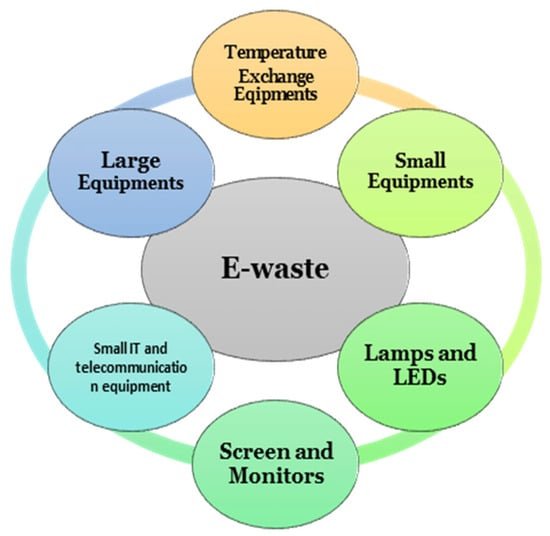
E-waste management involves the proper disposal, recycling, and reuse of electronic devices that have reached the end of their useful life. As technology advances rapidly, more electronic devices are being produced, leading to an increase in electronic waste (e-waste). Proper management of e-waste is crucial because it contains hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can harm the environment and human health if not handled correctly.
Key Components of E-Waste Management:
Collection: Gathering e-waste from households, businesses, and other sources. This can be done through designated drop-off points, take-back programs, or scheduled pickups.
Recycling: Breaking down e-waste into its components to recover valuable materials such as metals, plastics, and glass. Proper recycling reduces the need for new raw materials and minimizes environmental impact.
Refurbishing: Some electronic devices can be repaired or upgraded for reuse. Refurbishing extends the life of the product and reduces the amount of waste generated.
Disposal: Safe disposal of non-recyclable or non-reusable components, ensuring that hazardous materials are treated and contained to prevent environmental contamination.
Legislation and Policies: Governments around the world are enacting laws and regulations to manage e-waste. These laws often include guidelines for proper disposal, recycling standards, and responsibilities of manufacturers and consumers.
Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of e-waste management and how to properly dispose of electronic devices.
Challenges in E-Waste Management:
- High Costs: Proper e-waste management can be expensive, especially in developing countries.
- Informal Recycling: In some regions, e-waste is handled by informal sectors that may use unsafe methods, leading to environmental and health hazards.
- Rapid Technological Change: As new devices are constantly released, older ones quickly become obsolete, increasing the volume of e-waste.
- Global Disparities: E-waste is often exported from developed to developing countries, where regulations may be less strict, leading to improper disposal and recycling.
Future Directions:
- Circular Economy: Emphasizing the reuse and recycling of materials to create a sustainable cycle.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal.
- Innovation in Recycling Technologies: Developing more efficient and environmentally friendly recycling methods.
Effective e-waste management is essential for minimizing the environmental impact of our growing reliance on electronic devices.
"Great post about e-waste management! 🌎 It's so important to raise awareness about the impact of our electronic devices on the environment and human health. I had no idea that informal recycling was a major challenge in some regions - it really highlights the need for proper regulations and education. 💡 What are your thoughts on how we can encourage more people to recycle their e-waste responsibly? 🤔"
I also gave you a 0.44% upvote for the delegations you have made to us. Increase your delegations to get more valuable upvotes. Cheers! 🎉
Help Us Secure the Blockchain for You
Your vote matters! Support strong governance and secure operations by voting for our witnesses:
Get Involved
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit