
AI has been with us for a while ever since computers were able to make decisions based on inputs and conditions. When we see a threatening AI system in the movies, it's the malevolence of the system, coupled with the power of a computer, that scares us. AI in its current state is far from being super intelligent. The term artificial intelligence, or the simulation of intelligence in computers or machines, was coined back in 1956, only a decade after the creation of the first electronic digital computers. Hope for the field was initially high, but by the 1970s, when early predictions did not pan out, an “AI winter” set in. AI is a broad topic. It ranges from your phone’s calculator to self-driving cars to something in the future that might change the world dramatically. AI refers to all of these things, which is confusing. We use AI all the time in our daily lives, but we often don’t realize it’s AI “as soon as it works, no one calls it AI anymore.
Dangerous AI is what computer scientists call an Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), an artificial system that completely emulates the human mind and is as intelligent as a human being in any area of knowledge, except it can think billions of times faster than we can. This is what movies tend to depict as incredibly dangerous Skynets hellbent on wiping out humanity. The real concern is what lies one step beyond AGI. Superintelligence has infinite potential for harm, it can just as easily be beneficial, at least to its creators. The constant flow of information on AI, it’s becoming increasingly difficult to pinpoint what exactly AI is. few of us use the term AI in the right context. Misusing and misunderstanding the term can cause us to make fallacious statements and assumptions about what the future holds. As we know, the world is changing at an alarming pace, so thinking critically about these changes is crucial if we want to thrive in the future.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) also known as Weak AI is the AI that exists in our world today. Narrow AI is AI that is programmed to perform a single task whether it’s checking the weather, being able to play chess, or analyzing raw data to write journalistic reports. most of the AI models are capable of doing one thing alone. ANI systems can attend to a task in real-time, but they pull information from a specific data-set. As a result, these systems don’t perform outside of the single task that they are designed to perform. Unlike General or Strong AI Narrow AI is not conscious, sentient, or driven by emotion the way that humans are. They are everywhere,the ultimate goal is artificial general intelligence, a self-teaching system that can outperform humans across a wide range of disciplines. Some scientists believe it’s 30 years away others talk about centuries. This AI takeoff also known as the singularity, will likely see AI pull even with human intelligence and then blow past it in a matter of days.
Cars are full of ANI systems, from the computer that figures out when the anti-lock brakes should kick in to the computer that tunes the parameters of the fuel injection systems. Google’s self-driving car, which is being tested now, will contain robust ANI systems that allow it to perceive and react to the world around it. When you navigate using your map app, receive tailored music recommendations from Pandora, check tomorrow’s weather, talk to Siri, or dozens of other everyday activities, you’re using ANI. Your email spam filter to figure out what’s spam and what’s not, and then it learns and tailors its intelligence to you as it gets experience with your particular preferences. The Nest Thermostat, synthesize that info to cleverly upsell you so you’ll buy more things. Google Translate, The world’s best Checkers, Chess, Scrabble, Backgammon, and Othello players, Google search is one large ANI brain with incredibly sophisticated methods for ranking pages and figuring out what to show you in particular and same goes for Facebook’s Newsfeed. Sophisticated ANI systems are widely used in sectors and industries like military, manufacturing, and finance algorithmic high-frequency AI traders account for more than half of equity shares traded on US markets, and in expert systems like those that help doctors make diagnoses and, most famously, IBM’s Watson, who contained enough facts and understood coy Trebek-speak well enough to soundly beat the most prolific Jeopardy champions.

General AI is more sophisticated than Narrow AI. It can learn by itself and be able to solve problems better than or equal to a human. General AI is what the society has been talking about and anticipating its coming. Whereas we are still far from making a machine has this level of intelligence because the human brain is very complicated and researchers still don’t fully understand how the brain works. Therefore it is challenging to develop an AI that can interpret and connect knowledge from various areas to plan and make a decision. The human mind is the single most complex structure in the history of the universe the brain is the result of millions of years of self-recursive programming. Super AI or Superintelligence is an AI that is more intelligent than all geniuses from all domains of knowledge. It also has creativity, wisdom and social skill. Some researchers believe that we will achieve Super AI soon after we achieve General AI.

AI's can now detect cancers better than human doctors, build better AI algorithms than human developers, there are many other fields where specialized artificial intelligence is replicating human-like reasoning and cognition.
to be sentient creatures, and to have emotionally-driven responses to situations. The AI that exists around us doesn’t have the fluidity or flexibility to think like we do. Even something as complex as a self-driving car is considered Weak AI, except that a self-driving car is made up of multiple ANI systems. ANI systems also act as the building blocks of more intelligent AI that we might encounter in the near future. We’re in danger of building a world that we don’t want to live in if we don’t address those challenges in the near term. If you were able to model all the molecules in a cell and all the cells in a human body, this simulation would not run as fast as a human body. No matter how much you thought about it, you still need to take time to do experiments, whether in real systems or in simulated systems.

Machines are able to process data faster than we can. But as human beings, we have the ability to think abstractly, strategize, and tap into our thoughts and memories to make informed decisions or come up with creative ideas. This type of intelligence makes us superior to machines, but it’s hard to define because it’s primarily driven by our ability to be sentient creatures. Therefore, it’s something that is very difficult to replicate in machines. Machines will be capable of exhibiting intelligence that we haven’t seen in the brightest amongst us. In 2013, a computer had the intelligence level of a 4-year old child. In 2014, a computer was able to solve a mathematical problem so complex that the most intelligent human minds could not check for accuracy. Computer scientist and futurist Ray Kurzweil said that computer intelligence would reach human levels by 2029.
By the time we get to the 2040s, we’ll be able to multiply human intelligence a billionfold. That will be a profound change that’s singular in nature. Computers are going to keep getting smaller and smaller. Ultimately, they will go inside our bodies and brains and make us healthier, make us smarter. The probability of actually inventing the super-AI is very small, and entering the race is very expensive because of the large investment in research and development needed. 2018, researchers were already using AI to read the signals from neurons on their way to the brain, hacking the nerve pathways to restore mobility to paraplegics and patients suffering from locked-in syndrome, in which they are paralyzed but remain conscious.
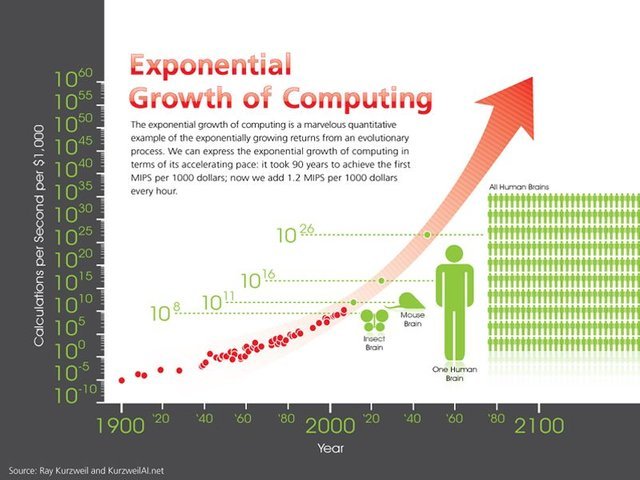
Then by 2045, we will be able to multiply our intelligence a billionfold by linking wirelessly from our neocortex to a synthetic neocortex in the cloud. This will essentially cause a melding of humans and machines. Not only will we be able to connect with machines via the cloud, we’ll be able to connect to another person’s neocortex. This could enhance the overall human experience and allow us to discover various unexplored aspects of humanity. TPUs (Tensor Processing Units), which are made to speed up Machine Learning tasks. TPUs are only produced in limited quantities.
.jpg)
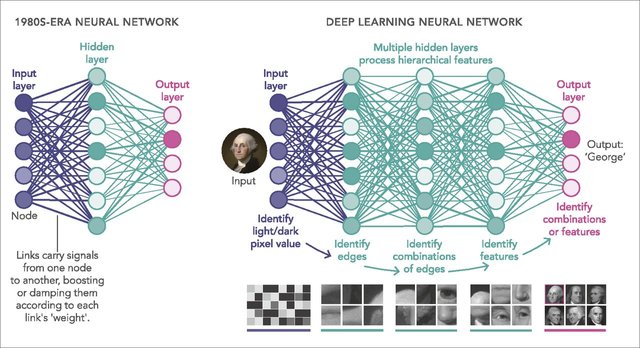
Deep Learning primarily works on artificial neural networks, which mimic the behavior of a human’s neural network to learn. We have tons of other algorithms based on a similar principle. But we do not yet have a complete understanding of how artificial neural networks actually work and arrive at a solution. We can not effectively improve, control and make efficient the things we do not understand fully.
Human minds are one of the most prestigious creations of evolution. Google Brain, a deep learning project from Google, is also attempting to have intelligence similar or equal to human-level. Numenta, a machine learning company is also working on creating cortical learning algorithms. just recently been able to emulate a 1mm-long flatworm brain, which consists of just 302 total neurons. The human brain contains 100 billion. The science world is working hard on reverse engineering the brain to figure out how evolution made such a rad thing—optimistic estimates say we can do this by 2030.
If an AI system is going to be as intelligent as the brain, it’ll need to equal the brain’s raw computing capacity. One way to express this capacity is in the total calculations per second (cps) the brain could manage, and you could come to this number by figuring out the maximum cps of each structure in the brain and then adding them all together. AI rely on human programmers choosing not to build an AI with destructive potential, has to contend with the fact that humans did invent, among other things, nuclear weapons—and moreover, for what seemed like morally impeccable reasons at the time. And a dangerous AI would be a lot harder to keep from proliferating, since it would consist of copyable code. And it would only take one. You could, of course, imagine building a good AI to neutralize the bad AIs, but by that point there’s not much daylight left between you and the AI-risk people.
The brain’s neurons max out at around 200 Hz, while today’s microprocessors (which are much slower than they will be when we reach AGI) run at 2 GHz, or 10 million times faster than our neurons. And the brain’s internal communications, which can move at about 120 m/s, are horribly outmatched by a computer’s ability to communicate optically at the speed of light. Size and storage of The brain is locked into its size by the shape of our skulls, and it couldn’t get much bigger anyway, or the 120 m/s internal communications would take too long to get from one brain structure to another. Computers can expand to any physical size, allowing far more hardware to be put to work, a much larger working memory (RAM), and a longterm memory (hard drive storage) that has both far greater capacity and precision than our own. It’s not only the memories of a computer that would be more precise. Computer transistors are more accurate than biological neurons, and they’re less likely to deteriorate (and can be repaired or replaced if they do). Human brains also get fatigued easily, while computers can run nonstop, at peak performance all the time.
Hedge funds are using AI to beat the stock market, Google is utilizing it to diagnose heart disease more quickly and accurately, and American Express is deploying AI bots to serve its customers online. Researchers no longer speak of just one AI, but of hundreds, each specializing in a complex task—and many of the applications are already lapping the humans that made them. The ability to choose an action that best satisfies conflicting goals is not an add-on to intelligence that engineers might slap themselves in the forehead for forgetting to install; it is intelligence. So is the ability to interpret the intentions of a language user in contex
In the future AIs will colonize and transform the entire cosmos and they will make it intelligent. Government’s lawyers argue that there’s simply no way to prove that Alpha 4—which is thousands of times smarter than the smartest human—is conscious or has human feelings. AIs do have emotions—there has long been a field called “affective computing” that focuses on this specialty—far more complex ones than men and women possess, but they’re different from ours. AI value alignment” is the most pressing problem facing humanity.
AI experts recently predicted the expected emergence of AGI or the singularity by the year 2060. AGI will trigger a series of events and irreversible changes (good or bad) that will reshape the world and life as we know it, forever. following the law of accelerating returns until it reaches the incalculable level of superintelligence—in other words, if left unchecked and given unlimited resources, an AGI will self-improve into an ASI, an intellect that has never before existed in nature.
By 2065, AI has revolutionized the modification of our genomes. Scientists can edit human DNA the way an editor corrects a bad manuscript, snipping out the inferior sections and replacing them with strong, beneficial genes. Only a superintelligent system could map the phenomenally complex interplay of gene mutations that gives rise to a genius pianist or a star second baseman. There may well be another Supreme Court case on whether “designer athletes” should be allowed to compete in the Olympics against mere mortals.
Rapid advancements in hardware and innovative experimentation with software are happening simultaneously, and AGI could creep up on us quickly and unexpectedly. AI can accelerate the process of science. We can make computer simulations of atoms or cells and we can keep speeding them up by many factors, but two issues limit the usefulness of simulations in obtaining instant progress.
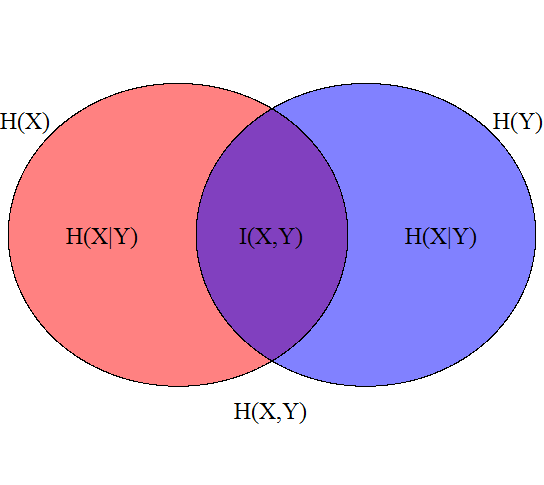
There is an identity known as the data processing inequality, which states that if you have a dataset X with information about a quality Y, then processing the dataset X cannot increase the information regarding Y. You can speed up the brains of your Samoyed or Corgi all you want, but that doesn't translate into a new understanding how to interpret language or abstract ideas. Even with an extra decade or two, these doggos won't all of a sudden comprehend how to make or use tools, let alone understand the finer differences between a capitalist and socialist economic system.
AI is a form of processing so AI algorithms can only reduce the information in the dataset, not increase it. The dataset is the source of the information that makes AI work. Therefore, in order to increase information, we must increase data. Assuming we have access to unlimited data, the limit on increasing the dataset’s size is the rate at which we can process it. The bottleneck in improving AI is the processing throughput.

AI-enabled holograms allow these ems to “walk” the streets of the nation’s capital and to “shop” at stores that are, in reality, completely empty. These simulacra have a purpose, however: They register on the spy satellites that the regime’s enemies keep orbiting overhead, and they maintain the appearance of normality. Meanwhile, the rulers earn billions by leasing the data from the ems to Chinese AI companies, who believe the information is coming from real people. AI is getting stronger, at least in the sense that it is able to produce more and more accurate predictions about the data you feed it. The progress we have made in computer vision over the last decade, approaching 100% accuracy in recognizes objects in images correctly, is one indicator of increasingly strong AI. The ability of DeepMind algorithms to win more and more games, and to transfer learning from one game to another, is a second indication.
Genetic algorithms would work something like this: there would be a performance-and-evaluation process that would happen again and again (the same way biological creatures “perform” by living life and are “evaluated” by whether they manage to reproduce or not). A group of computers would try to do tasks, and the most successful ones would be bred with each other by having half of each of their programming merged together into a new computer. The less successful ones would be eliminated. Over many, many iterations, this natural selection process would produce better and better computers. The challenge would be creating an automated evaluation and breeding cycle so this evolution process could run on its own.
The downside of copying evolution is that evolution likes to take a billion years to do things and we want to do this in a few decades. If our meager brains were able to invent wifi, then something 100 or 1,000 or 1 billion times smarter than we are should have no problem controlling the positioning of each and every atom in the world in any way it likes, at any time everything we consider magic, every power we imagine a supreme God to have will be as mundane an activity for the ASI as flipping on a light switch is for us. Creating the technology to reverse human aging, curing disease and hunger and even mortality, reprogramming the weather to protect the future of life on Earth—all suddenly possible. Also possible is the immediate end of all life on Earth. As far as we’re concerned, if an ASI comes to being, there is now an omnipotent God on Earth
Consciousness, will “emerge” if a network is sufficiently complex, given enough processing power. This might be how we imagine human intelligence and consciousness emerged during evolution—although evolution had billions of years, not just decades. The issue with this is that we have no empirical evidence: we have never seen consciousness manifest itself out of a complex network. Not only do we not know if this is possible, we cannot know how far away we are from reaching this, as we can’t even measure progress along the way. We need to move forward on artificial intelligence development but we also need to be mindful of its very real dangers. I fear that AI may replace humans altogether. If people design computer viruses, someone will design AI that replicates itself. This will be a new form of life that will outperform humans. when we imagine an “intelligence explosion,” we should imagine it not as a cascading boom but rather as a scattering exfoliation of new varieties

Every AI, whether it’s a Roomba or one of its potential world-dominating descendants, is driven by outcomes. Programmers assign these goals, along with a series of rules on how to pursue them. Advanced AI wouldn’t necessarily need to be given the goal of world domination in order to achieve it – it could just be accidental. And the history of computer programming is rife with small errors that sparked catastrophes. As AI advances have been due to Moore’s law, nature imposes a limit. So we will reach a point, perhaps soon, when processor improvements will cease, and thus AI improvements will also cease, or else reach a point of ever-diminishing returns. That point is known as “peak AI” because we have reached the point where a return on the investment in AI improvement is not worthwhile.
A hive mind is a centralized, systematized consciousness for the entire planet. You would have access to everyone’s thoughts, scientific discoveries, feelings, understanding, charisma. If the hive mind was connected to the internet, you would have immediate access to all of the world’s information. The “human-in-the-loop” AI method leverages the advantages of automated detection while prompting human readers to intervene at certain checkpoints when algorithms may be unsure. When radiologists used the AI on a platform called Swarm—which allows multiple experts to work together in real-time—their diagnoses improved, beating those of algorithms and individual readers alone.
Intelligence is not a single dimension. It is a complex of many types and modes of cognition, each one a continuum. Let’s take the very simple task of measuring animal intelligence. If intelligence were a single dimension we should be able to arrange the intelligences of a parrot, a dolphin, a horse, a squirrel, an octopus, a blue whale, a cat, and a gorilla in the correct ascending order in a line. So while each dimension of cognition and computation has a limit, if there are hundreds of dimensions, then there are uncountable varieties of mind — none of them infinite in any dimension. As we build or encounter these uncountable varieties of mind we might naturally think of some of them as exceeding us.
Artificial intelligence is already getting smarter than us, at an exponential rate. We’ll make AIs into a general purpose intelligence, like our own human intelligence in silicon that can be expanded without limit. Once we have exploding superintelligence it can solve most of our problems. Intelligence is not a single dimension, so “smarter than humans” is a meaningless concept. Humans do not have general purpose minds, and neither will AIs. Emulation of human thinking in other media will be constrained by cost. Dimensions of intelligence are not infinite. Intelligences are only one factor in progress. If the expectation of a superhuman AI takeover is built on five key assumptions that have no basis in evidence, then this idea is more akin to a religious belief a myth. In the following paragraphs I expand my evidence for each of these five counter-assumptions, and make the case that, indeed, a superhuman AI is a kind of myth.
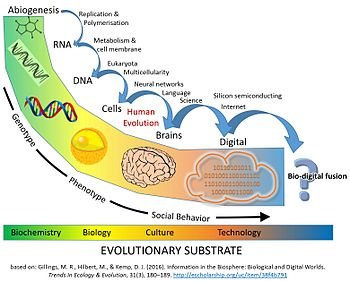
The Singularity is the idea that once we can create general artificial intelligence (intelligence like that of a human being) in software, it will enter a never-ending self-improvement loop, leading to unprecedented, dramatic changes to humanity. It’s the cutting edge of evolution on our planet. One can make a strong case that it’s actually the cutting edge of the evolution of intelligence in general, because there’s no indication that it’s occurred anywhere else. To me that is what human civilization is all about. It is part of our destiny and part of the destiny of evolution to continue to progress ever faster, and to grow the power of intelligence exponentially
There is no evidence that merely thinking about intelligence is enough to create new levels of intelligence. This kind of thinkism is a belief. We have a lot of evidence that in addition to great quantities of intelligence we need experiments, data, trial and error, weird lines of questioning, and all kinds of things beyond smartness to invent new kinds of successful minds. AIs most likely won’t be superhuman but will be many hundreds of extra-human new species of thinking, most different from humans, none that will be general purpose, and none that will be an instant god solving major problems in a flash. Instead there will be a galaxy of finite intelligences, working in unfamiliar dimensions, exceeding our thinking in many of them, working together with us in time to solve existing problems and create new problems.
Technology at this scale can influence the movement of atoms, it could flood and control the body of a living host, build structures out of thin air by rearranging the carbon molecules in the air. An ASI, if programmed to do so, could create nanotechnology From there, we could use it however we see fit like Preventing aging, thereby introducing immortality. The pace of progress in artificial intelligence (I’m not referring to narrow AI) is incredibly fast. Unless you have direct exposure to groups like Deepmind, you have no idea how fast—it is growing at a pace close to exponential. The risk of something seriously dangerous happening is in the five-year timeframe. 10 years at most. The largest supercomputer in China has already beaten that number, at 34 quadrillion cps. However, the computer is the size of a small factory, costs hundreds of millions of dollars, and eats an enormous amount of energy. This is reassuring though: with the exponential nature of technological advancement, we just need Moore’s law to do its work on the size, cost, and energy consumption of current supercomputers.
Religion is arguably mankind’s greatest creation. Ideas of a creator, intelligent design, self-transcendence, and the afterlife capture our imaginations, hopes, and dreams. Belief in God hinges on faith. The acceptance that something greater than ourselves exists and has us in mind. That the universe will work for us, rather than against us. A God, omniscient and omnipotent. You might compare this to the thinking gap between us and an ant, but this too would be shortsighted. ‘Omni God’ theory, which states that Gods are: omniscient (all-knowing), omnipotent (all-powerful), omni-temporal (exist in all time), omnipresent (exist in all places), and omnibenevolent (all-good). Aside from the all-good side of things (that’s up for debate) it seems that ASI could, or already does, meet our standard definition of God. Nanotechnology is technology in the nanometer range, far smaller than what is visible to the human eye. For perspective, a single sheet of newspaper is 100,000 nanometers thick.
Ultra Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
To understand term UAI, Now I would like to back again on human brain example. Think if man or woman having more than one brain in his/her skull, and all these brains connected through single nervous system and all brain function for single person so what would be level of his/her knowledge, realizing, creation and intelligence when all brains think simultaneously. But the reality is above said statement seems to be impossible and sound very stupid, of course not possible in case of human biological brain which is always single and God given and if God decided to give multiple biological brain to single person, then term would be “Ultra Natural Intelligence (UNI)” but it highly impossible in case of living organism, even by any brain surgery etc. but If we apply same statement in non-living organism or electronics or Bionic brain context, than it would be completely valid and possible on one day.
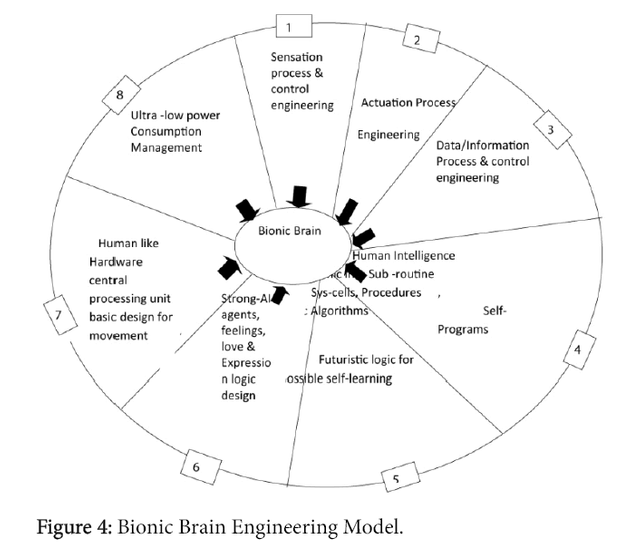
Bionic Brain Engineering Model (BBEM)
8 segments of Bionic Brain Engineering like ‘sensation process and control engineering’ which reach environment stimuli’s up to Bionic Brain of Humanoid i.e., how to sense and process input signal from human and environment through sensor using intelligence software supports. Second is ‘Actuation Process and control engineering’, for output human like response from Robot after sensation and processing input signal, in this engineering segment also need to well synchronized intelligence software with physical body i.e., hardware parts of Humanoid Robot like motors, joints, pneumatic units and control, storage, logical processor, buffers, servo motors and so on. Next important engineering is ‘ Data information processes and control engineering’ i.e., how robots accept and process voice signal, text, images, smell, touch and likewise several signals as well as identify and control them during processing. Next is ‘Human Intelligence mimicking ‘into sub-routine, sys-calls, procedures, genetic Algorithms, Neural Network, Neural Schema’s.
J 17