetch, decode and execute the steps. Intel’s 8080, Motorola’s 6800 & 6809 and Zilog’s Z80 were 2nd generation microprocessor introduced in late 1970s(may be year 1978). The distinction between the first- and second-generation devices was primarily the use of newer semiconductor technology to fabricate the chips which was 5 times rise in instruction, speed, execution and higher chip densities than the first generation. They were manufactured using NMOS technology which offered faster speed and higher density than PMOS. It was TTL compatible.
Source
Third Generation Microprocessors (1979-80)
In 1979, Intel’s 8086 and the Zilog Z8000, with 16-bit processors represented the third-generation microprocessor. These were performed like minicomputer. This generation came about as IC transistor counts approached 250,000. Motorola’s MC68020, for example, incorporated an on-chip cache for the first time and the depth of the pipeline increased to five or more stages. By all major workstation manufacturers began developing their own RISC-based microprocessor architectures (Computer, 1996) this generation of microprocessors was different from the previous ones. This time was dominated by 16 – bits microprocessors.
Source
Fourth Generation Microprocessors (1981-1995)
This era introduced the beginning of 32 bits microprocessors. Intel promoted 432, which was bit problematic and then Intel 80386 was launched. Motorola introduced 68020/68030 which was fabricated using low-power version of the HMOS technology called HCMOS. Motorola introduced 32-bit RISC processors called MC88100.Microprocessors entered their fourth generation by converting from commercial microprocessors to in-house designs surpassing a million transistors.
Source
Fifth Generation Microprocessors (1995- Till date)
Fifth generation Microprocessors entered the market with revolution cause it has employed decoupled super scalar processing and design surpassed 10million transistors."PCs were a low-margin, high-volume-business dominated by a single microprocessor, In this generation."
In this era the emphasis was on introducing chips that carry on-chip functionalities and enhancements in the speed of memory and I/O devices along with introduction of 64-bit microprocessors.
"Intel took the attention here with Pentium, Celeron and very recently dual and quad core processors working with up to 3.5GHz speed."
| Processor | Year | Transistors | Data width | Clock Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8080 | 1974 | 6,000 | 8 bits | 2 MHz |
| 8085 | 1976 | 6,500 | 8 bits | 5 MHz |
| 8086 | 1978 | 29,000 | 16 bits | 5 MHz |
| 8088 | 1979 | 29,000 | 8 bits | 5 MHz |
| 80286 | 1982 | 134,000 | 16 bits | 6 MHz |
| 80386 | 1985 | 275,000 | 32 bits | 16 MHz |
| 80486 | 1989 | 1,200,000 | 32 bits | 25 MHz |
| PENTIUM | 1993 | 3,100,000 | 32/64 bits | 60 MHz |
| PENTIUM II | 1997 | 7,500,000 | 64 bits | 233 MHz |
| PENTIUM III | 1999 | 9,500,000 | 64 bits | 450 MHz |
| PENTIUM IV | 2000 | 42,000,000 | 64 bits | 1.5 GHz |
Microprocessor builder companies:
As a microprocessor we usually think about Intel and AMD. But there are many companies in the world who create a microprocessor. Several microprocessor companies include Intel, AMD (Advanced Micro Devices), Analog Devices, Atmel, Cypress, Fairchild, Fujitsu, Hitachi, IBM, Infineon, Intersil, ITT, Maxim, Microchip, Mitsubishi, MOS Technology, Motorola, National, NIC. , NXP (Philips), OKI, Renesas, Samsung, Sharp, Siemens, STM, Toshiba, TSMC, UMC, Unibond etc. But Intel and AMD processors are the most used.
Image SourceReferencequote SourceProcessor, Microprocessor, Google Chrome Logo, Nokia 1100 | Pixabay.com This Is Not a Computer: Negotiating the Microprocessor,29 May 2013 IEEE Xplore | General-Purpose Microprocessors | Charles Babbage | wikimedia.org Key note lecture - Microprocessors evolution,17-18 Dec. 2013,Conference Location: Mosul, Iraq IEEE Xplore | Dedicated microprocessor | TMS 1000 | wikimedia.org The history of the 4004, Dec 1996 IEEE Micro | Fifth generation | Intel 4004 | wikimedia.org History of the Development of Swiss Watch Microprocessors IEEE | Motorola 6800 | wikimedia.org The Intel 4004 microprocessor: what constituted invention? IEEE | Zilog Z8000, | wikimedia.org Microprocessor specification in Hawk,Conference: 16-16 May 1998,IEEE | Intel 80386, | wikimedia.org The M68000 Family | Processor Image, wikimedia.org | The History of The Microprocessor | |
|---|



Great info! Some of the Electron Microscopes I service have 8086 based computers. I even work on older ones that do not have processors at all, and use a few 1702 or 2718 EPROMs to store their electron optic alignment programs. I found a loose 1702 recently and tested it, and it still worked. I did a little write up of it here, on STEEMIT 1702 EPROM
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
It's an antic piece May be the chip you found belongs to 1971 or mid 70s. It was use to boot the early microcomputers.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
It stored the code for a digital readout, and presets for electromagnetic lens currents. The Electron Microscopes that used them did not have processors.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This post has received a 10.44 % upvote from @boomerang.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This is a good article
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit