Introduction to Complex Thought and Complexity Part 2 Gestalt, Systems, Cybernetics, Information, Game & Organization theories
Gestalt, Systems, Cybernetics, Information, Organization & Game theories
4- What is Cybernetics and Auto Regulation ?
- Cybernetics is the science of communication and control, whether of natural living beings (man) or artificial beings (machine).
"Communication sets the interaction between the sender and the receiver, while existing regulatory control sets, made by the feedback".
- Cybernetics sees Communication as interaction and Control as Regulation
"Cybernetics is a theory of communication based control systems (information transfer) between the system and the environment, and within the system itself, and control (feedback) the function of the systems with respect the environment. " -Bertallanfy(1975),
- The cybernetics field of study are systems
- What is Homeostasis?
- "Homeostasis is the ability to have to maintain a dynamic equilibrium systems between different components or parts, through the feedback mechanism (self-control or self-regulation)."
-. "Homeostasis, or homeostasis, it is the ability to have systems to maintain a dynamic balance between its various components or parts, through the feedback mechanism (self-control or self-regulation)
The homeostatic systems tend to progress and development ". - Bertallanfy
- What is Entropy ?
- Entropy is the second law of thermodynamics, according to which "a system that does not exchange energy with the environment tends to entropy, it means tends to degradation, disintegration and, finally, the disappear or extinguished."
Cybernetic Regulations
- Cybernetics: in Greek kubernetike (pilot), the science that deals with management processes in dynamic and complex communication systems and their application in technique, in human society and in living organisms.
Robert Wiener creates cybernetics as the generalized theory of messages and the concept of automatic adjustment between the elements of a set and its connection with the medium or environment.
- Transmission of information intra and inter systems to analyze inputs and outputs of information in terms of processes and system standards.
- Enables self-regulation or objectification with directivity or construction
5- Game Theory by John von Neumann (1903-1957)
"I can't understand why people are frightened of new ideas. I'm frightened of the old ones" John Cage
John von Neumann (1903-1957) was the mathematical genius behind the creation of the Game Theory
Game theory is the science of strategy. It attempts to determine mathematically and logically the actions that “players” should take to secure the best outcomes for themselves in a wide array of “games.”
Game theory made major contributions to a number of fields including mathematics, physics, economics, computing, and statistics
John von Neumann worked on the philosophy of artificial intelligence with Alan Turing and gave seeds to the most important discoveries of the century like the modern computer, game theory, cellular automata, the atom bomb, radar and so on
"If people do not believe that mathematics is simple, it is only because they do not realize how complicated life is. "
"Any one who considers arithmetical methods of producing random digits is, of course, in a state of sin. For, as has been pointed out several times, there is no such thing as a random number — there are only methods to produce random numbers, and a strict arithmetic procedure of course is not such a method" John von Neumann
"The factor 'game' is a disorder factor, but also of malleability: the will to impose within an organization an inexorable order is not effective." Edgar Morin
6 - Systems Complexity and Complex Thought as a paradigm shift in human organizations
"It was at last to know the concept of organization as the central concept of biology" (J. Piaget, Biologie et connaissance, Paris, Gallimard, 1967)."
"So, as we just saw, and each in its own way, cybernetics, systems theory, information theory, while in fecundity, and its shortcomings, ask an organization theory.
In correlative way, modern biology has organicism to organizationism." Edgar Morin
Edgar Morin found three stages of complexity in human organizations
"First stage of complexity: we have simple knowledge that do not help to know the set of properties".
This means that the whole is more than the sum of the parts that constitute it ( as Gestalt proposed the whole more than the parts).
"Second stage of complexity: the fact that there is a tapestry makes the qualities of this or that type of yarn can not all be expressed fully. They are inhibited or virtualized. The whole is then smaller than the sum of the parts."
"Third stage: this presents difficulties for our understanding and our mental structure."
The whole is simultaneously more and less than the sum of its parts.
As that human organizations are "a perceptible and knowable phenomenon, which can not be explained by any simple law."
"The organization, a living organism, self-organized if and makes his self-production. At the same time makes the self-eco-organization and self-eco-production. "
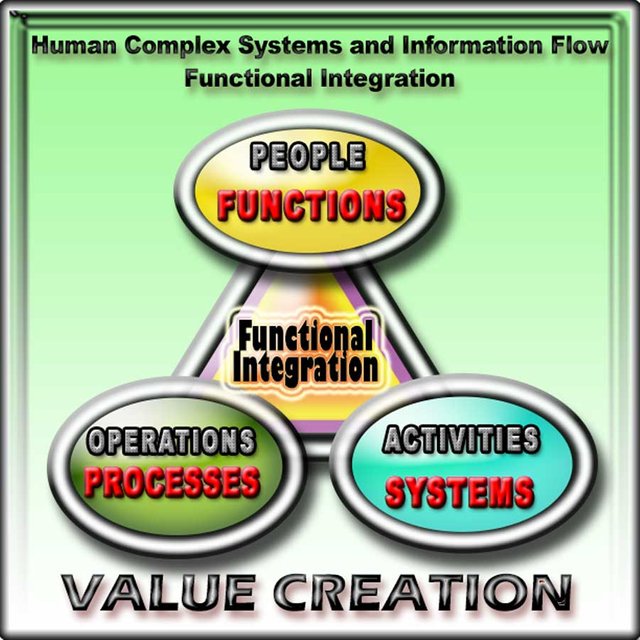
"The principle of self-eco-organization has hologramatic value: as well as the quality of hologramatic image is linked to the fact that each point has the quasi-totality of all the information, so in a certain way, all the while .all that we are part of, is present in our mind.
The simplified view would say the part is the whole.
The complex view is: not just the part is in all; the whole is inside the part that is inside all!
This complexity is something different from the confusion that everything is in everything and vice versa.
This is true for every cell in our body contains the entire genetic code present in our body. This is true
for society: from childhood she prints it as all in our mind, the family education, by education, by university education.
We are facing extremely complex systems where the part is in the whole and the whole is in the part. This is true for a organization that has its operating rules and within which play laws .The whole society. "
Edgar Morin in Introduction to Complex Thought
"The society based on production is only productive, not creative." Albert Camus
Organization Theory - Mantra for an integrative model of the main theories involved in Systems Complexity and Complex Thought
A system can theoretically be represented as:
- A) description and function of all components
- B) virtual and and visual mathematical image
- C) a description of all operations performed by the system using the elements shown in the image
- D) The exchange of messages as inter(info theory) and intra (cybernetic) regulatory tending to equilibrium and adaptation, self regulation and transformation due to operations
- As such we can study the functional aspect within and between systems of communication flows and their feedback cycles as well as the structural aspect (defining the boundaries, the elements, the reservoir of information and its spatial organization.
Visual Cybernetic Machine and Diagram descriptions
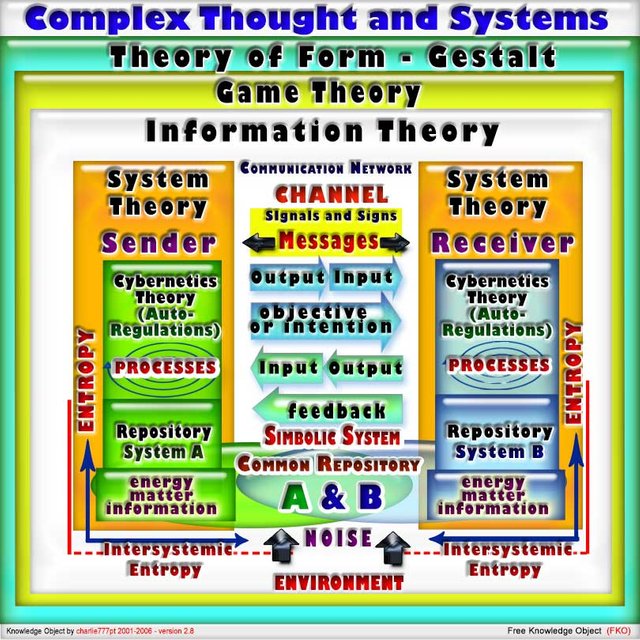
"The impossible is just a question of time" - Alberto Saltiel
A new vision in integration of the concept of Human organizations and Visual Cybernetic Machines
A possible Vision and Conceptualization of the Whole
- Cybernetics refers to the study of any type of systems capable of receiving, storing, explore information and use them for the purpose of control and adjustment (cybernetic self-regulation).
- Therefore, the Cybernetic Machines represent images taken as math hypotheses of the internal structures of the objects under study, like an abstract and symbolic system used as the ideal model of the studied object.
- This paradigm should be assisted by a functional analysis as a set of elements (structure) has only reason to exist is served or serves some function.
- Any structure must therefore be defined in cybernetic terms through the following points:
- Assortment of basic elements, with which the specific structures are built.
- Operations necessary to the construction of such structures, using the basic elements.
- Diagrams or structural descriptions of the structures built only to be related to the functions and being able to explain the meanings.
- This epistemological perspective includes two levels:
- I - Descriptive diagram of the structures of the Real(ity) to observe and definition of construction and basic operations (because the structure can not be dissociated from its operations and genesis).
- Visual Cybernetic Machine
- II - List the structures with functions to find the transformational interactions (as a system consists of several sub-structures).
- Conceptualization of the Whole
- The processing interactions is an inter-relational system that changes from the beginning a sub-structure and at the same time explains the variations of the whole (because the considered structures are open to changes by changing messages and embedded with meanings, although a closed system with self-regulatory capacity and totality).
This in short means that with the computer power of today we can "almost" define
the Whole of a System by nominating his parts or constituent elements, the functions or operations between them as its Genesis , and finally the total messages exchanges which constitutes the history of the System and Sub-Systems plus the self regulatory transformations generated by the messages inside any Element or Sub-System
I think that the the development of science in artificial intelligence, robotics, computer science, neuroscience, cognitive psychology, physiology, mathematics, memetic and other social human bio engineering trends
This poses a final idea that Systems are perishable by the problem of entropy in simple terms, meaning the energy spend in organizing and the resulting rigidity on organizational structures can diminish the organization capacity to survive
"Organizations need to order and need to disorder. In a universe where systems suffer the increase in disorder and tend. to disintegrate, their organization allows crack down, capture and use disorder.
Any organization, as any physical, organizational phenomenon, and, of course, alive, tends to degrade and degenerate."
"The phenomenon of disintegration and decay is a normal phenomenon. In other words, what is normal is not that things will last without modifying, that would be disturbing the contrary. There is no balance of revenue. The only way . to fight degeneration is the permanent regeneration, in other words, in fitness, organization together to regenerate and reorganize itself, to deal with all the processes of disintegration."
Edgar Morin in Introduction to Complex Thought
I'm doing a post on Artificial Intelligence (AI) that will make possible the computational models to explain the conceptual paradigm of Cybernetic Machines in it's fractal Visual and Operational Model Representation and in other new concept in systems of Extropy by Max More
Can a system grow infinitely without friction? that puts the question against Entropy - the second law of thermodynamics!!!!
Is Bitcoin and blockchain a new Technological Singularity of Ray Kurzweil ? we hope so :)
"Change alone is eternal, perpetual, immortal." Arthur Schopenhauer
Watch this with English subtitles!!!
Edgar Morin: Seven Complex Lessons in Education
WISE 2013 Special Address: Dr. Edgar Morin
For people who wants to know more read this beautiful essay of Edgar Morin, translated to English by Sean Kelly and learn the difference between the Whole and the Holistic Principle
"The Whole is Not a Catch-All
Holism is a partial, one-dimensional, and simplifying vision of the whole. It reduces all other system-related ideas to the idea of totality, whereas it should be a question of confluence.
Holism thus arises from the paradigm of simplification (or reduction of the complex to a master-concept or master-category)." Edgar Morin
Read Part I of this Post Introduction to Complex Thought and Complexity Part 2 - Gestalt, Systems, Cybernetics, Information, Organization & Game theories
Morin, E. (1990) Science avec conscience. New ed. Paris: Points/Seuil.
Morin, E. (1990) Introduction a la pensee complexe. Paris: ESF. (accessible
summary statement of Morin's philosophy of complexity).