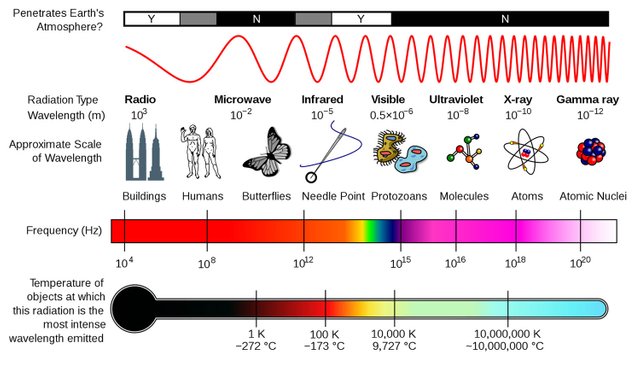
"X-Rays, used for diagnostic imaging in CT scanners, have average energy around 60 keV which is 10,000 times higher than the energy of regular light we see around us.
So, x-rays are electromagnetic radiation just like the light around us but with much higher energy.
Because x-rays have much higher they have shorter wavelength. Since their wavelength is so short in most scenarios we can treat x-rays like particles traveling through space (i.e. just ignore the fact that they are really waves). We call each of these individual packets x-ray photons."
https://howradiologyworks.com/basic-x-ray-properties/
"X-Rays or X-radiation as a form of electromagnetic radiation. They are powerful waves of electromagnetic energy. Most of them have a wavelength ranging from 0.01 to 10 nanometres, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 100 eV to 100 keV."
https://byjus.com/physics/x-ray/#
"X-rays have smaller wavelengths and therefore higher energy. We usually talk about X-rays in terms of their energy rather than wavelength. This is partially because X-rays have very small wavelengths!"
https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/5-8/features/F_X_Rays.html
"An antenna receives the beat frequency radiation. The beat frequency radiation from the antenna is transmitted to a converter via a conductor or waveguide and converted to electrical energy having a desired voltage and waveform."
https://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/ciencia/secret_projects/project111.htm