
There are still some misconceptions in the world of cannabis-related products. Regardless of the growing awareness, most people are ill-informed — or completely ignorant — about the difference between hemp oil and CBD oil, the difference between cannabis and hemp, or even between CBD and THC.
Common among frequently asked questions include:
- What is CBD?
- What are the different types of CBD oil?
- Any difference between hemp oil and CBD oil? Is hemp oil the same as CBD?
- What are the methods of extracting the CBD oil?
- What differentiates CBD from THC?
Read on for answers to these and many other CBD-related concepts to get an in-depth understanding of hemp-derived oil and how it differs from other forms of cannabis-infused products.
What is CBD? CBD vs THC
CBD — an acronym for cannabidiol — is a compound extracted from the cannabis plant. CBD oil — derived from hemp plants — with under 0.3%THC, is legal for sale, possession, and consumption — across the US.
Research says CBD does not cause any effects like 'highness', paranoia, anxiety, and other related reactions commonly known among the users of the whole cannabis plant. Instead, CBD reduces the psychoactive effects caused by THC.
THC — short for Tetrahydrocannabinol — is another widely used cannabis extract. But, unlike CBD, this compound begins to alter users’ perception a few minutes after dosing. This euphoric sensation may gradually decline after about 2 hours — based on dosage and individual tolerance levels.
The calm and euphoria this chemical introduces is — arguably — the primary reason for marijuana’s widespread usage. Slightly similar to the effects produced by the body’s cannabinoids, THC controls perception, memory, thinking, concentration, and motor movement.
An In-depth Look
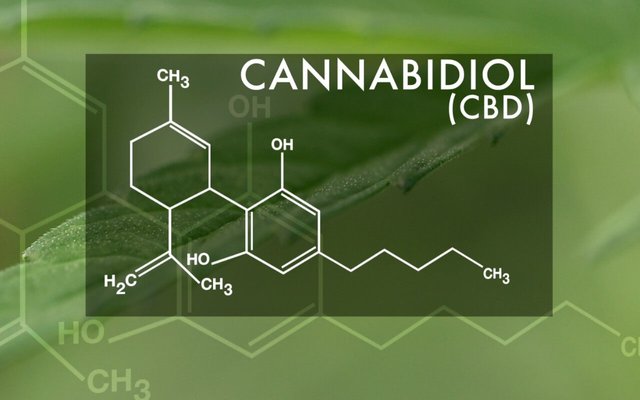
Chemical Structure
Although CBD and THC contain the same molecules — 30 hydrogens, 21 carbon and 2 oxygen atoms — their effects vary, due to the slightly different arrangement of atoms.
Both compounds, however, produce a similar chemical effect to the body’s internal endocannabinoids, which binds with the cannabinoid’s receptor.
This interaction triggers the production of the brain’s neurotransmitters, which control body functions — like immune, pain, sleep, stress, among others.
Psychoactive Components
Although similar in chemical structures, while THC is psychoactive, CBD does not cause a high.
THC interacts with the brain’s CB1 (cannabinoid 1) receptors and triggers a euphoric feeling — or a high.
CBD, conversely, barely interacts with the CB1 receptor. In fact, CBD is said to disrupt THC’s interaction with the receptors, thereby reducing the supposed high effect.
Legality
The legality of cannabis species in the US evolves regularly. Possession, usage, production, and sales of THC and, at large, marijuana products are prohibited — federally.
Several states have decriminalized THC-rich medical marijuana products. Usage is, however, strictly on prescription by certified health practitioners.
Hemp-based CBD is legal — for sale, consumption, or production — across the US. The hemp plant does not only contain higher CBD level than marijuana, but its THC content is also insignificant — below 0.3%.
To avoid legal penalties, before you opt for any cannabis product, confirm its legality status in your state.
Potential Health Benefits
Both compounds offer users relief to some common health conditions. CBD, however, does not give the same euphoria as THC does.
This, perhaps, explains the increasing acceptance of CBD-based products over THC-concentrated alternatives.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018, licensed Epidiolex — the first CBD based medical prescription — for treatment of several types of epilepsy.
Besides, CBD comes handy in the management of a long list of health conditions — namely, nausea, pain, stress, inflammation, migraines, inflammatory bowel disease, seizures, anxiety, and depression.
Side Effects
CBD is widely tolerated — no such thing as ‘overdose’. Research says side effects may occur when users consume CBD alongside with particular medications. However, mild cases of mouth dryness, nausea, and drowsiness may occur.
For THC, the following effects are likely: dryness of mouth, red eyes, memory loss, slow reaction to stimuli, increased heart rate — mostly caused by the chemical’s psychoactive property.
While none of the compounds’ effect is fatal, THC is widely thought to cause psychiatric issues — particularly for people with low tolerance and adolescents who consume large amounts. This effect may increase the risk of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders.
CBD and Drug Testing
CBD and THC remain stored up in the body for up to two weeks after consumption. The compounds may reflect in your drug test within this period.
While CBD may not show on most drug tests, currently, there are CBD-sensitive tests. However, most drug tests are designed to detect only THC chemicals. So THC will, in almost every case, ruin your drug test.
That said, it is noteworthy that some hemp-based CBD may come with THC.
Difference Between Hemp and Marijuana
It is somewhat tricky to distinguish marijuana and hemp plants. But here's an easy-to-grab explanation.
Hemp
Hemp refers to cannabis plants with not more than 0.3% THC content. Before the 2018 Agricultural Act which legalized this definition, hemp was initially used to describe non-psychoactive cannabis species, grown for industrial purposes.
Marijuana
Marijuana describes a variety of cannabis that comes with over 0.3% THC level and causes euphoric or psychoactive effects on users.
Typically, the marijuana plant is cultivated, primarily, for its relaxation, euphoric and psychoactive effects. Marijuana comes with high THC content – up to 30%. Regarded as a Schedule I substance, possession, sale or dosage of marijuana-based products remain illegal in the US federal laws.
However, some states have decriminalized its usage for recreational and medical use – albeit, only on prescription by a certified medical expert.
Summarily, these plants are primarily distinguished based on one factor — THC level in the plants. Better still, their tendency to cause a high.
What are the Types of CBD Oil?
CBD oil can be extracted from two sources:
- Hemp-derived CBD Oil
- Marijuana-derived CBD Oil
Let’s briefly straighten out some mixup between hemp CBD oil and Cannabis CBD oil
Take note: CBD oil is the same — regardless of its source.

However, other ‘contaminating’ chemicals that come with the oil during extraction is essentially what makes hemp oil different from cannabis oil — not the CBD oil per se.
Hemp-Derived CBD Oil
Simply put, hemp refers to a type of cannabis — sativa. The plant is grown, specifically, for industrial and nutritional purposes — not recreational and medicinal. The oil contains low CBD and THC levels.
Hemp seed produces a high amount of nutritious CBD oil — about 50% of the seed’s weight. The oil is rich in healthy nutrients such as omega -3 and -6 fatty acids, as well as vitamin E. Its nutty taste makes the oil a nice additive for meals.
For legal reasons, hemp farmers get rid of the flowers and other restricted parts of the plants. This is the current practice — pending when the law permits usage of the entire plant for its broad-ranged benefits.
Marijuana-Derived CBD Oil
Marijuana-derived CBD oil is commonly referred to as cannabis oil. The CBD oil derived from marijuana is not different from that obtained from hemp.
However, when extracting the oil from the hemp plant, some other compounds mixes with the CBD oil — this distinguished marijuana-based CBD from hemp-based. The combination of CBD and the other compounds offer a more potent effect which cannabis enthusiasts call the entourage effect.
Typically, CBD oil from marijuana contains high CBD and THC levels — and other compounds in the plant. With over 0.3% THC level, marijuana-based CBD oil may cause 'highess' and is prohibited under the federal law of the United States.
How is CBD Oil Produced?
Hemp oil and cannabis oil are gotten through different extraction methods. While hemp seed is pressed to derive the hemp oil, cannabis oil may be extracted by a range of methods — depending on the product you seek to derive.
Cannabis oil is derived mainly from leaves, stalks, and flowers of the plants. Solvents including CO2, butane, petroleum ether, ethanol, olive oil, naphtha, or whole plant extractions are common extraction methods.
Extraction may be simple, or complex — or anywhere between — based on whether the process is done at home or by licensed manufacturers.
Hemp oil, however, is derived from pressured seeds — as with sesame or olive oil. This extraction method results in high yield — precisely, the CBD oil makes up about 50% of hemp seed’s weight.
CBD Concentration
Typically, the hemp plant has between 3% to 5% CBD content. This means a large number of hemp plants may be needed to extract a significant among of hemp-based CBD oil. This difficulty in extracting pure CBD oil tempts many manufacturers to include additives — dampening its quality.
However, CBD oil produced by regulated producers may contain between 18% to 20% CBD. In most cases, THC is added for an entourage effect — achieved by supporting CBD with other chemicals, including THC. This synergy is thought to give users a more potent effect.
Hemp-Derived CBD Health Benefits
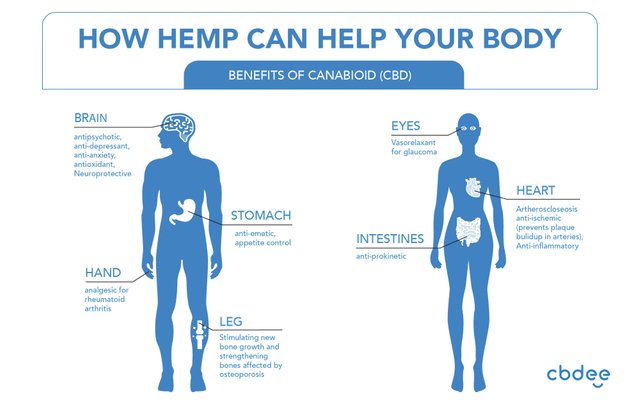
Ingredients
CBD oil from the hemp plant offers broad-spectrum nutrition. It gives users robust biochemical effects with different components working together for an enhanced effect. Hemp-based CBD oil contains essential fatty acids — like omega-6 and omega-3 — phytocannabinoids, chlorophyll, plant sterols, terpenes, and high levels of vitamin E. These effects may help bring relief to the following conditions:
Pain Relief
Over the years, several people have moved from over-the-counter drugs to CBD for natural pain relief. Why so? Everyone seems to prefer more natural alternatives.
A study published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine suggests CBD’s potency in handling pain and chronic inflammation in rats and mice.
The authors believe the no-high compound in cannabis plant could offer relief from severe pains.
Anxiety Management
Physicians have, over time, warned people with anxiety against cannabis dosing as its THC content may cause — or amplify — paranoia and anxiousness.
Conversely, a review published in the Neurotherapeutics says CBD may help curb anxiety related issues.
The review says CBD is possibly a potent option against anxiety-related defects — such as panic disorder, general anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
While many pharmaceuticals have caused a range of side effects — and even aggravated symptoms — CBD has, so far, proven effective and with little or no side effects.
Neurological Anomalies
Research underway seeks to explore the benefits of CBD for persons with neuropsychiatric anomalies. A study says CBD comes with anti-seizure properties which reduce the effect of epilepsy — with little or no side effects.
CBD may also reduce the effect of several forms of epilepsy-induced complications — neuronal injury, neurodegeneration, and psychiatric diseases inclusive.
A publication in Current Pharmaceutical Design sites another study which suggests CBD may create a similar effect as some antipsychotic pharmaceuticals. This makes the compound a natural alternative for schizophrenia patients. Further research is, however, needed to verify this acclaimed effect.
Brain Health
Efforts to link hemp seed oil and improvement in brain health seem productive. The oil, rich in healthy fats, boosts brain functions.
Recent mice-based research suggests that hemp oil compounds may help fight against inflammation in the brain. The report explains that hemp CBD oil is rich in polyphenols, a property notable for brain protection.
That said, since the research is mice-based, scientists may need to carry out some research on humans to verify if the same effects apply.
Heart Health
With its rich nutrient profile, oil derived from hemp seeds may have some goodies for the heart. However, present reports refer to older researches conducted on animals.
Nutrition and Metabolism journal sites one of such old studies that list the nutrients packed in the hemp seeds and propose their possible benefits on a range of health conditions — including, high blood pressure, cholesterol and atherosclerosis levels.
A 2014 report says a rise in alpha-linolenic acid — a fatty acid found in hemp — may manage cardiovascular anomalies. Same fatty acid — scientifically termed linolenic acid — is also found in flaxseed oil and fish oils. However, more clinical may be needed to certify the claimed effects.
Skin Health
Hemp oil is widely thought to offer a range of benefits to the skin. The oil contains fatty acids and vitamins that help fight against skin breakout, preserving skin health — a 2014 study says.
Its rich fatty acid profile makes the oil an ideal source of nourishment for the skin — preventing oxidation, inflammation, and other factors that speed up aging.
A 2014 review suggests that topical application of hemp-derived oil fortifies the skin against infections. The reviewers believe the oil may come handy in management of skin problems, including Psoriasis, eczema, dermatitis, acne, rosacea, lichen planus, Varicose eczema and more.
Wrap Up
So, is hemp oil the same as CBD? The fact is that hemp-derived oil and cannabis oil are extracted for different purposes, but from the same plant family which is cannabis. Besides that their extraction process and methods which are the main difference between hemp oil and CBD oil, they are grown under different conditions.
However, before you dose on any cannabis-based alternative, do well to consult your physician — if for nothing else, but to be cocksure it won’t interfere with other medications.