There are numerous choices for those wishing to consider a horticulture based degree because of the idea of the expansiveness of the subject. With the investigation of present day ideas, for example, GM, ecological change, supportability and in addition the business and logical sides, potential understudies are ruined for decision for work and degree choices. As a rule, a college degree ought to be sufficient to discover great work and understudies in the US taking a college degree have a particular advantage over different nations because of the measure of the business here. There remains a shortage of horticulture graduates as well, so it ought not be hard to discover beneficial work. For those going into farming as a vocation, once you have picked this as a noteworthy it is savvy to pick such related subjects as science, sustenance, science and any ecological choices your school or college may offer. With a college degree, you can manage farms and farms, fisheries and woodlands, work with soil protection or numerous other "outside" alternatives.
For look into degrees, for instance those identified with the earth, hereditary qualities and particular rearing, agrarian building and innovation, a propelled degree is a presumable prerequisite - commonly a MS on the off chance that you need to center around lab work as opposed to handle work.
Take in more about the numerous professions in farming.
Agribusiness is characterized as the development and misuse of animals, plants (counting parasites) and different types of natural life for human utilize including sustenance, fiber, solutions, fuel and whatever else. It is, and has been since there was a farming business sector, one of the biggest bosses of individuals; in the USA today, agribusiness speaks to 20% of the US economy. Before sorted out agribusiness, it is trusted that the nourishment supply could accommodate only 4 million individuals all around.
Indeed, even as innovation changes, horticulture adjusts and would never end up old - even in a period when it may possibly be endlessly not quite the same as what it may have been at the beginning of agribusiness. All things considered, we are continually going to need to build the quantity of crops we develop for sustenance and for attire, colors and oils, seed advancement and designing to adapt to the developing needs of the total populace, regardless of whether the photo isn't as somber as the most preservationist concerns may recommend. Today, agribusiness is as much a science as a workmanship. With a need to adapt to the developing needs of the planet's populace, and to discover approaches to continue delivering nourishment and different crops as we venture into peripheral scenes, and adjust to an evolving atmosphere, changes in horticulture hones, sustenance innovation and bio innovation will keep on being a major piece of human progress.
The History of Agriculture
Prehistory
For a large portion of our reality, people were hunter-gatherers. This implies individuals carried on with an itinerant way of life, moving with the seasons to take after the nourishment supply. As the icy masses withdrew and plant life examples and development zones changed accordingly, it implied that the need to move so regularly turned out to be marginally less basic - however without a doubt the way of life carried on for a great many years as individuals looked to augment their asset procurement. Hunter-gatherer social orders would have known which crops were best to abuse with each season.
The "hunter-gatherer" moniker can be a misnomer as it is trusted today that itinerant groups didn't all of a sudden simply choose one day to quit moving and to set up lasting settlements - however the purposes behind the progress have been investigated in awesome arrangement is as yet not settled. It is likely that some level of semi-roaming way of life created where individuals essentially set up camps for quite a while at once, cordoning off zones of wild crops that had the most bottomless assets. It is additionally likely that they had groups of livestock that they took with them wherever they moved, keeping them secure to misuse for drain, meat, hide and different assets. The need to secure stores of sustenance for the following season may likewise have had an impact.
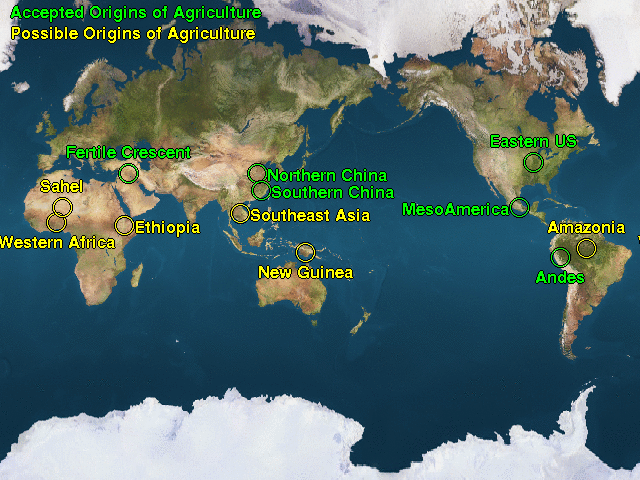
Archaeologists and scientists have followed the causes of farming to around 10,000 years prior, to some place in the Indus Valley, and perhaps as a different advancement in China along the Yangtze River. It is realized that people initially tamed crops and later livestock in sufficiently incredible numbers to perceive the indications of ponder abuse.
Early Civilization
Early development can be viewed as a blast time in rural science and innovation. Around 5500 BC, the Sumerian human progress of the Middle East and other early pre Greco-Roman developments comprehended the requirement for a specific farming workforce for their social orders to flourish. It is in this period that we saw the innovation of water system in addition to other things, and this particular workforce, and spotlight on agrarian innovation permitted the advancement of the main urban communities. Thusly, these drove the main composed laws and prompted the advancement of complex social orders. Starting here of view, horticulture drives civilisation: including religious practices, social states of mind and lawful codes.
Antiquated Egypt had a standout among the most complex social orders of the old world before the ascent of the Greek human advancement, and it was for the most part on account of their agrarian framework. The River Nile depended intensely on the seasons and every year, the waterway would surge its banks and part of the encompassing wide open (called The Inundation). Their human advancement and to be sure their religious structure, was worked around the nurturing idea of the River Nile and the kingdom's substantial dependence on the waterway and delta framework. A large portion of Egypt was and still is desert with a couple of key desert springs, which implies that the agribusiness focused on a little piece of the nation.
The Greeks and Romans took quite a bit of their horticultural innovation from different developments with which they had contact - most outstandingly those of the antiquated Near East, for example, Mesopotamia, by means of Sumeria. From Egypt, those social orders took coordinate impact once the nation was vanquished by Alexander the Great and later by the Roman Republic. It was here at the introduction of current development that we saw genuine extensive scale animal and plant agribusiness. Innovation might not have propelled an incredible arrangement, but rather the procedures made farming sufficiently proficient to manage the domain's extensive urban areas, making it a vital industry.
Early to Modern Civilization
The Middle East kept on observing much advancement in the horticultural ventures, something that students of history allude to as The Arab Agricultural Revolution. This was because of the decent variety of the nearby geologies, the crops developed in the Middle East and Indus Valley that European social orders desired, and later went about as an exchange connect between Far East and Europe.
In Europe, minimal changed before the ascent of the kingdoms around the eleventh century when the Church wound up real landholders and brokers, pioneers, instructors and held both worldly and profound forces. The frameworks affected through feudalism, regardless of whether mainstream rulers or church possessions, tried to enhance yields with the developing populace, and normally we saw noteworthy innovative advances in this period as well. It was a time of huge specific cross-reproducing, especially in animal livestock, and frameworks of association. In a few regions of Europe, we can see the remainders of the agrarian framework today as medieval edge and wrinkle strip farming. It is because of the cloisters of Europe that we see propels into what we call "minor scenes" - zones where crops don't develop in awesome numbers the we see rural building on an extraordinary scale. Floodplains were depleted, wild forests changed over to fields and bracken cleared for field, territories with low ripeness were changed over or adjusted to make legitimate utilization of them; for instance, grain develops well on salty soil, making it perfect to develop on floodplains. Present day rural practices saw its last current improvement in the sixteenth century when farmers thought of crop turn - the possibility that one could expand yields by exchanging land use around consistently all together not to deplete the dirt. One year the field would have crops planted, the next year it would be utilized for livestock and the third it would be kept decrepit. In spite of the fact that prior social orders had utilized it to a specific degree, just in the sixteenth century was the technique culminated.
The Americas
Mass agrarian practices were not especially introduce in North America until the entry of the European pilgrims. It's unquestionably not genuine that the Native Americans had no horticulture; to be sure, there is prove for some restricted agrarian practices yet it was not widespread over the clans. Some were totally itinerant and some were to a great extent static - these were not topographical either, a few clans in the east had totally trained crops. When we take a gander at the south-western states, especially Arizona and New Mexico, we see horticulture on a mechanical scale - particularly the development of maize crops that were presented from current Mexico, whatever is left of Americanism and past. It is likely that agribusiness went toward the North America generally late, maybe in the vicinity of 2500 and 2000 BC and we see it broadly with so much human advancements as the Hohokam, the Anasazi and old Pueblos, perhaps creating in Mesoamerica around 6000 BC with the training of maize.
In Mesoamerica and South America, with the Inca, the Maya, Olmecs and the Aztecs, generally early advancement of farming allowed the working of colossal urban areas that awed the European colonizers; it was immediately distinguished that these civic establishments had an amazing horticulture construct economy that remained in light of a standard with Europe, testing what was then comprehended about the improvement of human advancement. In Mesoameric
the history of agriculture is a long one with twists and turns but its brought us this far...............STEEMCHURCH FARMS WILL FEED THE WORLD THROUGH STEEM ONE SMALL FARM AT A TIME

.jpg)
.jpg)
Amazing publication, well taught.... we @farms has gain more knowledge about agriculture
Resteem
(to be a part of this community; ensure to always use #farms and #steemchurch for agricultural related post)
SteemChurch Farm ( @FARMS)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
An excellently detailed historical background about agriculture. Just one question remains, how did agriculture start in Africa and West Africa especially...... Or are there no records of our written history??!!. Thanks for the lovely and detailed post. 👍👍👍
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
What a detailed educatuve post about the history of agriculture. I lived every bit of it. Now i know how agriculture started.
Thanks for sharing.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit