Preliminary
Head CT examination is an examination using the CT Scan modality to show the organs in the head. This head CT examination is the most commonly performed examination at the Radiology Installation of Teungku Chik Ditiro Sigli Hospital, more than 60% of the examinations using CT scan modalities are head CT examinations, and head injury cases are the most common cases besides infarction. Almost every day there is a demand for head CT with a head injury case.
Head injury is a condition where the head structure has collisions from the outside and has the potential to cause disturbances in brain function.
Anatomy of Head
The scalp consists of 5 layers called SCALP namely; skin, connective tissue, aponeurosis, loose connective tissue and pericranium. Skull bones consist of calvaria bone and skull base, skull bones consisting of frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal bones. While the skull base consists of 3 fossa, namely the anterior fossa, media fossa and posterior fossa.
In the head there are also sutures, which consist of sagittal sutures, coronary sutures and lambdoidea sutures.
Inside the skull there is a brain wrapped in a membrane called meninges, these meninges lining the central nervous system which consists of
duramater, arachnoid and piamater.
The brain is a heavy gelatinous structure in adults around 14 kg. The brain consists of several parts, namely; proensefalon (forebrain) consists of the cerebrum and diensefalon, mesensefalon (midbrain) and rhombensefalon (hindbrain) consisting of pons, medulla oblongata and cerebellum.
Fissures divide the brain into several lobes, namely the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe.
The brain is supplied by two internal carotid arteries and two vertebral arteries. These four arteries anastomose on the inferior surface of the brain and form the Willis circular. The cerebral veins do not have muscle tissue in the walls that are very thin and have no valves. The vein exits the brain and empties into the cranial venous sinus.
Head Injury Pathology
Head injury is a trauma involving calvaria or skull base and internal organs, which is caused by the mechanical force from the outside so that physical, cognitive and social disturbances arise and are associated with decreased levels of consciousness.
Head injury according to pathophysiology is divided into two, primary head injury and secondary head injury. Primary head injury is a direct consequence of the dynamic mechanism, whereas secondary head injury is further damage because the primary injury continues beyond the limit of skull space compensation.
Bleeding is often found in head injuries, namely epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracranial hematoma.
Head CT Examination Technique In Head Injury Case At Radiology Installation of Teungku Chik Ditiro Sigli Hospital
Patient Identity
Name: Mr. Zf
Age: 32 years old
Sex: Men
Medical Record Number: 232590
Address: Sigli
Diagnosis: Severe head injury
Examination Date: 9 September 2018Preparation of Tools and Materials
a. CT equipment: Philips Ingenuity CT 128 Slice
b. Printer: Agfa Drystar 5300 Laser Imager
c. Fixation tools
d. Head HolderPatient Preparation
There are no special preparations for head CT examination in cases of head injury, patients are just released solid objects such as necklaces.Examination Technique
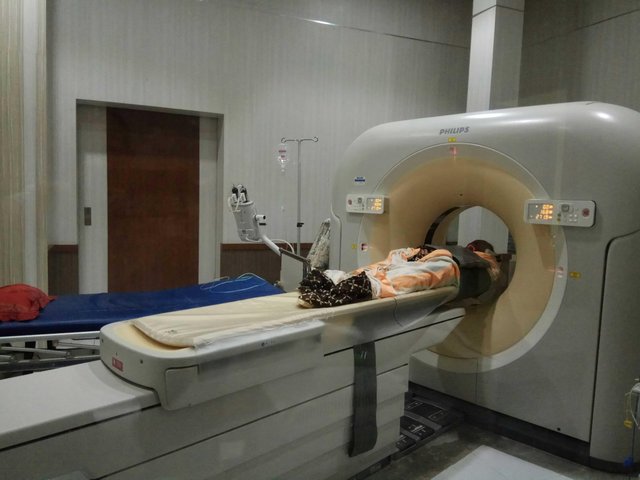
Patient position:
The patient is laid on the examination table in a head position close to the gantry (head first).
Object Position:
The head is placed on the head holder. The head is positioned so that the mid sagittal plane of the body is aligned with the longitudinal indicator lights and the interpupilary line is aligned with the horizontal indicator lights. The patient's arm is placed on the stomach or next to the body. To reduce the movement of the forehead and body the patient should be familiarized with a special belt on the head holder and examination table. Knee is given a booster for patient comfort.
Parameter Scan
Scanogram: lateral head
Range: from Cervical 3 to vertex.
Slice Thickness: 1.50 mm
FOV: 242 mm
Gantry tilt: 0 degrees
kV: 120
mAs: 450
Scan time: 8.32 Sec
Length: 180.8 mm
Reconstruction Algorithma:
Soft Tissue:
Window width: 80 HU
Window level: 40 HU
Bone:
Window width: 1500
Window level: 500
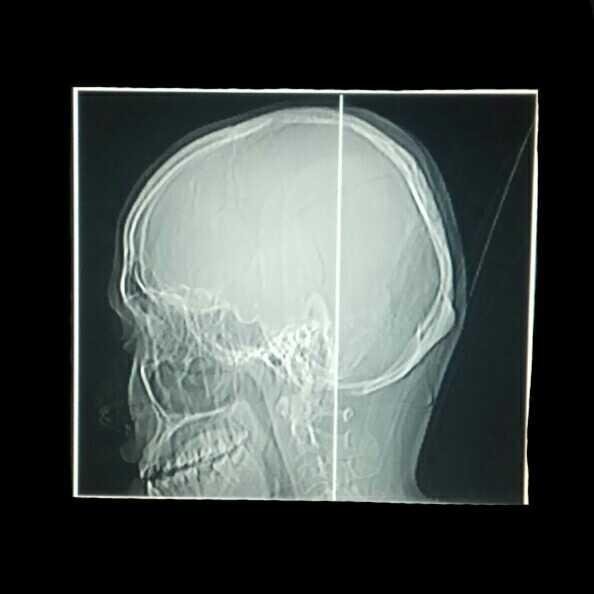
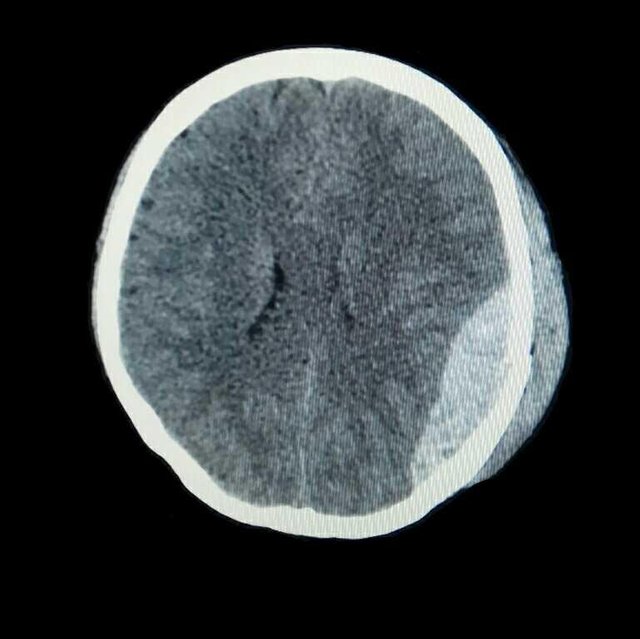
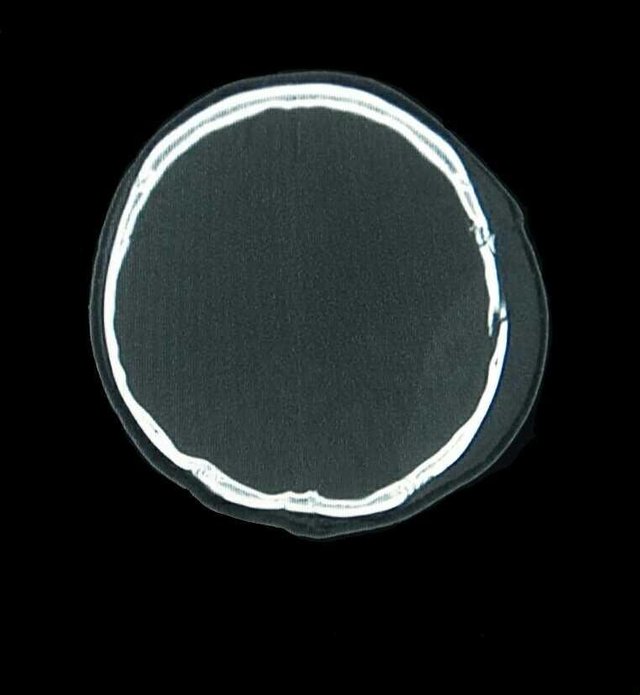
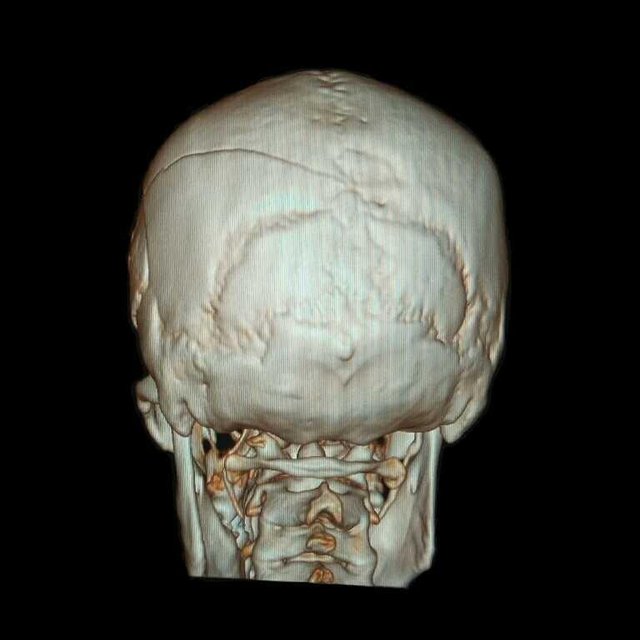
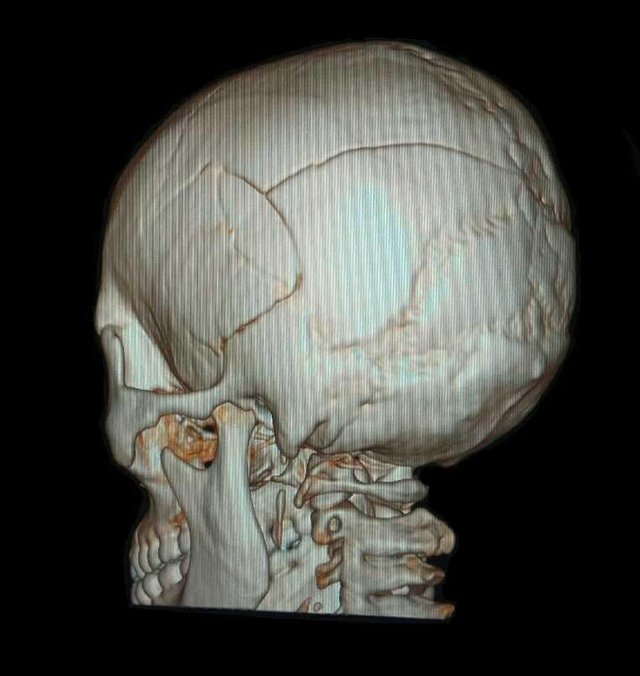
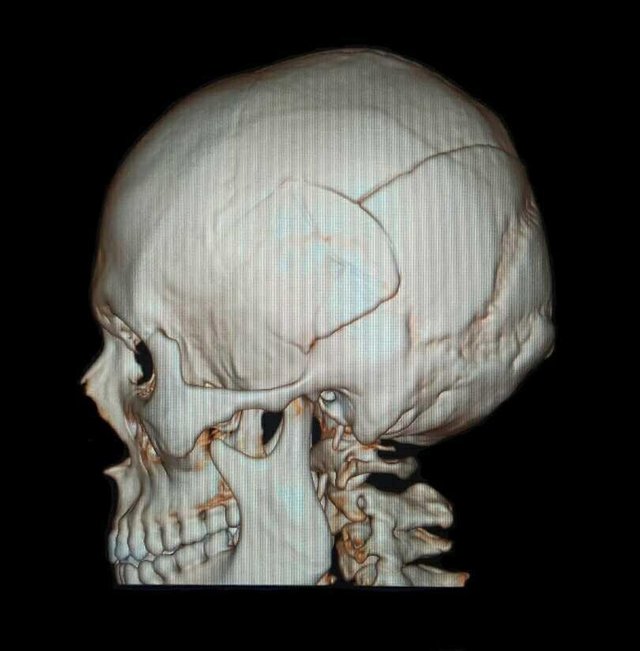
- Examination result
- There is a multiple calvary fracture in the left temporoparietal region.
- There is a curd-shaped hyperdence lesion in the left temporoparietal epidural.
- No midline shifting
- Normal ventricular and cystern system
- Sulci and Guri narrow
Conclusion:
Epidural hematoma in the left temporoparietal region with multiple calvary fractures of the left temporoparietal region and brain edema.
 *all images original by: @anroja*
*all images original by: @anroja*
References: >Healthline - Head Injury >Wikipedia - Head Injury >Radiopedia - CT Head Technique >Kenhub - Head & Neck
Very good knowledge brother @anroja, but anyway I was afraid to hear about head injuries, this made me imagine some cases of accidents that often happened and sometimes cause severe head injuries.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you brother @yati for visiting my blog. So it is highly recommended to use a helmet to protect the head in the event of a traffic accident. About the positive effect of the helmet on my post a few weeks ago.
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Very good article dear.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for commenting and visiting my blog fatima92
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@anjora
Informative post...
I like your post
I waiting for your next post...
Thanks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for visiting my blog and commenting on the article @hirshan
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
great...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Terimakasih telah menjadi delegator di Inisiatif arTeem, @anroja.
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Terima kasih juga telah mendukung dan membimbing saya @arteem. Semoga @arteem semakin eksis.
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Informative article. Nice writeup. Thanks, @anroja. Looking forward to seeing more from you.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you too, my brother @aneukpineung78. Guidance from my brother is still needed so that my writing will be better for coming
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Any obstacles, any questions, drop it on our server and we can discuss them. Never hesitate.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for your attention, my brother @aneukpineung78
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for your attention, my brother @aneukpineung78
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
it is very detail post from what I can see @anroja
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you brother @el-nailul for your comments and visit to my blog
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by anroja from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Bang @anroja CT Scan itu beda ngga sama MRI? Kalau beda, letak perbedaan nya dimana? Serem ya ngebayangin masuk situ?
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Terima kasih atas pertanyaannya kak @ristianti. CT Scan itu memanfaatkan Sinar-X dalam proses pembentukan gambar dan lebih bagus dalam mencitrakan tulang, sedangkan MRI memanfaatkan magnet yg tinggi, lebih bagus dalam mencitrakan jaringan lunak. Karena CT Scan menggunakan Sinar-X, makanya ada efek dari sinar-X tersebut. Sedangkan MRI lebih aman. Tapi pemeriksaan dengan MRI harganya lebih mahal. diatas 3 juta untuk sekali pemeriksaan.
Semoga penjelasan singkat saya ini bermanfaat kak @ristianti
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Sangat bermanfaat sekali bang @anroja. Dulu dokter saya pernah menganjurkan CT Scan gara-gara sakit kepala, headache akut. Tapi ga jadi, takut. Sekarang kadang-kadang aja sakitnya. Ngeri juga kalau CT Scan ada efek sampingnya ya? MRI di sini kemarin kakak saya Medical cek up, hanya untuk MRI saja 3,8juta kurleb. Tetap saja sekalipun dianggap mahal tidak sembarangan bisa minta MRI. Harga segitu di rumah sakit pemerintah, entah kalau di rumkit swasta.
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Tapi kalau masih sakit kepala dan sudah dianjurkan oleh dokter untuk di lakukan pemeriksaan CT Scan, sebaiknya kak @ristianti memberanikan diri untuk dilakukan pemeriksaan tersebut. karena hasil diagnosa dengan CT Scan akan sangat membantu dalam pengobatan sakit kepala yang kakak rasakan. Kalau tentang efeknya, kakak bisa mengambil contoh dalam hal kita mengkonsumsi obat. Obat itu kita tau ada efeknya, tapi kalau manfaat yang didapat lebih besar dibandingkan efeknya, pasti kita akan mengkonsumsi obat tersebut, begitu juga pemeriksaan CT Scan ini.
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Iya, kalau sakit lagi. Tapi mudah-mudahan tidak ya. Hehehehe...
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Iya kak @ristianti. Mudah-mudahan segala penyakit dijauhkan dari kita. Amin..
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Aamiin...
Posted using Partiko Android
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit