Child Development...
Child development entails the biological, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the end of adolescence, as the individual progresses from dependency to increasing autonomy. It is a continuous process with a predictable sequence, yet having a unique course for every child. It does not progress at the same rate and each stage is affected by the preceding developmental experiences. Because these developmental changes may be strongly influenced by genetic factors and events during prenatal life, genetics and prenatal development are usually included as part of the study of child development. Related terms include developmental psychology, referring to development throughout the lifespan, and pediatrics, the branch of medicine relating to the care of children. Developmental change may occur as a result of genetically-controlled processes known as maturation, or as a result of environmental factors and learning, but most commonly involves an interaction between the two. It may also occur as a result of human nature and our ability to learn from our environment.
Promoting child development through parental training, among other factors, promotes excellent rates of child development. Parents play a large role in a child's life, socialization, and development. Having multiple parents can add stability to the child's life and therefore encourage healthy development. Another influential factor in a child's development is the quality of their care. Child care programs present a critical opportunity for the promotion of child development.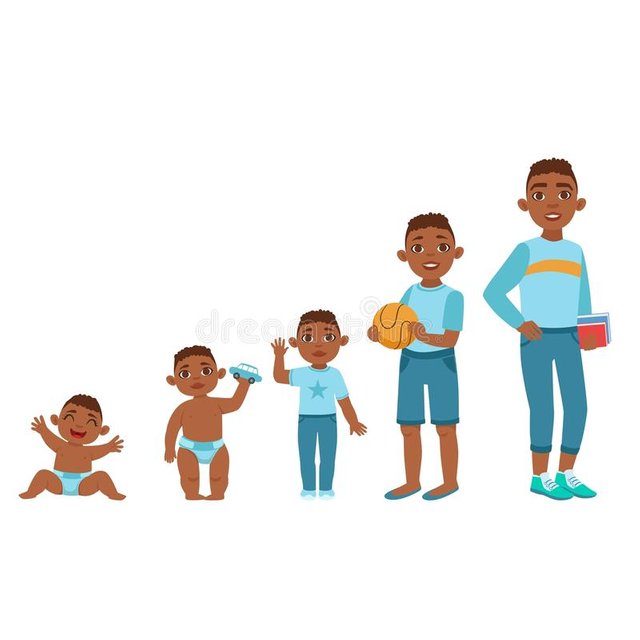
The optimal development of children is considered vital to society and so it is important to understand the social, cognitive, emotional, and educational development of children. Increased research and interest in this field has resulted in new theories and strategies, with specific regard to practice that promotes development within the school system. There are also some theories that seek to describe a sequence of states that compose child development.
Stages In Child Development....
NEWBORN DEVELOPMENT
Between the time of birth and one month, the newborn child exhibits movements that are automatic in in response to external stimuli, according to "Child Development: An Illustrated Guide." Some milestones include the rooting reflex, where a newborn opens his mouth and turns his head toward your hand when you stroke his cheek; the grasp reflex, which is when the newborn involuntarily grasps at any object put in his hands such as your finger; and the startle reflex, where a child stiffens, extends his arms and legs and then quickly brings his arms together in front of his chest in response to sudden noises or position changes. At this stage, a newborn is able to see objects that are close to his eyes such as his parents' faces, recognize certain smells, move his head from side to side, smile and cries to indicate his needs.
INFANT DEVELOPMENT
Between one and 12 months, infants displays new developmental abilities. A three-to-six-month-old child is able to control her head movements and play with her hands together. An infant is able to sit without support, respond to her name and babble between six and nine months old. Between nine and twelve months, a baby can crawl, stand with support and pick up objects with her index finger and thumb or a pincer grasp.

TODDLER DEVELOPMENT
Children between one and three years old are toddlers. At this age, they display ritualistic behavior, such as a bedtime routine, which gives them a sense of reliability and comfort. Although toddlers are clumsy, they can walk without help, go up a staircase, jump in place, hold a crayon, draw a circle, build a tower of two blocks, follow simple directions and use short sentences.
PRESCHOOLER DEVELOPMENT
Preschool development occurs between the ages of three and five years. This stage of child development is characterized by increased refinement of fine motor skills, according to the book "Maternity and Pediatric Nursing." The preschooler can throw a ball over his head, skip, hop, stand on one foot for 10 seconds or longer, draw a person with features, take care of his toileting needs and dress himself. He can also have long conversations.
SCHOOL-AGE DEVELOPMENT
The school-age developmental stage is between six and 12 years old. Children at this stage are more capable, independent and responsible, according to the book "The Developing Person through Childhood and Adolescence." The school-age child has greater motor skills and begins to develop secondary sexual characteristics. Peer relationships become important here and are typically with members of the same sex.

ADOLESCENT DEVELOPMENT
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, during the adolescent years, physical, mental, cognitive and sexual changes occur. Girls are physically mature while boys might still be maturing. Teenagers develop their identity and opinions. They have concerns about their looks. Eating disorders may occur at this time. Adolescents develop interest in members of the opposite sex and spend more time with their friends and less time with their parents.
Image 1
Image 2
Image 3
Article Reference 1
Article Reference 2
Article Reference 3
Article Reference 4
Still Your Humble Boy @gprince
Thanks...
superb blog..
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thanks sir, ☺
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit