While world stock indexes day by day, updating the historical highs, the real state of the world economy, more and more is happening to the feast during the plague.

US: fiscal crisis is gaining momentum (according to the end of July)
Report to the U.S. Treasury in July:
1. Tax revenues in July amounted to 93.1% from July 2015 - the worst level since the first wave of super crisis, second only to April.
2. Tax revenues for the period April-July was 96% from April to July 2015 - the worst of the changes (at the 4-month interval) with the first wave of super crisis.
3. Tax revenues for the previous 12 months amounted to 101.5% of the previous 12 months. For comparison, the average of the same indicator in 1980-2015 amounted to 105.7%, and in the period 2011-2015 and is 109.4% (Hello from the printing press). This low figure was the last time only in 2010.
4. From the point of view of the Parallels with the beginning of the first wave of super crisis this indicator is at the level of June 2008.
A quarter of the developers of San Francisco looking for a job outside of Silicon valley
The study, published in the recruiting company Indeed showed that a quarter of the developers working in San Francisco, interested in working in other States with a lower cost of living and more affordable housing.
26 percent of software developers working in San Francisco, looking for a job in another state, the researchers note. Most of all they were interested in working in Seattle, Portland, Austin and Denver — cities that evolve as technology nodes, but where the wages are much less than in the Valley.
According to Indeed, the it workers in San Francisco earn about $113 thousand per year. In Seattle, they can count on $98 thousand per year. However, the inhabitants of the Valley have to pay 40% of wages on housing, when in Seattle, the figure is about 20%.
"We rented a house together with another couple for $6200 per month. If we wanted to buy this house to live in it with children, it would cost $2.7 million every month we would have had to pay $12 thousand for the mortgage, tax and insurance. That's $146 thousand per year all salary of a qualified specialist to the payment of tax. It is not permissible". — Kate Virchow Downing, associate ServiceNow
As noted by Buzzfeed, moving developers from San Francisco becomes new trend is the city has given way to a Washington and Austin in attractiveness among job seekers.
The structure of the debt load of American families with children from 8 to 14 years
New research investment Fund, T. Rowe Price (one of the largest in the US running $ 776,6 bln), privodya data on the debt load of American families with children from 8 to 14 years.
Just note that this survey and it is devoted to the education of children and educational loans. The survey involved both adults and children. For example, 62% of American children expect that parents will pay for their College education. At the same time, only 12% of parents said that they will be able to pay the entire cost of education, 35% - able to cover most of the costs. This means that credit slavery Americans will worsen more and under "education loan". By the way, according to the latest fed us residents have for education $ 1,363 trillion, 2011 was $ 961 million.
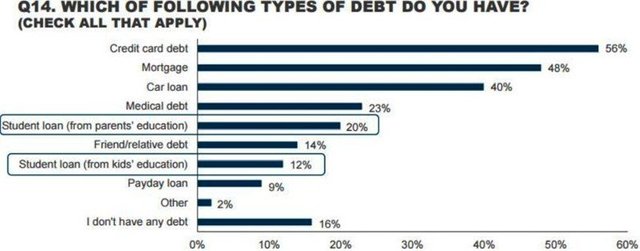
What types of debts do you have?
As you can see, the most common debt is debt on a credit card - 56%, in second place residential mortgage - 48%, the third loan of 40%. The top five medical debt 23% and a private education loan is 20%. At the same time, another 12% of parents have a loan for children's education, and both types of education loans (for myself and kids) have 5% of parents. That they have no loans declared by 16% of respondents. 61% of parents have more than one duty, the average number of 2.25 debt.
U.S. Industrial production falls for 11th month in a row
Industrial production in the US fell in July by -0.56%, despite the unusually warm summer caused an increased load on the electric power plants (there was an increase of 3.5%). Falling prey resources amounted to 10.2% (despite the fact that last year was a crisis), and the manufacturing industry formally increased by 0.2%, but per capita, this fall.
The drop in the composite index compared with the same month last year lasts for 11 months in a row (which has never been observed outside officially declared the crisis), with the peak of industrial production, "accidental" coincidence took place in November 2014 (when QE is turned off, reducing "free" recharge of debt pyramids).
World fleet cut into the metal with wild speed - for vessels more than cargo 30%
Another ominous green sprout in the world this year will be cut for scrap about a thousand vessels with a total carrying capacity of 52 million tonnes. It's almost the historical record, second only to 2012. Usually before disassembling the metal vessel operates an average of about 30 years, in this year of age is only 15 years old.
The volume of orders for new vessels with a minimum of the first wave of super crisis.
The reason is simple - now more ships than cargo, about 30%, and transport prices fell so much that barely cover the fuel costs.
The collapse in the price of resources reflects a growing General decline and the collapse of effective demand, inflated previously using the debt pyramid and the printing press. And now even the printing press does not prevent the continuation of the Banquet, which began in 2008.
http://radikal.ru/Img/ShowUploadedImg?id=eff3bbe8491746bc824c8a1918dcd9c5

The Bank of Japan will get control of 55 companies
Over the next year, the Bank of Japan plans to acquire ETF 6 trillion ($58 billion), and over the next two years, the figure will reach $116 billion by June 2018, the regulator, apparently, will accumulate on your balance ETF 20.5 trillion ($200 billion).
This crazy strategy of the Central Bank means that very soon the Bank of Japan will become the largest shareholder of 55 major public companies. As of late June, the regulator already owned 60% of the domestic ETF Japan, and this figure was half that a few months ago.
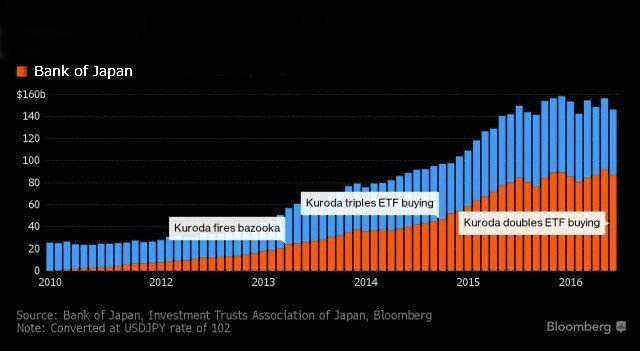
The pace of asset purchases was simply unprecedented. The bulls, of course, happy about this turn of events, but the Central Bank artificially inflates asset prices and prevent public companies to become more efficient.
Traders fear that the active presence of the monetary authorities will complicate the buying process actions: this phenomenon has already led to problems in the government bond market this year.
While the Bank of Japan in General are not worried about what has become the only dominant force in the securities market.
Central Bank buys individual stocks directly but does it through ETFs. Active buying means that the impact of the Central Bank is already competing with major traders.
By the end of the year, the Bank of Japan intends to become the largest shareholder in five companies from the Nikkei 225. And in 2017 he will become a major shareholder about a quarter of the companies included in the index, including Olympus Corp., the world's largest manufacturer of endoscopes, Fanuc Corp., the largest manufacturer of industrial robots, and Advantest Corp., one of the leading manufacturers of semiconductor devices.
In this, the Japanese Central Bank does not see anything wrong. CB representative said that the purchase of ETF will help to achieve the inflation target of 2%. At the moment, in June consumer prices fell by 0.4% in annual terms, and this is the fourth reduction in a row.
In addition, Kuroda argues that the purchase of ETF will help to stimulate economic activity and inflation by increasing risk appetite in Japan.
The good news is that at least for now the liquidity in the stock market in Japan is not decreasing, in contrast to the debt market, where there are practically no sellers.
So far there is little evidence that the purchase of the Bank of Japan undermine the normal functioning of the Japanese stock market, analysts said. But that may change if the volume of purchases will increase.
Basic problems may occur with stocks of companies that are characterized by a small proportion of shares in free circulation. In any case, if the Bank of Japan will sell the shares, the liquidity will decline. That is, the stock market will repeat the scenario of the bond market.
And there remains the question of control, because nobody knows how the Bank of Japan will conduct themselves as a major shareholder in many public companies.
Some investors are concerned that the intervention of the regulator will lead to a deterioration of corporate governance.
Apparently, Japan's stock market as the bond market, are facing hard times. And sooner or later, the Central Bank can buy assets, as they simply will not be on the market. This moment is gradually approaching, and while there is no evidence that the regulator will achieve its goals.
...