Source
White Worm Life Cycle
It only reproduces when it reaches maturity and can not do so in a larval state, so it is important to look for adults in crops. The females deposit on average 4 to 22 eggs every 3 to 5 days, so they can release a total of approximately 260 eggs in their life cycle (about 280 days).
Eggs: they are cylindrical, slightly oval, they measure between 1.12 and 1.25 mm in length, they have a white coloration >that turns yellowish, they are covered by a mucilaginous and soft substance, they hatch in 20 and 30 days.
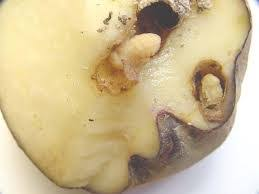
Larva: present between five and six larval instars (intermediate stages). The first instar measures 1.12 mm in length and >the last, between 11 and 13 mm. The larva is creamy white and has a well differentiated head. The larvae have a "C" >shape and lack legs, however they have movement. The type of damage caused by the larva renders the tubers useless >for both food and seed.
Pupa: They are white and develop in a cell formed of earth; in this state they live 20 to 32 days. This is the most >susceptible stage, because there are microorganisms that can parasitize them, such as the fungus Beauveria bassiana. >In this state is when the insect goes through a period of melanization (mechanism defense of insects against invading >organisms), which changes from a yellowish to dark brown.
Adult: The adult is an insect about 7 mm long and 4 mm wide, can not fly because their forewings are welded together, >and the hind wings are atrophied, however, they are very good at walking. The body is gray and easily camouflaged >with the ground, making it difficult to detect.

What kind of damage does this pest cause and what hosts does it have?
The greatest damage is caused by the larvae, they perforate the tubercle forming holes, there they deposit their excrements, leaving holes. Adults have nocturnal habits and feed on the leaves, on the edges they produce damage in the form of a half moon, it is important to monitor the crop looking for this type of damage.

Alternatives to control the white worm
Application of different forms of control: biological, cultural, physical and chemical. Biological control refers to the reduction of the pest by natural enemies (insects) that are responsible for destroying them or making them sick, causing their death.
Entomopathogenic nematodes such as Steinernema and Heterorhabditis, or entomopathogenic fungi such as Bauveria >bassiana and Metharizium anisopliae can be used. These being the inhabitants of the soil have the ability to search, >parasitize and cause death to a large number of insect pests such as the white potato worm.

Attitude of the farmer to the adoption of new technologies
It is necessary to generate informative and educational processes that present the advantages of the new technological tools and a greater understanding of the cost-benefit relationship. Since the adoption of new technologies in the farmer are estimated low.

For more information about this white potato worm (Gorgojo) you can visit the website
http://www.agrositio.com/vertext/vertext.php?id=146459&se=
