Tubers are extended structures in some plant species utilized as storage organs for nutrients. They are used for the plant's perennation to give strength and help to regrowth amid the following developing season, and as a methods of asexual reproduction. Stem tubers form from thickened rhizomes (underground stems) or stolons (horizontal associations between creatures). Basic plant species with stem tubers include potato and yam. A few sources additionally treat adjusted lateral roots(root tubers) under the definition; these are experienced in sweet potato, cassava, and dahlia.
The term begins from Latin tuber, signifying "protuberance, knock, swelling". A few sources characterize the expression "tuber" to mean just structures inferred from stems; others utilize the term for structures got from stems or roots.
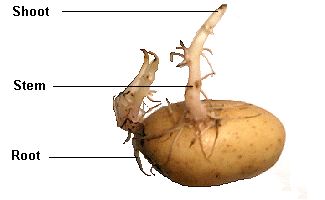
A stem tuber forms from thickened rhizomesor stolons. The best sides of the tuber create shoots that develop into run of the mill stems and leaves and the under sides deliver roots. They tend to shape along the edges of the parent plant and are frequently situated close to the dirt surface. The underground stem tuber is typically a fleeting stockpiling and regenerative organ creating from a shoot that branches off a develop plant. The offsprings or new tubers are appended to a parent tuber or frame toward the finish of a hypogeogenous (started subterranean) rhizome. In the harvest time the plant bites the dust, with the exception of the new posterity stem tubers which have one predominant bud, which in spring regrows another shoot delivering stems and leaves, in summer the tubers rot and new tubers start to develop. A few plants likewise frame littler tubers and/or tubercules which act like seeds, delivering little plants that take after (in morphology and size) seedlings. Some stem tubers are seemingly perpetual, for example, those of tuberous begonia, yet numerous plants have tubers that survive just until the point when the plants have completely leafed out, and soon thereafter the tuber is decreased to a wilted husk.
Stem tubers for the most part begin off as extensions of the hypocotyl section of a seedling yet additionally once in a while incorporate the primary hub or two of the epicotyl and the upper segment of the root. The stem tuber has a vertical introduction with one or a couple of vegetative buds on the best and sinewy roots delivered on the base from a basal segment, commonly the stem tuber has an elongated adjusted shape.
Tuberous begonia, yams and Cyclamen are usually developed stem tubers. Mignonette vine (Anredera cordifolia) produces elevated stem tubers on 12-to-25-foot-tall (3.7 to 7.6 m) vines, the tubers tumble to the ground and grow.
The tuber has every one of the parts of a typical stem, including hubs and internodes. The hubs are the eyes and every ha a leaf scar. The hubs or eyes are organized around the tuber in a winding design starting on the end inverse the connection point to the stolon. The terminal bud is created at the most remote point far from the stolon connection and tubers along these lines demonstrate the same apical dominanceas an ordinary stem. Inside, a tuber is loaded with starch put away in enlarged parenchymalike cells. Within a tuber has the average cell structures of any stem, including an essence, vascular zones, and a cortex.
The tuber is created in one developing season and used to perennate the plant and as a methods of propagation. At the point when fall comes, the over the ground structure of the plant kicks the bucket, however the tubers make due finished winter underground until the point that spring, when they recover new shoots that utilization the put away nourishment in the tuber to develop. As the principle shoot creates from the tuber, the base of the shoot near the tuber produces extrinsic roots and sidelong buds on the shoot. The shoot likewise delivers stolons that are long etiolated stems. The stolon prolongs amid long days with the nearness of high auxins levels that counteract root development off of the stolon. Before new tuber development starts, the stolon must be a specific age. The chemical lipoxygenase makes a hormone, jasmonic corrosive, which is engaged with the control of potato tuber improvement.
The stolons are effectively perceived when potato plants are developed from seeds. As the plants develop, stolons are delivered around the dirt surface from the hubs. The tubers frame near the dirt surface and in some cases even over the ground. At the point when potatoes are developed, the tubers are cut into pieces and planted considerably more profound into the dirt. Planting the pieces further makes more zone for the plants to produce the tubers and their size increments. The pieces grow shoots that develop to the surface. These shoots are rhizome-like and create short stolons from the hubs while in the ground. At the point when the shoots achieve the dirt surface, they create roots and shoots that develop into the green plant.
Tuber, particular storage stem of certain seed plants. Tubers are normally short and thickened and ordinarily develop underneath the soil. Generally made out of starch storing parenchyma tissue, they constitute the resting phase of different plants and empower overwintering in numerous species. As adjusted stems, most tubers bear minute scale leaves, each with a bud that has the potential for forming into a new plant. The potato is an average tuber, as is the Jerusalem artichoke.
Tubers vary from root edits in three different ways. Tubers are amplified stems instead of expanded roots. Cut up a tuber, and each area will grow a plant; root crops can't do this. Tubers contain more starch than root crops.
The Difference Between Tubers and Root Crops
While at the same time all tubers are root crops, not all root crops are tubers. Tubers share a few characteristics with root crops, yet they contrast. Nutritionists and governments think about the two gatherings vegetables and critical parts of an adjusted eating routine. Root harvests and tubers give starches, vitamins, minerals and smaller scale supplements.
Similarites between Root Crops and Tubers
Tubers give plants an indistinguishable administrations from typical roots.
Roots perform two essential capacities. They retain minerals and water from the dirt to maintain plant development. They likewise grapple the plant set up by giving a basic establishment. Root harvests and tubers achieve both these capacities.
Tubers contrast from root trims in three different ways. Tubers are expanded stems as opposed to augmented roots. Tubers contain more starch than root crops.
Tubers and root crops frame from various sorts of plant tissues. Despite the fact that a tuber develops underground, it is a kind of specific stem tissue that stores supplements for the plant. A potato is really an extended stem. Root crops get from root tissue. Carrots are an expanded tap roots.
Unlike root edits, a few tubers can develop per plant. Root harvests and tubers have an alternate sort of root structure. Root crops are tap roots. They are a solitary root that drills down into the dirt like a carrot or parsnip. They can be a solitary adjusted changed root like a beet. The key point being, root crops frame one vegetable for each stem. With tubers, a solitary plant can create a few tubers. A carrot plant will have one carrot, while at the same time a potato plant can create a few potatoes.
Potatoes give a high vitality nourishment asset for societies around the globe.
Root yields and tubers shift in their starch structure. Root crops contain more basic sugars, for example, glucose. Tubers contain long chains of glucose called starch. Potatoes are an essential sustenance edit far and wide in light of the fact that they contain a lot of starch, a great wellspring of vitality for individuals' digestion. Plants store the vitality in tubers for spread. A cut up radish gives a tidbit; a cut up potato can develop more plants. Numerous elaborate plants can be spread by cutting a bit of stem and staying it in water. The stem will in the end develop roots. Potatoes are a similar way.
Both root harvests and tubers offer plentiful nourishment. Tubers offer heaps of vitality and vitamins. Root crops offer vitamins, minerals and small scale supplements. Carrots contain beta-carotene, a forerunner to vitamin A which, as indicated by the Mayo Clinic, is useful for the eyes.

.jpeg)
Source
There is reasonable evidence that this article has been spun, rewritten, or reworded. Repeatedly posting such content is considered spam.
Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
More information and tips on sharing content.
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #disputes on Discord
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Indeed we @farms has come to think about it too, agriculture has remain the backbone of our economy growth.
Resteem
(to be a part of this community; ensure to always use #farms and #steemchurch for agricultural related post)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit