image from unsplash.com by Pietro De Grandi
上篇文章我们用强化学习的方法玩了小车爬山,平衡车的游戏。两个游戏有一个共同点,即动作空间(Action Space) 是非连续的。也就是说只能控制动作 (Action) 方向,无法控制动作大小。这篇文章我们就来看看动作空间连续的情况,用Q-learning 该如何处理。
完整代码请见:
https://github.com/zht007/tensorflow-practice
1. 环境简介
同样是小车爬山与 "MountainCarContinuous-v0“ ,的动作空间是连续的,你不仅能决定动作的方向,同时还能控制动作的大小。当动作大于0的时候动作方向向右,小于0的动作方向向左。环境的其他变量,包括奖励,结束条件均与 “MountainCar-v0” 环境相似。
2. 离散化动作空间
由于 Q-learning 的Q表是离散的,所以第一步就是要将动作空间离散化。 这里我将动作从-1到1分成6份,reshape 动作空间以匹配环境对 action 的要求。当然读者可以尝试进一步细分动作空间。
action_space = np.array(range(-10,11,4))/10.
action_space = action_space.reshape(len(action_space),1)
初始化Q表与之前没有太大差别,但是所有env.action_space.n 的部分均要替换成我们自己定义的 len(action_space)。
DISCRETE_OS_SIZE = [Q_TABLE_LEN] * len(env.observation_space.high)
discrete_os_win_size = (env.observation_space.high - env.observation_space.low) / DISCRETE_OS_SIZE
q_table = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1,
size=(DISCRETE_OS_SIZE + [len(action_space)]))
Code from github repo with MIT liscence
3. 帮助函数
此处的离散化状态和 take_epsilon_gready_action 帮助函数与“MountainCar-v0” 环境相似,但是需要注意的是,Q表的Action index 不在表示 action 数值,action 数值需要到 action_space 中索引。
def get_discrete_state (state):
discrete_state = (state - env.observation_space.low) // discrete_os_win_size
return tuple(discrete_state.astype(int))
def take_epilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon):
discrete_state = get_discrete_state(state)
if np.random.random() < epsilon:
action_indx = np.random.randint(0,len(action_space))
else:
action_indx = np.argmax(q_table[discrete_state])
return action_indx, action_space[action_indx]
Code from github repo with MIT liscence
4. 训练智能体
训练部分也与“MountainCar-v0” 环境相似,但是还是需要注意 action_indx 和 action_space 以及 action 的关系。
for episode in range(EPISODES):
# initiate reward every episode
ep_reward = 0
if episode % SHOW_EVERY == 0:
print("episode: {}".format(episode))
render = True
else:
render = False
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action_indx, action = take_epilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon)
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
ep_reward += reward
# if render:
# env.render()
if not done:
td_target = reward + DISCOUNT * np.max(q_table[get_discrete_state(next_state)])
q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action_indx] += LEARNING_RATE * (td_target - q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action_indx])
elif next_state[0] >= 0.5:
# print("I made it on episode: {} Reward: {}".format(episode,reward))
q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action_indx] = 0
state = next_state
# Decaying is being done every episode if episode number is within decaying range
if END_EPSILON_DECAYING >= episode >= START_EPSILON_DECAYING:
epsilon -= epsilon_decay_value
# recoard aggrated rewards on each epsoide
ep_rewards.append(ep_reward)
# every SHOW_EVERY calculate average rewords
if episode % SHOW_EVERY == 0:
avg_reward = sum(ep_rewards[-SHOW_EVERY:]) / len(ep_rewards[-SHOW_EVERY:])
aggr_ep_rewards['ep'].append(episode)
aggr_ep_rewards['avg'].append(avg_reward)
aggr_ep_rewards['min'].append(min(ep_rewards[-SHOW_EVERY:]))
aggr_ep_rewards['max'].append(max(ep_rewards[-SHOW_EVERY:]))
Code from github repo with MIT liscence
5.训练效果
我们训练了 10000 次,将每200次的平均奖励,最大奖励,最小奖励结果画出来如下
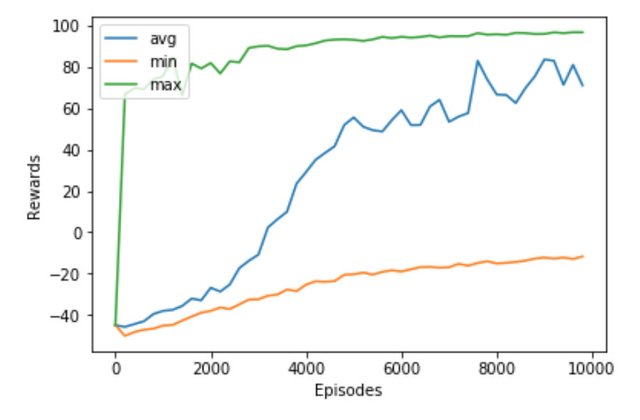
可见智能体很快就发现了上山的方法,并通过不断地学习强化收敛,平均奖励和最低奖励也平滑上升。
参考资料
[1] Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (2nd Edition)
[2] David Silver's Reinforcement Learning Course (UCL, 2015)
[3] Github repo: Reinforcement Learning
相关文章
强化学习——MC(蒙特卡洛)玩21点扑克游戏
强化学习实战——动态规划(DP)求最优MDP
强化学习——强化学习的算法分类
强化学习——重拾强化学习的核心概念
AI学习笔记——Sarsa算法
AI学习笔记——Q Learning
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(1)
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(2)
AI学习笔记——MDP(Markov Decision Processes马可夫决策过程)简介
AI学习笔记——求解最优MDP

This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider setting @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post to get a stronger support.
Please consider using the steemstem.io app to get a stronger support.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit