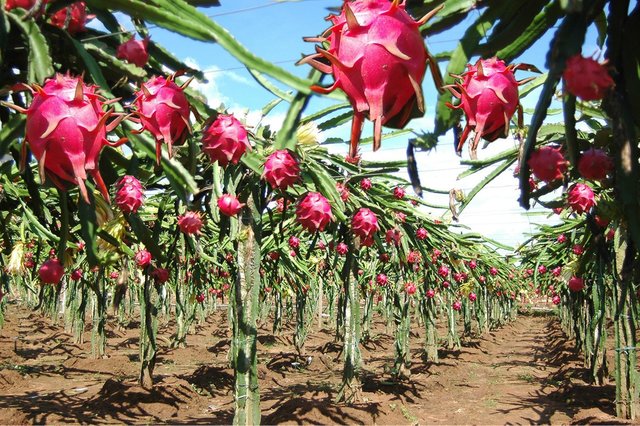



Genus Hylocereus
Species H. undatus
H. megalanthus

The root of the pitahaya has two types of roots, a primary one where a group of thin and superficial roots with absorption function and a secondary one where airs with support function are formed.
The stem, are very branched green, with three edges and articulated by straight sections. At the edges they present areoles in which they have spines of 2 to 4mm, the stem acts as a water regulator and participates in photosynthesis.
Flower: It presents hermaphrodite flowers, large (15-30cm long), tubular and white, yellowish or pink. Its flowers open during the night, which are oriented towards the light of the moon.
Fruit: It is a berry with oval shape, about 6-12cm in diameter and red or yellow. Most species have a fleshy epidermis with waxy-looking triangular bracts. The pulp of the fruit is translucent, containing in its interior numerous black seeds.

Temperature: pitahaya prefers subhumid warm climates. However, it also develops well in dry climates. The optimum temperature for the development of the plant oscillates around 16-25ºC, not tolerating the low temperatures.
Light: The cultivation of pitaya requires high luminosity for the development of different physiological processes. Proper lighting stimulates the sprouting of the flower buds.
Prolonged exposure to direct solar radiation can be harmful to the pitaya, so it is convenient that its exposure is partial (shade by 30%). However, an excess of shade can cause a decrease in production.Substrate: It is a plant, which due to its rusticity, adapts to dry, poor and stony soils. However, they prefer sandy-loam soils, humid, with good drainage due to their sensitivity to ponding, rich in organic matter and slightly acidic pH (5,5-6,5).
Irrigation: It is a plant that does not require abundant water. Risks of support must be given during the first two years of planting in order to stimulate an adequate vegetative growth.


The preparation of the land must be done at least one month before planting. Subsoiling should be done to keep the soil aerated and with good drainage capacity.
The planting of the pitahaya takes place at the beginning of winter, previously rooted. If the plantation is carried out during the dry season, abundant watering must be done, as before and after planting.
Tutorado: This work is carried out at the beginning of the plantation. There are two types of tutors:
Live: They must be trees of fast growth and rooting, of soft bark, resistant to plagues and diseases and that are not host of plagues and diseases that affect the pitaya. This type of tutor has the advantage of offering the pitahaya the shade they need. In any case, they should be pruned frequently in order to avoid sprouts that compete for sunlight. Some of the most frequent plants are: Black Madero (Gliricidia sepium), Helequeme (Erithrina poepigiana) and Chilamate (Ficus alobata).
Inert: These tutors are usually made of wood and must be resistant, since they have to support the weight of the pitahaya plant.

Pests
- Pathobattle (Leptoglossus zonatus): It is a pest that affects the pitaya during the dry months. Both the larvae and the adults cause damage by feeding on the pods, since they suck the sap causing chlorosis in them. In addition, they also affect the flower buds, whose symptoms manifest themselves with a certain reddish color.
Fly of the floral button (Dasiops saltans): It is a dipteran that usually affects the yellow pitaya (H. megalanthus). This plague causes damage by feeding on the internal structures of the floral bud, causing deformation and subsequent fall of it. Affected flower buds turn reddish.
Ant (Atta cephalotes): This pest affects pods, flower buds and fruits, producing damages that reduce the quality of the fruit.
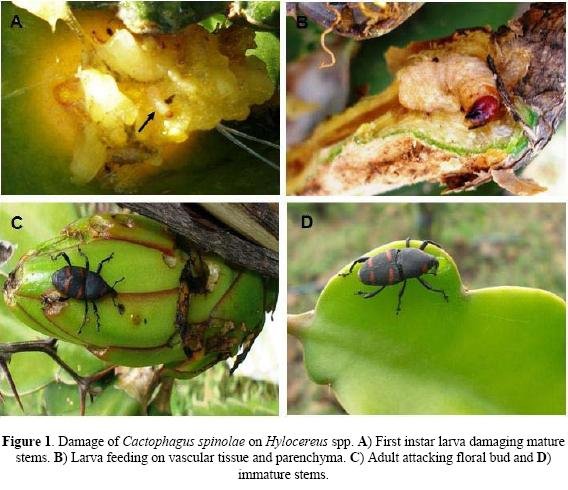
Black weevil (Metamasius sp.): It is a pest, whose main damage is caused by the larvae when perforating galleries inside the stems. The adult causes damage to the leaf sheaths as a result of oviposition.
Stem borer (Maracayia chlorisalis): The damage is caused by the larvae that penetrate inside the pods, causing cavities inside. As a result, the plant tissue begins to rot.

Diseases
- Stem rot (Erwinia carotovora): This is the most harmful disease for pitaya. The symptoms are manifested with chlorotic spots, which can cover the entire pod, leading to an aqueous rot.
fish eye (Dothiorella sp.): The symptoms of this disease are manifested in the pods by the presence of small brown circular spots with orange spots in the center.
Anthracnose (Colletotrichum sp.): The fungus causing this disease is favored by the presence of high relative humidity and temperature (20-30ºC). The symptoms are manifested in pods and fruits with the presence of black and sunken circular spots.

Delays cellular aging
Strengthens the immune system
Stimulates the production of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets
It can prevent arteriosclerosis
Help us regulate intestinal transit
Reduces the risk of suffering cerebral and cardiac infarction
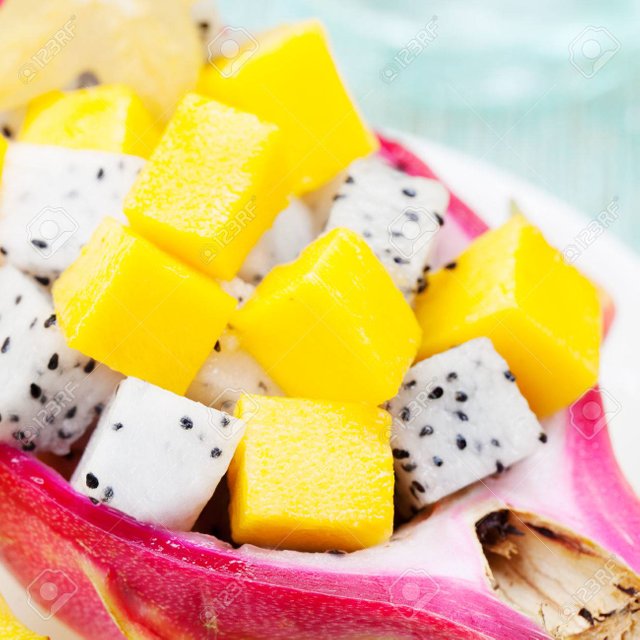
Tropical fruit salad in pitahaya, mango, dragon fruit bowls with a glass of diet juice, healthy breakfast fruit salad, weight loss concept

INGREDIENTS
The pulp of half pitahaya
Juice of a lemon
Ice
Sugar
Water
PREPARATION:
- Place the pitahaya, lemon juice, ice, sugar and water in a blender. Blend well.
- Serve and enjoy.
http://www.infoagro.com/documentos/el_cultivo_pitahaya.asp
https://www.ecoagricultor.com/pitaya-fruta-dragon-retrasar-envejecimiento-sistema-inmunologico-dientes-huesos-fuertes/
https://www.google.com/search?biw=1366&bih=582&tbm=isch&sa=1&ei=_bB5W5HcBoud5gLw4LOwBg&q=la+pitahaya&oq=la+pitahaya&gs_l=img.3...0.0.0.4301.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0..0.0....0...1c..64.img..0.0.0....0.qZFN2aI82pw