Freshwater waters, one of the reservoirs and lakes occupy less space than ocean or land, yet ecosystem and freshwater ecology play a very important role because it is a cheap source of household water and industry. Freshwater waters are an easy and cheap dump
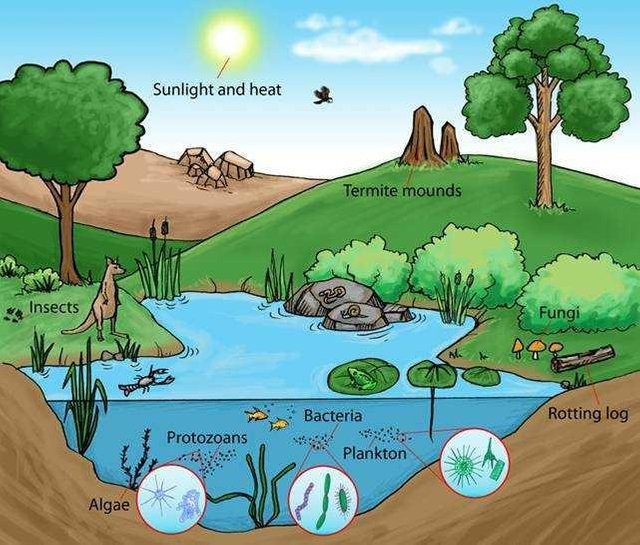
An ecosystem can be formed by the interaction between the creature and its environment, both between living creatures with other living things and between living creatures with abiotic environment (habitat). The interactions within the ecosystem are based on the mutual relationship between fellow creatures and the existence of abiotic environmental exploitation for the basic needs of life for living things.
In the preparation of this discussion, I have several goals. That is :
Provides information on ecosystems, especially freshwater ecosystems.
Inviting readers to keep each other on the ecosystem
The benefits of the preparation of this discussion, namely:
Can have a broader insight, especially about the ecosystem.
Get to know about nature.
Can know the components ekositem.
Freshwater ecology is very useful in everyday life. Fresh water itself is important because it is a cheap source of household water and industry, fresh water component is a hydrological cycle, and freshwater ecosystem is an easy and cheap disporsal / disposal system.
- Freshwater habitat:
Freshwater ecosystems are classified into calm water and running water. Including calm water ecosystems are lakes and swamps, including a flowing water ecosystem is a river.
1.Water stagnant / lentik (origin of the word lenis = quiet) example: lake, pond, and swamp.
2.Water flowing / lotik (origin of lotus word = washed) for example: springs, streams / streams and gullies.
The difference between stagnant water and running water is:
Current flow
The exchange between water on a more intensive basis due to the current.
In running water, oxygen levels are higher than calm water
Mixing temperature and substance content more evenly.
Organisms in the Flooding Waters (Lentic)

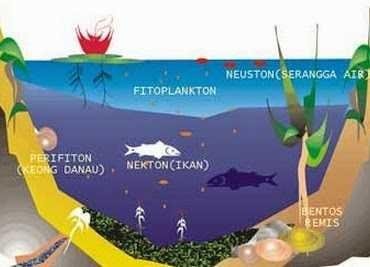
Stagnant waters (lentik) is a form of aquatic ecosystem in which the flow or flow of water does not play an important role. This is because the flow of water is not so great or does not affect the life of the organisms in it. In these waters a very important factor to note is the division of vertical water areas that have different properties for each layer, examples and types of these waters are lakes, swamps, situs, ponds and other stagnant waters. The waters are pooled in three main layers based on the presence or absence of penetration of sunlight and aquatic plants, namely: Littoral, limnetic and profundal, while on the basis of the difference in temperature of the waters, the pooled waters are divided into 3 groups: metalimnion, epilimnion, and hipolimnion. Groups of organisms in stagnant waters based on the main niche in food chain positions include producer (autotroph), consumer macro (heterotroph) and microcomputer (decomposer). Groups of organisms that exist in stagnant waters based on their way of life include: benthos, plankton, perifiton, nekton and neuston.
Distribution of Organisms in Waters
In the litoral zone, the main producers are rooted plants (members of spermatophyta) and non-rooted plants (phytoplankton, algae and floating green plants). While the consumer includes some water insect larvae such as, platyhelminthes, rotifer, oligochaeta, mollusks, amphibians, fish, turtles, snakes and so forth. In the limnetic zone, the producers are primarily phytoplankton and free floating water plants such as water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes), Cerratophyllum spp, Utricularia spp, Hydrilla verticillata, duckweed (Lemna spp); and vascular plants, such as: Equisetum spp. Ioetes spp and Azolla spp. While the consumer includes zooplankton from copepoda, rotifera and some types of fish. In the profundal zone, many are inhabited by the types of bacteria and fungi, the bloodworm, which includes the chironomidae larvae, and the haemoglobin-containing annelids, small shell species such as members of the sphaeridae family and the phantom larva or Chaoboras (corethra). The food chain is a transfer of energy from plants through a series of organisms by way of eating-eating. In each transfer there are 80-90% of potential energy lost as heat. Therefore the food chain in a series of numbers is limited, usually 4 - 5 levels. The shorter the food chain, the more available energy can be utilized.
- Lake
The lake is a collection of water that seems to be in a basin and has no connection with the sea or is a water body that pools and extends from several square meters to hundreds of square meters. In the lake there is a division of the region based on the penetration of sunlight. Areas that can be penetrated by sunlight so that photosynthesis occurs called the area fotik. Areas that are not impenetrable to sunlight are called afotic areas. In the lake there is also a drastic temperature change area or thermocline. The thermocline separates the warm region above with a cold area at the base. Plant and animal communities are scattered in the lake according to the depth and distance from the edge.
Lake function ecosystem is
As a source of germplasm that has the potential to contribute genetic material
As the venue of the life cycle of an important type of flora / fauna
As a source of water that can be used directly by the surrounding community (household, industry and agriculture)
As storage of excess water originating from rainwater, surface flow, rivers or from underground water sources
Maintaining a microclimate, where the existence of a lake ecosystem can affect the inertia and local rainfall levels
As a means of transportation to move agricultural products from one place to another
As an energy producer through plta
As a means of recreation and tourism object.
Based on the lake is divided into 4 regions
1.The littoral area
2.The limnetic area
3.Profundal area
4.Bentic area
- Pool
>The pool is generally defined as a shallow collection of water and its general properties are relatively calm and rich in vegetation.
The pond comes from a vast lake.
Pond unrelated to lake, small size.
Ponds man-made
Swimming is a good dwelling place for invertebrate animals eg:
Flagellata consists of Euglena, Pandoria, Rudorina and volvox.
Among Coelenterata, hydra is often seen attached to plants under water
Platyhelminthes phylum such as turbellaria come under rock and between vegetation.
Annalida is represented by freshwater worms such as Limicoloa,
Arthropods are the dominant forms found in pond waters.
- Swamp

Swamp and brackish is a transitional form between open water and the terrain. Swamps are usually surrounded by vegetation, generally shallow and floating plants. The swamp vegetation consists of the always-green evergreen plants interspersed with the creeping creeps. Variation or animal biodiversity is very small. There are protozoa, rotifer, nematode, dragonfly larvae, Amphisoda, Isopoda, fish, and turtles. In the base layer there are insects, snails, and fish. In the unfortunate circumstances of swamp residents form cysts. For example fish (lepidosiner and ceratodus) wrap themselves in mud for several months.
The important limiting factors in fresh water are
- Temperature
Water has several unique properties associated with heat that together reduce the temperature change to a minimum, so the temperature difference in water is smaller and the changes are slower than in the air. The most important thing is
High heat types
High fusion heat
High evaporative heat
The highest water density occurs at 4C
- Clarity
Light penetration is often inhibited by substances dissolved in water, limiting the photosynthesis zone where aquatic habitats are constrained by depth. Turbidity, especially when caused by mud and particles that can stagnate, is often important to be considered a limiting factor. Conversely, if turbidity is caused by an organism, the turbidity measure is indicative of productivity.
- Current
The water is quite solid, so the flow direction is very important as a limiting factor, especially in the flow of water. The current also greatly determines the distribution of vital gases, salts, and small organisms.
- Gas Respiratory Concentration
Unlike the marine environment, the concentrations of oxygen and carbón dioxide are often confined to fresh water
- Concentration of Dissolved Salt
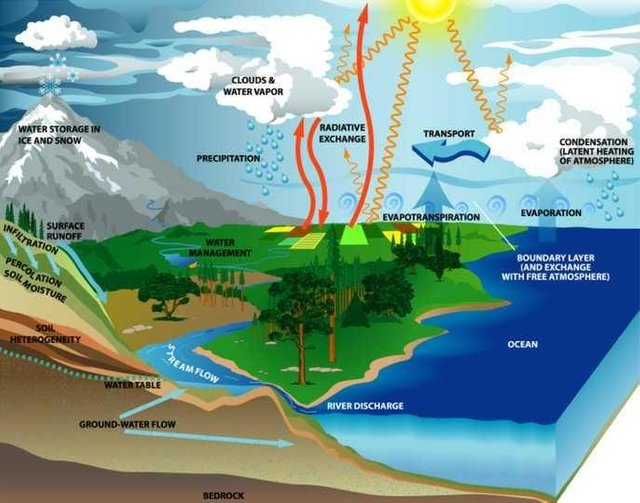
Freshwater habitat is an intermediary of marine habitat and terrestrial habitats. The classification of organisms in water can be based on the flow of energy and living habits.
1. Based on energy flow
Autotroph (manufacturer), green plants and microbial microorganisms.
Phagotroph (macro consumer), herbivore, predator, parasite.
Saprotroph (microcomputer or decomposer), classified according to the organic material described
2. Based on living habits
a. Plankton
Consists of the base of phytoplankton and zooplankton, floating organisms whose direction of movement is approximately dependent on current. Although some zooplankton show an active swimming motion that helps maintain a vertical position, the overall plankton can not move against the current.
b. Nekton
Organisms that can swim and move on their own, such as fish, amphibians, large water insects.
c. Neuston
Organisms that float or swim in the water or surface
located on the water surface, such as water insects.
d. Perifiton
It is an embedded or dependent plant or animal
in plants or other objects, such as snails.
e. Bentos
Animals and plants that live on the ground or live on
precipitate. Bentos can be sessile (attached) or move freely,
such as worms and mussels
https://www.google.co.id/amp/s/saragusti22.wordpress.com/2012/11/23/ekologi-air-tawar/amp/
https://berkahkhair.com/ekosistem-air-tawar/
https://www.scribd.com/mobile/doc/40207680/Ekologi-Air-Tawar
Freshwater ecosystems are divided into two: stagnant water and running water. With the characteristics of very low salt levels, very low temperature variations, less sunlight penetration, and influenced by climate and weather.
You received a 10.0% upvote since you are not yet a member of geopolis and wrote in the category of "geopolis".
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-4
If you do not want us to upvote and comment on your posts concerning earth and earth sciences, please reply stop to this comment and we will no longer bother you with our love ❤️
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks @geopolis
I love science :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit