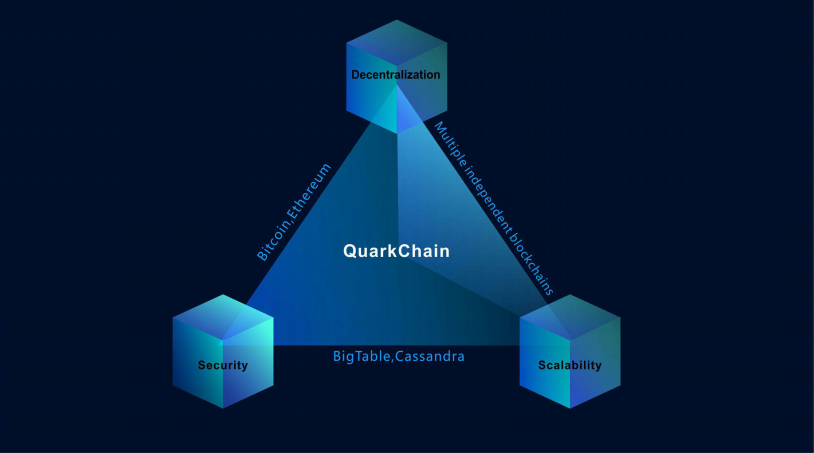
With the growth of the global financial transactions volume - one of the biggest blockchain technologies problems is a low capacity of the existing networks. The primary challenge of blockchain now is to extend the scalability and at the same time to keep security and decentralization on the highest level.
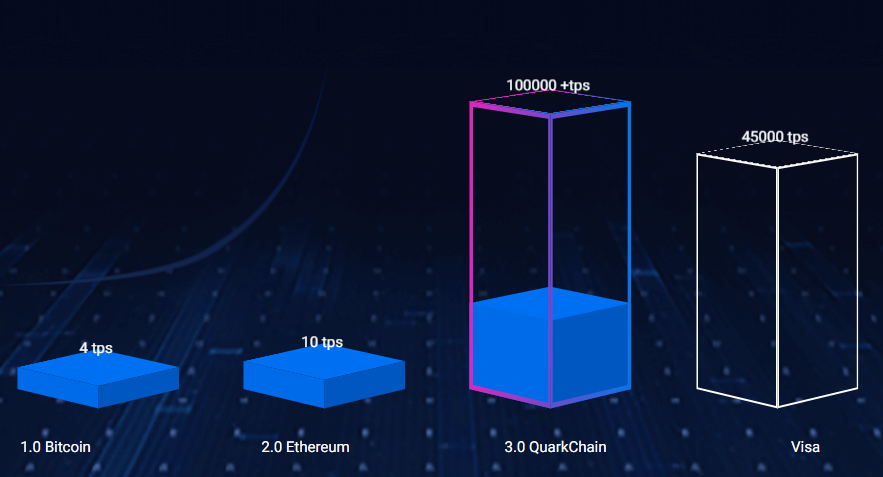
QuarkChain - is a high-capacity peer-to-peer transactional system, that utilizes sharding to provide a high-capacity peer-to-peer transactional network. This system offers a highly-scalable blockchain that claims to be able to process 1 million on-chain transactions per second.

How QuarkChain’s team is going to achieve that?
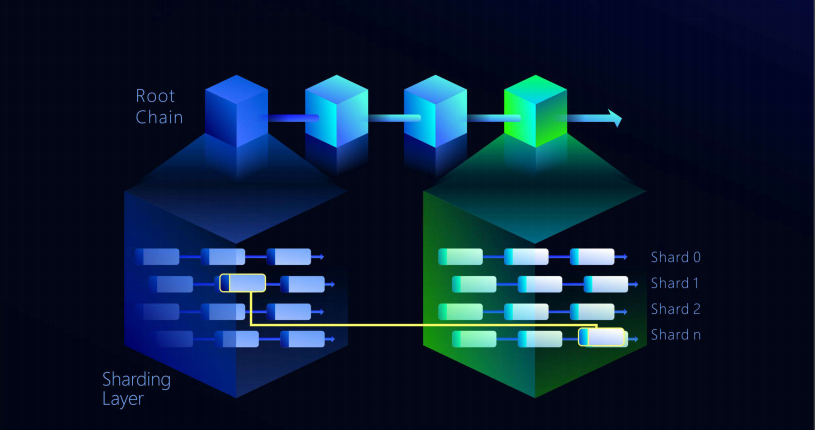
The main feature of the project is better scalability using a two-layer structure.
The first one is the sharding layer, which allows for high throughput by efficiently distributing data, and the second one is - root layer, which serves to confirm the blocks of the first. Using this design, QuarkChain aims to satisfy the tradeoff between the three pillars of a blockchain – decentralization, security, and scalability.
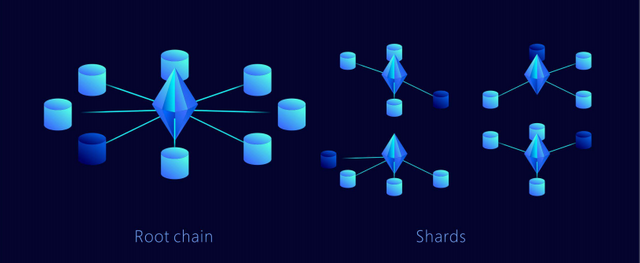
- The first layer offers elastic sharding, which is a type of database partitioning that separates large databases into smaller, faster, and easily managed components called data shards. Data shards are a key part of the QuarkChain project.
- The second layer, meanwhile, is known as the root blockchain. This is the component that confirms the transactions (the blocks) pushed by the first layer. The second layer of QuarkChain can be “resharded” as needed without changing the root layer.
Another unique feature of QuarkChain is the ability to offer guaranteed security through market-driven collaborative mining. Essentially, this means that 50% of the network’s hash power is devoted to the root blockchain to specifically prevent double-spending attacks.
Furthermore, multiple cheaper, low-resource nodes can form a cluster to create a supernode. Technological architecture Anti-Centralized Horizontal Scalability Expansion QuarkChain has a node that validates all minor blocks and root chain blocks. This is called the super-full node. Running a super-full node on your own would be costly. That’s why QuarkChain came up with an innovative solution: they allow multiple smaller nodes to group together in a cluster and run as a super-full node. Each node in the cluster only validates a sub-set of chains, and the rest of the nodes are still able to fully validate any blocks even if one node fails.
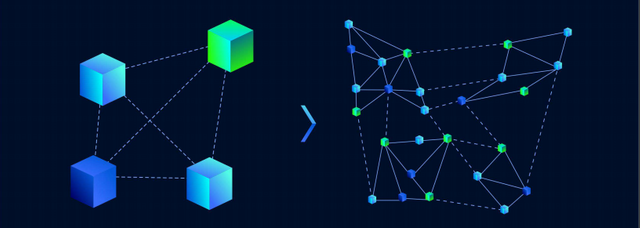
QuarkChain will offer efficient cross-shard transactions in two varieties, including in-shard and cross-shard transactions. In-shard transactions occur when the input and output addresses of the transaction are in the same shard, while cross-shard transactions occur when the input and output addresses are in different shards. Cross-shard transactions can be issued at any moment and confirmed within minutes. As the number of shards increases, the speed of the cross-shard transactions will also increase.
QuarkChain allows cross-chain transactions because it maintains only one root chain. The root chain facilitates token transactions from another chain using an adapter. Then, the blockchain performs the transaction like a cross-shard transaction from the QuarkChain side.
QuarkChain will have a smart wallet that will have two levels, including your primary account and secondary account. The primary account is the address of the user in a default shard, while the secondary account manages the rest addresses of the user in the rest shards. Finally, users will interact with the QuarkChain blockchain through a simple account dashboard. That dashboard will allow you to view all cryptocurrencies from different blockchains – i.e. different shards – from one wallet screen. Plus, you can manage all addresses using a single private key.
QuarkChain will also support smart contracts. In fact, the blockchain specifically supports smart contracts running within the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which means developers can directly deploy their smart contracts to QuarkChain. The end result of all of these technologies is that QuarkChain has 8 minor blockchains with a target block time of 10 seconds along with a root blockchain with a target block time of 150 seconds.

What about competitors?
The main and strong competitor is Zilliqa.But Zilliqa uses PBFT and PoW, while QuarkChain uses just PoW. PBFT gives finality while PoW requires confirmations. Also, Zilliqa does not support turning-complete smart contract, while Quarkchain support turning-complete such as evm. And Quarkchain has scalable cross-shard tx, while Zilliqa’s cross-shard tx is pretty limited
Token model
Total supply: TBAToken distribution:TBA
QKC are used as transaction fees for transactions performed on QuarkChain. It will also be used as a reward for miners. These value of QKC coins should depend on the usage of QuarkChain. The more activities and transactions being made on QuarkChain, the more valuable QKC coins should be.
The initial tokens released will be ERC-20, and a placeholder for the value of the actual coins which will be released with the mainnet that is scheduled in Q4 2018. At time of mainnet release, there will be a token swap.
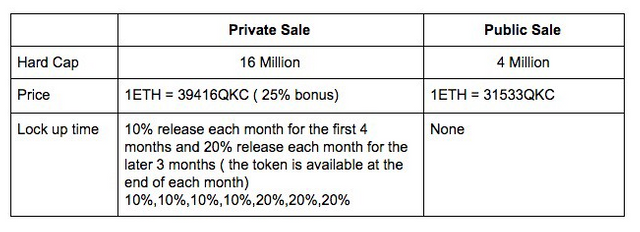
Token sale structure
Hard cap: $20m
ICO date: May-June
Private pre-sale is oversubscribed
Whitelist: TBA
KYC: +
Use of proceeds: TBA
Team
Qi Zhou,Founder and CEO
PhD in Electric and Computer engineering with 5 years’ experience in engineering and software engineering with the most recent being with Facebook as a software engineer.
Zhaoguang Wang,
Software Engineer
7 years’ experience in software engineering with tech giants such as Facebook, Instagram, and Google.
Yaodong Yang,
Research Scientist
PhD in engineering, and a Tenure Track Professor at Xi'an Jiaotong University, and co-founder of Demo++ Technological Incubator.
Xiaoli Ma,
Research Scientist
Professor at Georgia Institute of Technology. PhD in electrical engineering and 7 years’ experience in the tech industry with the most recent being the CTO of Ratrix Technologies.

Advisors
Wang Leo - founder and CEO of PreAngel, a Beijing-based investment fund focused on early-stage internet and blockchain startups. Lijie has invested over €150 million in nearly 300 technology start-ups in Asia and the USA. Wang started with mobile apps but now blockchain is his main focus. NEO’s first investor in China. Bill Moore-President at DELL EMC (2014–2016), Engineer at Sun Microsystems from 2003 to 2010,(acquired by Oracle). Currently Partner/Managing director of Walden International (huge VC).Mike Miller - Ph.D., Yale University(top), Research Assistant Professor at Affiliate Professor (present) at University of Washington (61st World) for about 10 years. Founder of Cloudant (later acquired by IBM). Cloudant was providing a distributed database-as-a-service that scales and manages the databases of web and mobile app developers and received 16.3 millions (as per Crunchbase) USD seed funding.
Kevin Hsu - rich experience in investment and has invested over 60 blockchain companies around the world.
Arun Phadke - University Distinguished Professor, Virginia Tech; Fellow of National Academy of Engineering, USA.
Zhiyun Qian: Intern at Microsoft and Cisco. Research Staff Member at NEC Laboratories America and currently Assistant Professor at University of California, Riverside.


Partners
PMDaniu, PRIMAS, CHIHUO, SegmentFault
Roadmap
 2017 Q2 - blockchain scalability problem research
2017 Q2 - blockchain scalability problem research2017 Q4 - WP draft
2018 Feb - Verification code 0.1; wp released
2018 Mar - Testnet 0.1 and Wallet 0.1 release (current position)
2018 Q2 - Testnet (up quark chain 0.1) Smart contract 0.1
2018 Q3 - Mainnet Quarkchain core 1.0; Smart wallet 1.0
2018 Q4 - Quarkchain core 2.0; Smart wallet 2.0
Subscribers (as for 05.11.2018):
Telegram: 81800+Twitter: 13600+
Green flags:
- The closed testnet is already demonstrating a TPS of 2,000 using just a few AWS node and
- Positive MVP feedback
- $20m hard cap - 2,8% of Zilliqa’s market cap
- Potential technology (scalability)
- Strong team and advisory board
Red flags:
- Lack of tokenometricks
- Strong competition (Zilliqa, Fusion)
- 1 million TPS may be not feasible
- Private repo on github
- Lack of technical whitepaper
Zil will start mining first so lets wait the result. If QC copy Zil success even on a half it would be awesome!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
We will see what happens. It will be hot :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
the article is good. it was very interesting to read. the project team seems to be professional, I think they will succeed))))
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I am sure that you are right! Let's see!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit