General Relativity And Quantum Cosmology
Integrability of anti-self-dual vacuum Einstein equations with nonzero cosmological constant: an infinite hierarchy of nonlocal conservation laws (1901.07527v1)
I. Krasil'shchik, A. Sergyeyev
2019-01-22
We present an infinite hierarchy of nonlocal conservation laws for the Przanowski equation, an integrable second-order PDE locally equivalent to anti-self-dual vacuum Einstein equations with nonzero cosmological constant. The hierarchy in question is constructed using a nonisospectral Lax pair for the equation under study. As a byproduct, we obtain an infinite-dimensional differential covering over the Przanowski equation.
Arbitrarily coupled massive scalar field in conical thin-shell spacetimes (1901.07524v1)
C. Tomasini, E. Rubín de Celis, C. Simeone
2019-01-22
We study the massive scalar field of a charged particle held at rest in conical thin-shell spacetimes with one or two asymptotic regions. Resonant and stable scalar Green's functions are characterized in terms of the coupling of the field to the trace of the extrinsic curvature jump at the shell. Stable coupling values, within the safety domain of the configuration parameters, are used to analyze the self-force of static point charges.
Vacuum energy decay from a q-bubble (1901.05938v2)
F. R. Klinkhamer, O. P. Santillan, G. E. Volovik, A. Zhou
2019-01-17
We consider a finite-size spherical bubble with a nonequilibrium value of the
-field, where the bubble is immersed in an infinite vacuum with the constant equilibrium value
for the
-field. Numerical results are presented for the time evolution of such a
-bubble with gravity turned off (
) and with gravity turned on (
and ratio of energy scales $E_\text{
-field}/E_\text{Planck}\sim 1/10$). For small enough bubbles and energy scale $E_\text{
-field}$ sufficiently below the gravitational energy scale
, the vacuum energy of the
-bubble is found to disperse completely. For large enough bubbles and nonzero
, the vacuum energy of the
-bubble disperses only partially and gravitational collapse occurs near the bubble center.
Extended quantum portrait of MGD black holes and information entropy (1901.07492v1)
A. Fernandes-Silva, A. J. Ferreira-Martins, R. da Rocha
2019-01-22
The extended minimal geometric deformation (EMGD) is employed on the fluid membrane paradigm, to describe compact stellar objects as Bose--Einstein condensates (BEC) consisting of gravitons. The black hole quantum portrait, besides deriving a preciser phenomenological bound for the fluid brane tension, is then scrutinized from the point of view of the configurational entropy. It yields a range for the critical density of the EMGD BEC, whose configurational entropy has global minima suggesting the configurational stability of the EMGD BEC.
On BPS World Volume, RR Couplings and their  Corrections in type IIB (1805.09455v2)
Corrections in type IIB (1805.09455v2)
Ehsan Hatefi
2018-05-23
We compute the asymmetric and symmetric correlation functions of a four point amplitude of a gauge field, a scalar field and a closed string Ramond-Ramond (RR) for different non-vanishing BPS branes. All world volume, Taylor and pull-back couplings and their all order
corrections have also been explored. Due to various symmetry structures, different restricted BPS Bianchi identities have also been constructed. The prescription of exploring all the corrections of two closed string RR couplings in type IIB is given. We obtain the closed form of the entire S-matrix elements of two closed string RR and a gauge field on the world volume of BPS branes in type IIB. All the correlation functions of
are also revealed accordingly. The algebraic forms for the most general case of the integrations
on upper half plane are derived in terms of Pochhammer and some analytic functions. Lastly, we generate various singularity structures in both effective field theory and IIB string theory, producing different contact interactions as well as their
higher derivative corrections.
dS Vacua and the Swampland (1901.02022v2)
Renata Kallosh, Andrei Linde, Evan McDonough, Marco Scalisi
2019-01-07
In this note we revisit some of the recent 10d and 4d arguments suggesting that uplifting of supersymmetric AdS vacua leads to flattening of the potential, preventing formation of dS vacua. We explain why the corresponding 10d approach is inconclusive and requires considerable modifications. We also show that while the flattening effects may occur for some extreme values of the parameters, they do not prevent the formation of dS vacua within the range of validity of the 4d KKLT models. The KL version of the KKLT scenario based on a racetrack superpotential requires parametrically small uplifting, which is not affected by flattening. We show that this scenario is compatible with the weak gravity conjecture for a broad choice of parameters of the KL model. Thus, the results of our analysis do not support the recent swampland conjecture.
A correspondence between modified gravity and General Relativity with scalar fields (1810.04239v2)
Victor I. Afonso, Gonzalo J. Olmo, Emanuele Orazi, Diego Rubiera-Garcia
2018-10-09
We describe a novel procedure to map the field equations of nonlinear Ricci-based metric-affine theories of gravity, coupled to scalar matter described by a given Lagrangian, into the field equations of General Relativity coupled to a different scalar field Lagrangian. Our analysis considers examples with a single and
real scalar fields, described either by canonical Lagrangians or by generalized functions of the kinetic and potential terms. In particular, we consider several explicit examples involving
theories and the Eddington-inspired Born-Infeld gravity model, coupled to different scalar field Lagrangians. We show how the nonlinearities of the gravitational sector of these theories can be traded to nonlinearities in the matter fields, and how the procedure allows to find new solutions on both sides of the correspondence. The potential of this procedure for applications of scalar field models in astrophysical and cosmological scenarios is highlighted.
General relativistic effects in the galaxy bias at second order (1901.07460v1)
Obinna Umeh, Kazuya Koyama, Roy Maartens, Fabian Schmidt, Chris Clarkson
2019-01-22
The local galaxy bias formalism relies on the energy constraint equation at the formation time to relate the metric perturbation to the matter density contrast. In the Newtonian approximation, this relationship is linear, which allows us to specify the initial galaxy density as a function of local physical operators. In general relativity however, the relationship is intrinsically nonlinear and a modulation of the short-wavelength mode by the long-wavelength mode might be expected. We describe in detail how to obtain local coordinates where the coupling of the long- to the short-wavelength modes is removed through a change of coordinates (in the absence of the primordial non-Gaussianity). We derive the general-relativistic correction to the galaxy bias expansion at second order. The correction does not come from the modulation of small-scale clustering by the long-wavelength mode; instead, it arises from distortions of the volume element by the long-wavelength mode and it does not lead to new bias parameters.
Elko under spatial rotations (1810.04985v3)
Dharam Vir Ahluwalia, Sweta Sarmah
2018-10-11
Under a rotation by an angle
, both the right- and left- handed Weyl spinors pick up a phase factor
. The upper sign holds for the positive helicity spinors, while the lower sign for the negative helicity spinors. For
radians this produces the famous minus sign. However, the four-component spinors are built from a direct sum of the indicated two-component spinors. The effect of the rotation by
radians on the eigenspinors of the parity - that is, the Dirac spinors -- is the same as on Weyl spinors. It is because for these spinors the right- and left- transforming components have the same helicity. And the rotation induced phases, being same, factor out. But for the eigenspinors of the charge conjugation operator, i.e. Elko, the left- and right- transforming components have opposite helicities, and therefore they pick up opposite phases. As a consequence the behaviour of the eigenspinors of the charge conjugation operator (Elko) is more subtle: for
a self conjugate spinor becomes a linear combination of the self and antiself conjugate spinors with
dependent superposition coefficients - and yet the rotation preserves the self/antiself conjugacy of these spinors! This apparently paradoxical situation is fully resolved. This new effect, to the best of our knowledge, has never been reported before. The purpose of this communication is to present this result and to correct an interpretational error of a previous version.
Exact holographic RG flows and the 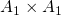 Toda chain (1803.06764v2)
Toda chain (1803.06764v2)
Irina Ya. Aref'eva, Anastasia A. Golubtsova, Giuseppe Policastro
2018-03-19
We construct analytic solutions of Einstein gravity coupled to a dilaton field with a potential given by a sum of two exponentials, by rewriting the equations of motion in terms of an integrable Toda chain. These solutions can be interpreted as domain walls interpolating between different asymptotics, and as such they can have interesting applications in holography. In some cases, we can construct a solution which interpolates between an AdS fixed point in the UV limit and a hyperscaling violating boundary in the IR region. We also find analytic black brane solutions at finite temperature. We discuss the properties of the solutions and the interpretation in terms of RG flow.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @minkowski
Keeping everyone inform.