Content
The spread and integration of DeFi At present, the DeFi ecosystem has the most projects on Ethereum, the fastest growing, and it is showing a siphonic trend. However, Ethereum's low throughput, slow speed, and high fees also made participants complain. Obviously, this is not a long-term sustainable development direction. Therefore, there have been many layer2 solutions, and Ethereum itself is also undergoing an iterative upgrade to 2.0.
However, both Layer 2 and Ethereum's 2.0 will take time to advance. At the same time, there is another trend that can arouse everyone's attention, that is, the opening of the DeFi ecosystem of other public chains. Various public chains from Cosmos to Polkadot and Solana are launching DeFi projects. For example, Thorchain and kava based on Comos, Serum based on Solana, etc., and there are more DeFi projects based on Polkadot, and a big wave is coming. More and more public chains realize that being an Ethereum killer does not make much sense in itself. The important thing is that different chains jointly develop DeFi, and mutual benefit is a better direction.
According to the current trend, it is impossible for Ethereum to unify or eliminate all other chains, and it is impossible for other public chains to replace Ethereum. The more likely trend is that other public chains and Ethereum build an encrypted DeFi world together, and different chains can realize the circulation of assets in different chains through cross-chain technology.
The circulation of assets between different chains is not only about tokenization or cross-chain transactions, but also the realization of assets from different chains to participate in the DeFi activities of different chains, such as the participation of assets from other chains in lending and lending on Ethereum. Trading, liquidity mining, etc., Bitcoin is already in progress. Conversely, the assets on the Ethereum can also be used for DeFi activities on other public chains. OIN's DeFi Road to the Ontology Network From the OIN white paper, the Ontology Network has a clear judgment on the current DeFi situation, and it does not exclude DeFi from other chains.
OIN is a DeFi exploration of Ontology Network. It not only wants to build a DeFi ecology on the Ontology network, but also tries to realize the circulation of assets in different chains through its cross-chain technology, and participate in the DeFi activities of different chain networks. In order to build its own DeFi ecosystem, OIN plans to build a series of basic products. From wallets and stablecoins to transactions, lending, DAO governance, etc.
These are the basic products of DeFi. These basic products can first of all help users perform DeFi activities such as pledge lending, trading, liquidity mining, and DAO governance. The Ontology network started the DeFi road. First, it can expand the ecological value of the Ontology network. By building DeFi, it can further enhance the value of the Ontology network's own chain. Second, opening the DeFi road also sees the current DeFi opportunities.
Due to the congestion and high cost of the Ethereum public chain, other public chains also have opportunities to develop DeFi. If it can help the further development of Ethereum's DeFi ecosystem, this itself is also a great opportunity. The integration of OIN and Ethereum DeFi must quickly promote the development of DeFi, and the most important thing is to follow the trend. Judging from its white paper, OIN is also aware of this. One of its key points is OIN's cross-chain technology, which can support decentralized cross-chain asset exchange. OIN's cross-chain architecture is an important tool for its development of DeFi. It can promote the integration of OIN's DeFi ecology with other public chain DeFi ecology, such as Ethereum, Polkadot, Cosmos, Solana and other public chains. The cross-chain architecture of OIN is as follows:
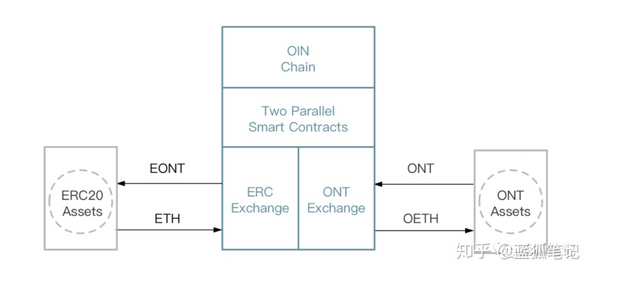
OIN has multiple nodes to form cross-chain nodes. These nodes are a decentralized network that handles the exchange of cross-chain assets. In addition, there is the Ethereum network and the target network. The decentralized cross-chain network can transfer tokens, smart contracts and other related data on Ethereum to the target network. The nodes of the OIN cross-chain network include Ethereum and other public chain nodes, broker nodes, broker nodes of the target network, and cross-chain nodes. Among them, ETH nodes can synchronize Ethereum data; broker nodes can monitor different networks and provide bridges for these networks.
Each blockchain system (such as ETH, ONT, BTC) corresponds to a different broker node. The ETH broker node retrieves data from the ETH node, monitors and makes judgments. The broker node of the target network synchronizes data from the trusted decentralized cross-chain network, monitors and makes judgments. A cross-chain node is a consensus node of a distributed cross-chain network that can execute transactions sent by a broker node.
The target node is the node of the target blockchain network, which can send various transactions to the network. From the perspective of the value transfer process, first, the ETH node continuously synchronizes transactions and smart contract data, and the ETH broker node monitors smart contract events. These events are created by the DeFi application and verify the Merkle Proof of the corresponding transaction. ETH broker nodes automatically generate special types of transactions and send them to a trusted, decentralized cross-chain network.
Cross-chain network nodes receive specific types of transactions, package and execute them, and send the execution results to other chain broker nodes. Other chain broker nodes continue to synchronize data. After receiving the execution result, it will send the smart contract transaction to the target chain node. The OIN cross-chain network uses Tendermint's consensus algorithm based on BFT, which can ensure certain performance and finality. In order to ensure that cross-chain nodes run the network, OIN will use USDO, a stable currency in its DeFi ecosystem, for incentives.
Anyone can participate in the network operation of the node by staking OIN tokens and receive rewards. Finally, in order to ensure the safety of the value transfer process, OIN uses Merkle Proof to achieve this.
Any OIN-related actions that occur on the Ethereum network will be stored on the Merkle Tree. The root of the Merkle Tree will be written into the block header and a Merkle Proof will be generated. After receiving the block header, the ETH broker node will verify its Merkle Proof to ensure the legitimacy of all recorded events. OIN's DeFi Ecological Basic Products At present, the core of DeFi products has several aspects: wallets, stablecoins, loans, transactions, derivatives, etc. These are the basis for launching DeFi activities. OIN's DeFi ecological products are no exception, including the following products: *OIN wallet OIN wallet supports both Ontology and Ethereum assets, and can also be connected to various DeFi projects on Ethereum. It is based on the underlying cross-chain technology.
OIN's follow-up plan supports Ethereum ecological projects Curve, Balancer, Compound, etc., as well as liquidity mining and DeFi pledge in the Ontology ecosystem.
*The first step of OIN-DAOOIN-DAO is the native token. OIN tokens are used as mortgage rewards, governance and liquidation compensation in OIN-DAO. Stable coins are the underlying foundation of the OIN node platform. ONT ecology has PAX stable coin (1:1 rivet USD). Generate USDO stable currency based on ONT mortgage and circulate on the Ontology network.
OIN will establish a mortgage pool in the Ontology ecosystem, and ONT holders can mortgage ONT to generate USDO. The initial mortgage rate is 300%. When the mortgage rate reaches 180%, liquidation will be triggered. Users can deposit USDO to OIN-Swap or OIN-Lend pool to earn liquidity mining and staking income. The initial USDO on OIN was generated by staking ONT, and subsequent USDO can participate in the liquidity mining of the Ethereum DeFi project through the OIN cross-chain function. After the cross-chain mainnet is released, OIN, as a governance token, can vote for more pledged assets. USDO's clearing mechanism is similar to MakerDAO. Once the mortgage rate is lower than 180%, the system will liquidate the user's CDP and auction the mortgage assets ONT to keep USDO repayable. The liquidation penalty is 13%. If there is a black swan event in the market and the price drops rapidly, causing USDO to become unpaid, then additional OIN will be issued and auctioned at this time, and the obtained funds will be used to destroy USDO, thereby maintaining the anchor. *OIN-Swap OIN’s DEX transaction is currently planned for two stages, one is V1 Pool, which is the first DEX based on Ontology and can trade ONT assets. Users can provide a liquidity pool of OIN or other ONT tokens. That is, the AMM pool mode we often refer to can refer to the Uniswap mode.
The second stage of DEX planned by OIN is V2 Pool, which is cross-chain asset exchange. This model is similar to the Thorchain model, which can realize the exchange of cross-chain assets. As mentioned above, OIN cross-chain technology allows REC20 assets to be transferred to the Ontology ecosystem. Just as Bitcoin enters the ETH network (there are wBTC, renBTC... on the Ethereum network). What OIN is trying to achieve is to circulate assets on the Ethereum chain on the Ontology network, such as OETH.
In this way, there is no need to issue more assets on the Ontology network, but assets from other chains can be circulated. For example, Ethereum assets can enter the Ontology network through a tokenization model, thereby providing users with more opportunities to participate in DeFi. For example, use ERC20 tokens or even NFT tokens to implement services such as pledge, lending, trading, and derivatives on the Ontology network, seeking greater revenue opportunities, while enjoying lower costs and higher performance. In particular, this demand will increase when Ethereum has congestion and high fees. For example, a project that issues tokens on Uniswap can use OIN tokenization to enter OIN-Swap for transactions, which can reduce transaction fees and delays. In other words, ERC20 tokens can form an interoperability pool based on Ontology’s assets:
This idea of OIN opened up an idea for the development of DeFi, not to replace Ethereum or any public chain, but to reduce the burden by integrating with the current DeFi system, expand the scale of the industry, and realize its own value at the same time. The important thing here is not which chain is first and which chain is second. In the end, these are all formed through the history of public chain evolution. It may form a super-strong, or multiple-strong ecology. In any case, even all public chains (including Bitcoin) have become Ethereum's side chains, and the entire ecology will not be the same as Ethereum. Different public chains may end up being blockchain scalability. important parts of. *OIN-LendOIN's lending platform includes decentralized lending of Ethereum assets and Ontology assets. Borrowers and lenders deposit tokens into OIN's smart contract. The assets deposited by borrowers and lenders become underlying assets. OIN will choose some tokens from Ethereum and Ontology network as the underlying assets. After the user has over-collateralized, he can borrow money in the money market. OIN-Lend is similar to Compound lending. It has a liquidity pool and does not require peer-to-peer transactions. The interest rate is determined by the OIN-Lend smart contract based on the supply and demand relationship in the currency market. Within the same block, all borrowers have the same interest rate. OIN-Lend accumulates interest by block. The borrower can repay the loan at any time. If the borrower's collateral is lower than the liquidation value, OIN-Lend will automatically liquidate the loan. The difference from Compound is that OIN-Lend does not charge at compound interest rates. It will give an annualized interest rate based on market liquidity. If there is sufficient liquidity, interest rates will become lower; if currencies tighten, interest rates will rise. The mortgage rate must exceed 150%. As shown below:
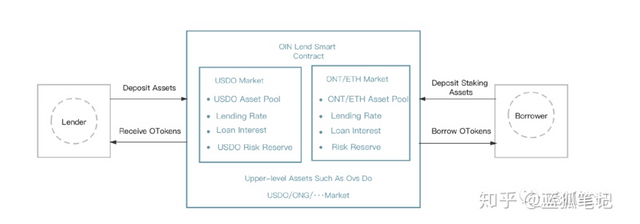
*OIN-Chain OIN-Chain is mainly an asset connecting the two networks of Ethereum and Ontology. As shown below:
*50% of the total amount of liquid mining and stakingOIN tokens are generated through liquid mining and staking. OIN tokens can be generated through staking, and they mainly come from the USDO staking pool in OIN-DAO and OIN-Lend. OIN tokens can also be generated through liquidity mining, which mainly come from OIN-Swap V1 pool and OIN-Swap V2 pool. After the OIN-Lend and OIN cross-chain networks are released, Ethereum assets can also be pledged in the ONT network and obtain liquidity benefits. This means that in the future, liquidity mining is no longer a matter of a single chain, no longer between different projects on the same chain, but also between cross-chains. As a result, 40% of daily mining tokens are generated through staking, and 60% of newly generated tokens are generated through liquidity mining. The subsequent proportion is adjusted by community voting. The future of multi-chain integration The development of DeFi has accelerated the future of multi-chain integration. OIN is a DeFi ecosystem based on the Ontology network. It conforms to this trend and participates in the construction of DeFi. It is also an active exploration of expanding the scale of the entire blockchain DeFi field. ------Risk warning: All articles of Blue Fox Notes cannot be used as investment advice or recommendation. Investment is risky. Investment should consider personal risk tolerance. It is recommended to conduct an in-depth inspection of the project and make your own investment decisions carefully.