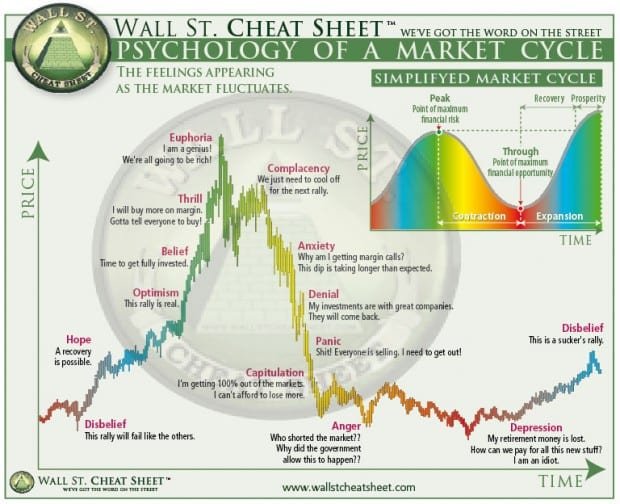
Investing is a critical aspect of personal finance, and its importance has increased significantly over the past few decades due to the shift from defined benefit to defined contribution retirement plans. However, investing is not just about numbers and facts; it is also about emotions and biases that influence investment decision-making. Understanding investor psychology is crucial to making informed investment decisions especially in highly volitile, low liquidity markets like cryptocurrency.
My article explores the various aspects of investor psychology, including the role of emotions and biases in investment decision-making, the impact of cognitive biases on investment outcomes, and the importance of self-awareness and emotional regulation in investment decision-making. Additionally, my article will examine practical strategies to overcome the negative effects of emotions and biases and to make better-informed investment decisions.
The Role of Emotions in Investment Decision-Making:
Investment decision-making is influenced by emotions, which are subjective responses to stimuli that may or may not be conscious. Emotions can be either positive or negative and can be influenced by factors such as personal beliefs, past experiences, and current circumstances. The most common emotions that affect investment decision-making are fear, greed, and regret.
Fear is the emotion of concern or anxiety over a real or perceived threat. Fear in investing is often driven by the fear of loss or the fear of missing out (FOMO). The fear of loss may cause investors to hold onto losing positions for too long or avoid investing in the stock market altogether. FOMO, on the other hand, may lead to impulsive investment decisions, such as investing in hot stocks or speculative investments.
Greed is the emotion of excessive desire for wealth or material possessions. Greed in investing may lead investors to take unnecessary risks or engage in unethical behavior, such as insider trading.
Regret is the emotion of disappointment or dissatisfaction with a past decision. Regret in investing may occur when investors miss out on an opportunity or make a poor investment decision. Regret may lead to overcompensating for past losses by taking excessive risks or investing in speculative investments.
The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Investment Outcomes:
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that affect judgment and decision-making. Cognitive biases can be caused by limited information processing, the over-reliance on heuristics, or the influence of emotions on decision-making. Some of the most common cognitive biases that affect investment decision-making include anchoring, confirmation bias, herding behavior, overconfidence, and loss aversion.
Anchoring is the tendency to rely too heavily on the first piece of information encountered when making decisions. In investing, anchoring may lead investors to focus on the price at which they purchased a stock and not the current market value, which may result in holding onto a losing position for too long.
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information that confirms existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts those beliefs. In investing, confirmation bias may lead investors to seek out information that supports their investment decisions and ignore information that may indicate a need to reconsider their investment strategy.
Herding behavior is the tendency to follow the actions of a larger group, even when those actions may be irrational. In investing, herding behavior may lead investors to buy or sell stocks based on the behavior of other investors rather than on objective analysis of the stock's fundamentals.
Overconfidence is the tendency to overestimate one's abilities or the accuracy of one's beliefs. In investing, overconfidence may lead investors to take excessive risks or engage in speculative investments.
Loss aversion is the tendency to be more sensitive to losses than gains. In investing, loss aversion may cause investors to hold onto losing positions for too long or avoid investing in the stock market altogether.
The Importance of Self-Awareness and Emotional Regulation in Investment Decision-Making:
To overcome the negative effects of emotions and cognitive biases on investment decision-making, it is essential to develop self-awareness and emotional regulation skills. Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand one's own emotions and how they affect decision-making. Emotional regulation is the ability to manage and control one's emotions in response to external stimuli.
Developing self-awareness and emotional regulation skills can help investors make more informed investment decisions by reducing the impact of emotions and cognitive biases on decision-making. Some practical strategies for developing self-awareness and emotional regulation skills include mindfulness meditation, cognitive behavioral therapy, and journaling.
Mindfulness meditation is a practice that involves focusing one's attention on the present moment and accepting one's thoughts and emotions without judgment. Mindfulness meditation has been shown to improve emotional regulation skills and reduce the impact of cognitive biases on decision-making.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. Cognitive behavioral therapy has been shown to improve emotional regulation skills and reduce the impact of cognitive biases on decision-making.
Journaling is a practice that involves writing down one's thoughts and emotions. Journaling can help investors develop self-awareness by identifying patterns in their emotions and decision-making processes.
Practical Strategies for Overcoming Emotions and Biases in Investment Decision-Making:
In addition to developing self-awareness and emotional regulation skills, there are several practical strategies that investors can use to overcome the negative effects of emotions and biases on investment decision-making. These strategies include diversification, dollar-cost averaging, and goal-based investing.
Diversification is a strategy that involves investing in a variety of asset classes to reduce the impact of market volatility on investment returns. Diversification can help investors reduce the impact of emotions and cognitive biases on investment decision-making by reducing the need to make frequent investment decisions.
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy that involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals. Dollar-cost averaging can help investors reduce the impact of emotions and cognitive biases on investment decision-making by removing the need to time the market.
Goal-based investing is a strategy that involves setting specific investment goals and developing a plan to achieve those goals. Goal-based investing can help investors reduce the impact of emotions and cognitive biases on investment decision-making by providing a framework for decision-making that is based on achieving specific financial goals.
Conclusion:
Investor psychology plays a critical role in investment decision-making. Emotions and cognitive biases can lead to irrational decision-making and negatively impact investment outcomes. To overcome the negative effects of emotions and biases on investment decision-making, it is essential to develop self-awareness and emotional regulation skills and to implement practical strategies such as diversification, dollar-cost averaging, and goal-based investing. By understanding the role of emotions and biases in investment decision-making and implementing practical strategies to overcome them, investors can make more informed investment decisions and achieve their long-term financial goals.
Regards,
Trader Greg