Chainlink is a decentralized network of nodes that connects off-blockchain data and information to on-blockchain smart contracts via oracles.
Summary
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that feeds real-world data to blockchain smart contracts. Smart contracts are pre-specified blockchain agreements that evaluate data and execute automatically when specific circumstances are satisfied. LINK tokens are digital asset tokens that are used to pay for network services.
To grasp the benefits of Chainlink and how it works, you must first grasp a few basic, interconnected principles. Let’s take a look at smart contracts first.
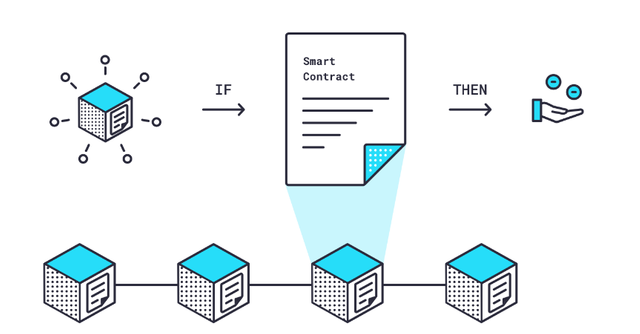
Smart contracts are pre-specified blockchain agreements that evaluate data and execute automatically when specific circumstances are satisfied. Crowdfunding is an excellent example: payment will be paid to the fundraiser if a certain quantity of Ether is deposited into a smart contract by a certain date; if it is not, payment will be returned to donors. Smart contracts are immutable (cannot be modified) and verifiable (everyone can see them) because they are stored on a blockchain, ensuring a high level of trust among parties that they accurately reflect the agreement’s specified parameters and will execute if and only if those criteria are met.
>>The Best Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Exchange Guide<<
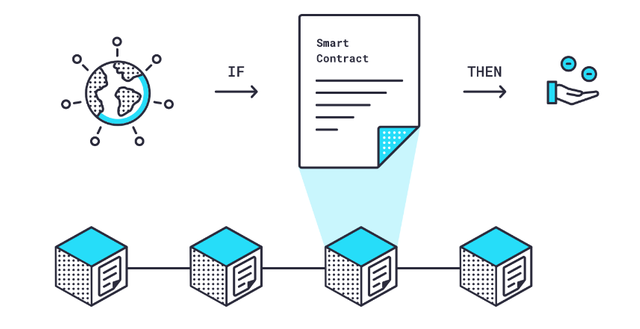
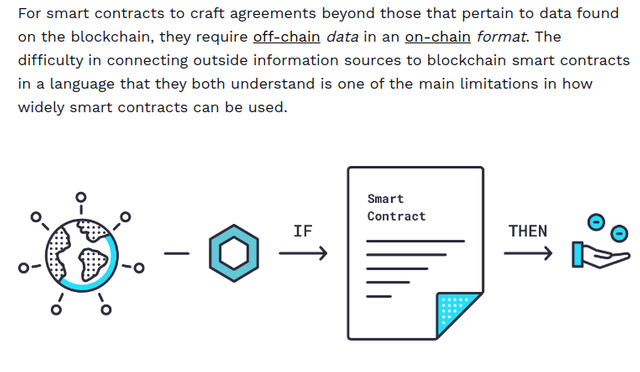
Oracles are useful in this situation. An oracle is a piece of middleware software that functions as a translator, converting data from the real world to smart contracts on the blockchain and back. A single centralized oracle, on the other hand, causes the precise problem that a decentralized, blockchain-secured smart contract is supposed to solve: a single point of failure.
How would you know whether your data is accurate if the oracle is faulty or compromised? What good is a safe, dependable smart contract on the blockchain if the data it relies on is suspect?
Let’s go over the basics of smart contracts and oracles:
- Smart contracts are immutable and verifiable contracts that, when certain conditions are satisfied, execute automatically in an IF/THEN framework.
- The blockchain has historically provided the data that establishes these conditions.
- Oracles, which provide off-chain data to on-chain smart contracts, have just been brought into the crypto industry.
- However, because centralized oracles may be untrustworthy or inaccurate, they reduce the benefits of on-blockchain smart contracts.
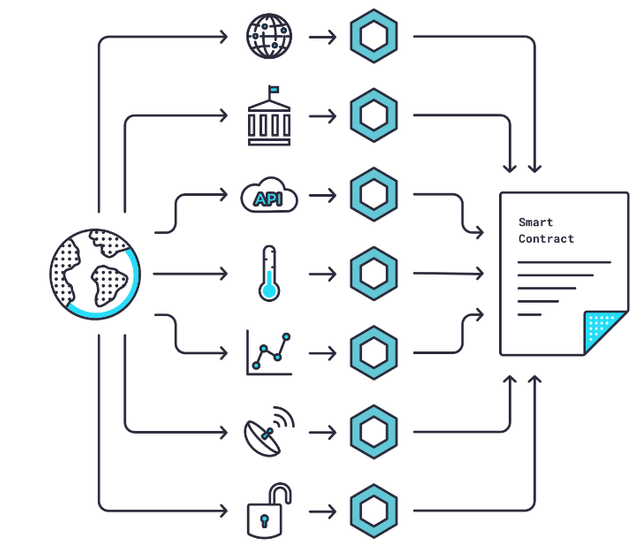
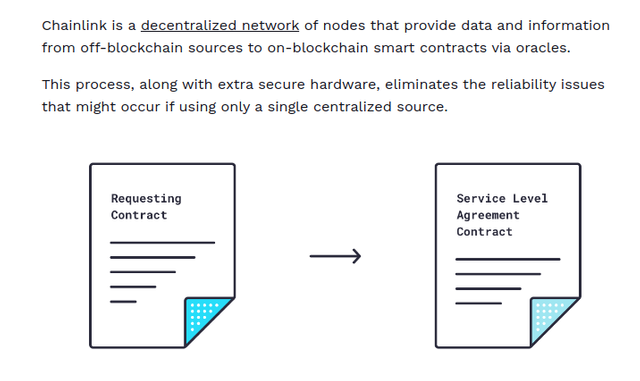
When a smart contract demands data, the process begins on a blockchain with smart contracts enabled. That smart contract sends out a request for information (Requesting Contract).
>>Cryptocurrency Trading Guide for Beginners<<
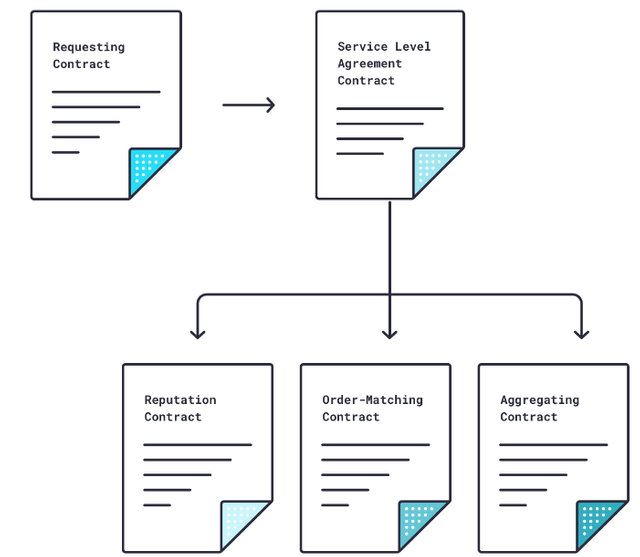
To obtain this off-chain data, the Chainlink protocol registers this request as a “event” and produces a matching smart contract (Chainlink Service Level Agreement (SLA) Contract), also on the blockchain. A Chainlink Reputation Contract, a Chainlink Order-Matching Contract, and a Chainlink Aggregating Contract are all created by the Chainlink SLA Contract.
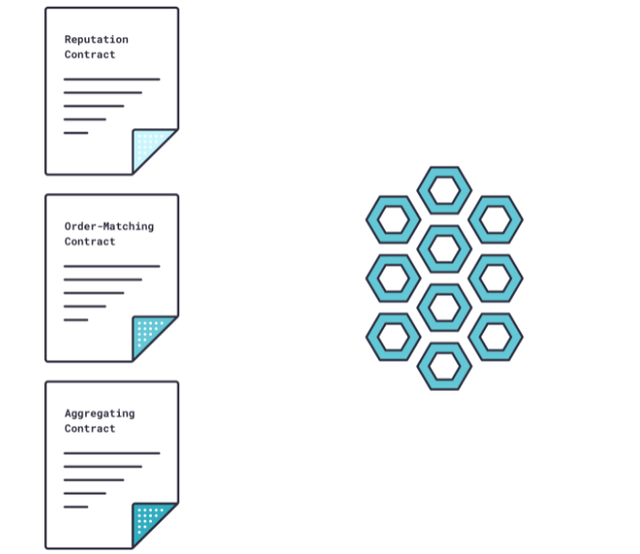
The Chainlink Reputation Contract verifies an oracle provider’s validity and performance history, then analyzes and discards untrustworthy or unreliable nodes.
When the Requesting Contract does not choose a specific set of nodes, the Chainlink Order-Matching Contract sends the request to Chainlink nodes and accepts their bids, then selects the proper quantity and kind of nodes to complete the request.
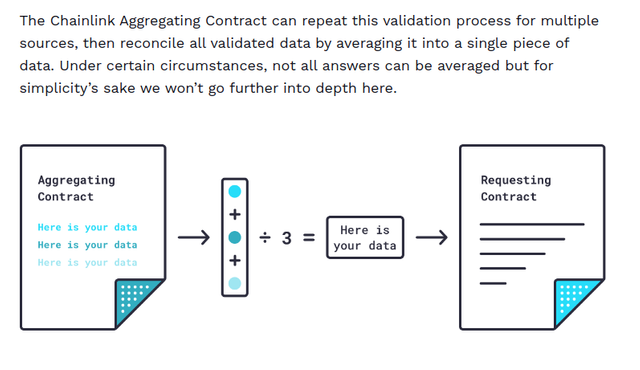
The Chainlink Aggregating Contract checks and/or reconciles all of the data from the chosen oracles to get an accurate result.
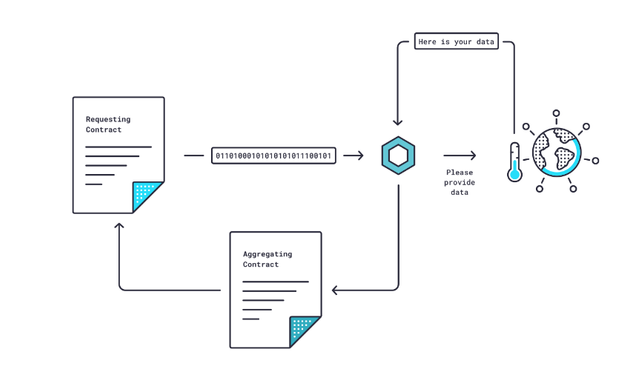
The Requesting Contract’s data request is then translated by Chainlink nodes using “Chainlink Core” software from an on-blockchain programming language to an off-blockchain programming language that a real-world data source can understand.
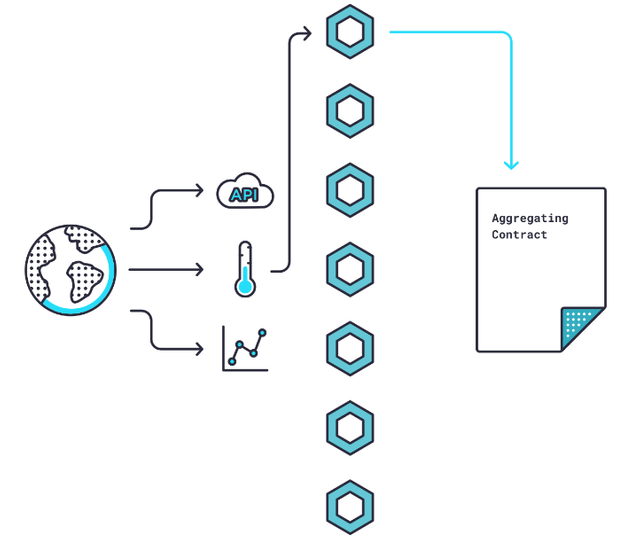
The freshly translated request is then forwarded to an external application programming interface (API) that collects data from the source. After the data is collected, Chainlink Core translates it into on-blockchain language and sends it back to the Chainlink Aggregating Contract.
This is when things start to get interesting. The Chainlink Aggregating Contract is capable of validating data from a single source as well as several sources, as well as reconciling data from multiple sources.
>>Bitcoin Wallet Guide, Reviews and Comparison<<
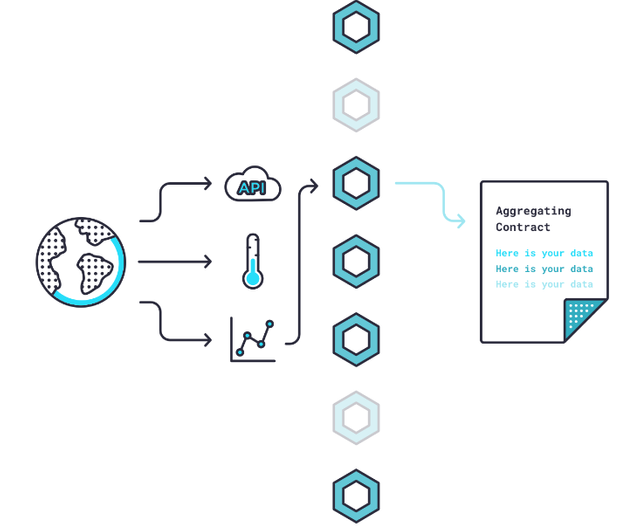
So, if five nodes produce one answer from a weather sensor and two other nodes deliver a different answer, the Chainlink Aggregating Contract will recognize that those two nodes are malfunctioning (or dishonest), and their answers will be discarded. Chainlink nodes can validate data from a single source in this way.
Aside from the data source, Chainlink has developed a method for providing accurate data to smart contracts on smart-contract enabled blockchains in a reliable and fast manner.
So, how do LINK tokens fit into the picture? Requesting Chainlink node operators are paid using LINK by contract holders. The Chainlink node operator determines prices based on the demand for the data they can give and the current market for that data.
Chainlink node operators must deposit LINK with Chainlink to indicate their commitment to the network and reward good service.
When matching nodes with data requests, the Chainlink Reputation Contract takes into account the size of a node’s stake (among other things). As a result, nodes having a higher stake are more likely to be chosen to fulfill requests (and thus earn LINK tokens for their services). In addition, the Chainlink network penalizes faulty or dishonest nodes by penalizing their LINK stake for bad service.
LINK is based on Ethereum and adheres to the ERC-20 token standard. It can be purchased and traded in exchange for fiat money or other digital currencies.
Caspian: Institutional-Grade Crypto Investing Simplified
Bitsquabi.com does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Bitsquabi.com article are solely those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions of Bitsquabi.com or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice. A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions.