
SAURCE
The production of marine shrimp is currently an export item of great economic importance for the region. The innovation of best farming practices and the sustained implementation of good practices. The following publication contains a series of tips for shrimp farming that have been developed in the last ten years and are aimed at the staff of shrimp farms.
The development of shrimp farming arises from the need to achieve higher levels of efficiency in shrimp production and as a result of the awareness on the part of shrimp producers that certain cultivation practices still in use are harmful to the environment where this activity takes place. Producers realize that the damage caused by poor farming practices is not only harmful to the coastal ecosystems where shrimp are grown, which, in the medium and long term, also end up negatively impacting production. A deteriorated and polluted environment only leads to poor production and economic losses.
THEN I WILL SHOW THEM A SERIES OF RECOMMENDATIONS THAT SHOULD BE PRESENT DURING THE DIFFERENT STAGES OF THE SHRIMP CROP CYCLE.
DRYING AND PREPARATION OF THE AQUACULTURE UNIT
A good drying and preparation of the ponds contributes to a healthy development of the shrimp, guaranteeing ponds free of harmful substances, pathogens and predators that could increase the mortalities affecting the final yield of the crops. Draining, drying, cleaning, disinfecting and liming are activities that also contribute to diminish the risks of dissemination of diseases to other neighboring farms and to the coastal environment. The general cleaning of the ponds and their surroundings also helps to eliminate possible sources of contamination of the crop, ensuring the safety of the final product.
The pond must be drained completely once the harvest is finished. Then the cleaning and disinfection of entrance and exit gates, pipes, tables and racks must be carried out. Areas that can not be drained completely should be disinfected with sodium hypochlorite or calcium oxide (quicklime). Once the drainage is completed, the water inlet and outlet gates of the ponds should be completely sealed to prevent water entry during high tides. Next, the floors of the ponds should be left to dry in the sun for ten to fifteen days or until they present cracks of 10 cm. of depth.
CLEANING THE PONDS
Garbage and all other plastic material, metal, or glass used during the crop cycle must be disposed of or incinerated in a place on the farm designated for this purpose. The remains of shrimp, crab and dead fish should be burned and / or buried in pits alternating layers of lime (approximately 1 kg / m2) with layers of remains of dead animals. This kind of waste should be buried at least half a meter deep to avoid being dug up by wild animals and should not be allowed to be returned to the aquatic environment.
EVALUATION OF THE STATE OF THE POND FUND.
The main parameters that determine the state of the bottom of the ponds are the percentage of organic matter present and the pH of the bottom of the pond. If the soil of the pond presents acidic conditions (pH <7), agricultural lime should be applied to correct the present acidity. The recommended methodology to perform the pH measurement.
FILLING THE POND
The water that enters the pond must be filtered through filters with a mesh size of 500 microns or less. These filters should be left in the hatches during the first 30 days of cultivation in order to avoid accidental leakage of the postlarvae. These filters can be changed by others of 1000 micron mesh size, which can be maintained until the end of the crop cycle.
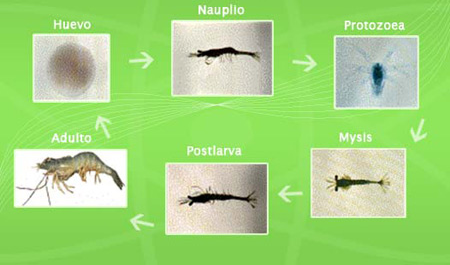
VERIFYING THE QUALITY OF THE POSTLARVA
Ensuring the obtaining of healthy and vigorous postlarvae is a necessary condition for a good start of the cultivation cycle. Having a reliable source of postlarvae helps to ensure the economic success of the harvest. The purchase of postlarvae of doubtful health and quality constitutes a high economic as well as environmental risk since the introduction to the farms of sick animals or carriers of infectious agents facilitates the transmission and dispersion of contagious diseases and may even infect the natural populations of shrimp Postlarvae of good quality should be free of infectious organisms and have a good general health status. In addition, they must present a good development and nutritional status according to their age.
ACLIMATION AND SOWING OF POSTLARVA
Shrimp postlarvae are one of the most expensive inputs in the production of farmed shrimp. The handling and careful handling of the postlarvae starting from their packaging in the laboratory, transport, reception in farm, acclimatization, until the moment of planting in the ponds are extremely critical for their survival. During the process of acclimatization all the efforts of the technical staff should focus on reducing the stress and mortality of the postlarvae as much as possible while they adapt gradually to the new water quality conditions of the ponds. Successful acclimatization helps to ensure the economic success of the crop cycle.
ACCLIMATIZATION FACILITIES
Acclimatization facilities must provide shade, air, filtered water and allow hygienic conditions to be maintained. Densities of 500 postlarvae per liter are adequate during acclimation. If you plan to keep the postlarvae for more than 24 hours, this density should be reduced. Similarly, postlarvae of ages PL-8 to PL-12 should acclimate to lower densities even if they are not maintained for a time longer than 24 hours.
PREPARATION OF ACLIMATION TANKS
The entire acclimatization installation must be washed and disinfected several days before the arrival of the postlarva. Tanks, surfaces and pipes should be washed and disinfected with chlorine. Then they should be rinsed with plenty of water and allowed to dry making sure to remove all chlorine residue. The reservoir tank must be filled with the water from the pond to be sown. Filter the water to be used in acclimatization through a 500 micrometer (0.5mm) filter. Place about 200 liters of water from the reservoir tank in the acclimatization tank and use ice in plastic bags to cool it to 26-27 ° C. The water in the acclimatization tanks should be adjusted to the salinity and average temperature of the water used to transport the postlarvae.
SOWING OF THE POSTLARVAS
The culture ponds should be carefully inspected before planting. These must have a good outcrop of algae and be free of fish, crabs, crabs or other organisms that usually seek shelter and food inside or on the banks of the ponds. It is recommended to release the postlarvae in the ponds as soon as possible. Ideally, sowing should be done during the cooler part of the day (6-8am) or during the night hours. Each transport tank should have a maximum final density of 800 postlarvae per liter, and should be oxygenated continuously. The postlarvae must be released at 50 meter intervals from the transport tanks to the pond with the help of a partially submerged hose. Care should also be taken to free the postlarvae from the side of the pond that is downwind, as the wind and waves help to disperse them after sowing.
SHRIMP HANDLING DURING HARVESTING
Harvested shrimp should be handled quickly and efficiently to freeze it when it is still alive so that its quality does not deteriorate. Once extracted from the pond, the product is emptied into clean containers to be weighed and then transferred to containers with enough ice to keep it at a temperature below 5 ° C while it is transported to the processing plant. They are recommended.
THE MANAGEMENT OF FOOD FOR SHRIMP
The poor management of food affects the growth and survival of shrimp in cultivation while increasing production costs. In addition, providing more food than necessary damages the quality of the soil at the bottom of the pond. In the same way, the nutrients in the artificial feed that are not used directly by the shrimp enter the water column to fertilize the pond, turning the feed into an expensive fertilizer.
THE FARM MUST CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING RECOMMENDATIONS REGARDING SHRIMP FOOD:
• Shrimp feed should be stored in a cool, dry place and kept away from rodents and other pests.
• The farm personnel should be prepared while waiting for the arrival of the food container to avoid exposure of the food sacks to the sun or rain.
• Only high-quality palletized food with a minimum of fine particles should be used
• Fresh fish meat should not be used to feed the shrimp
• Feed requirements should be calculated based on regular estimates of population, biomass and with the help of feeding tables
• Disperse the feed evenly throughout the pond surface avoiding large and repeated applications over small areas
• Manage the daily food ration in more than one application when the conditions of the farm allow it
• Do not feed when the oxygen concentrations are less than 2.5mg / L
• Consider the use of feeding trays to monitor the feeding behavior of shrimp.
USE OF FERTILIZERS
The application of fertilizers helps to increase the densities of algae, the natural productivity and indirectly to improve the oxygen levels of the water in the ponds. However, excessive fertilizer applications increase the production costs of the operation and can produce imbalances in the water quality conditions both in the pond system and in the natural environment to which the discharge waters are released during the refills. As in the case of shrimp feed, moderate fertilizer use should be made.
USE OF AGRICULTURAL CAL
The use of lime is beneficial when there are problems of pH (acidity), low hardness and low alkalinity in the waters of ponds. In these cases, the applications of lime improve the survival and growth30 Good Management Practices for Shrimp Farming of the animals in cultivation and contribute to a better response of the natural productivity of the pond to the use of fertilizers. However, the application of lime to the brackish waters of shrimp ponds is rarely useful since they normally have high hardness and high alkalinity.
SAURCE
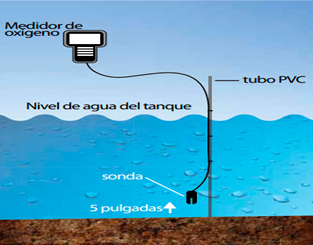
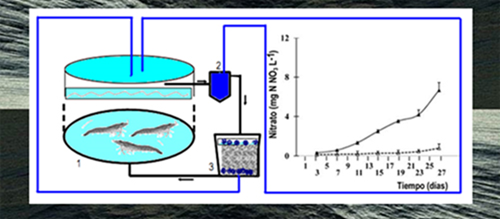
MEASUREMENT OF WATER QUALITY PARAMETERS
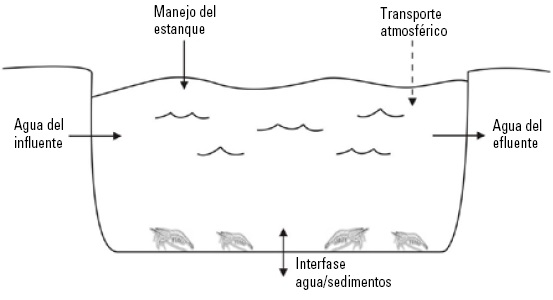
The deterioration of water quality in the ponds can severely affect the health of shrimp to the point of endangering the entire crop. Hence the need to implement a system of daily monitoring of the physical and chemical parameters of water that allows to anticipate and correct the development of adverse conditions of water quality in order to re establish optimal conditions in the farming system. The activities of monitoring water quality in shrimp culture ponds begin with the selection of appropriate sites for the measurement of physical and chemical parameters. Usually a pond sampling station is built. Generally these are the most preferred places for shrimp because they have sufficient depth and favorable water quality conditions.
The quality of the water discharged from the shrimp ponds is a reflection of the food and fertilizer management practices used during cultivation. The deterioration of water quality in shrimp ponds can be caused by excessive planting densities, excessive feeding rates and by the excessive use of fertilizers. Improving management practices in these areas will have a positive impact on the water quality of the ponds and will help reduce the loads of pollutants released into the environment.
SOURCE:
https://www.crc.uri.edu/download/PKD_good_mgt_field_manual.pdf
http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0258
I hope that my article has served you well.





We have take due note about the recommendation presented to us by you for shrimp cultivation... thanks for sharing this post with us today
Resteem
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @chilarengel! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness and get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit