Welcome to forward, estimated reading time, 10 minutes.
Disclaimer: The following text does not constitute any medical advice, but only information sharing. Please proceed under the guidance of professionals.
Nowadays, food is everywhere, and more and more people are becoming overweight or even obese.
The combination of three meals a day and long periods of sitting will cause a series of chain reactions.
Most importantly, eating too much will make your mind dull and your memory impaired.
Many studies have found that intermittent fasting and starving yourself have huge benefits for the brain.
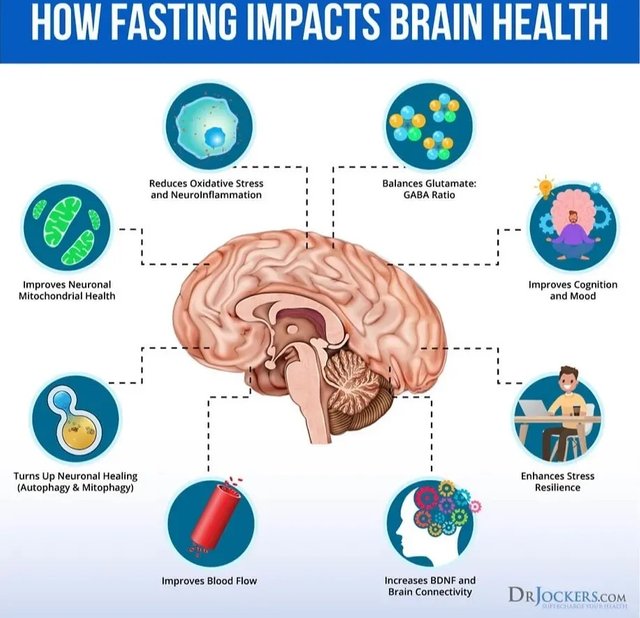
Eating patterns like time-restricted eating, alternate-day fasting (ADF), and the 5:2 diet not only help manage weight, but also have positive effects on brain health and cognitive function.
How does fasting affect the brain?
→ Fasting helps produce ketone bodies (the brain’s favorite fuel)
After fasting for 12–36 hours, the body enters a physiological state of ketosis, which is characterized by low blood sugar levels, depleted liver glycogen stores, and the liver producing fat-derived ketone bodies, which are the brain’s main source of energy.
The liver is the main site of ketosis, but brain astrocytes also produce ketone bodies, which become the brain’s preferred fuel source within a few days of starting fasting, providing up to 70% of energy needs.
Studies have found that rodents treated with a ketogenic diet for 5 days showed improved spatial learning and memory. ①
Ketone bodies are not only a source of energy for neurons, but the primary blood ketone beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) also has important signaling functions.
In hippocampal and cortical neurons, BHB upregulates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) by inhibiting histone deacetylase (an enzyme that inhibits BDNF expression). ②
→Fasting improves mitochondrial health
Fasting improves mitochondrial health by upregulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), promoting the expression of mitochondrial master regulators.
BDNF is a key regulator of neuronal function and has antidepressant effects. The most commonly used antidepressant drugs are mediated by BDNF.
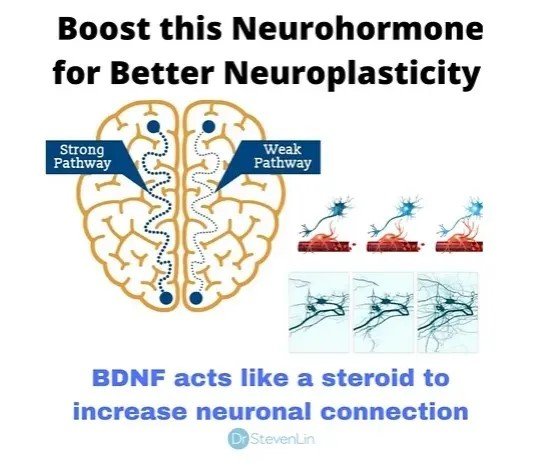
It stimulates mitochondrial production, promotes the formation and maintenance of synapses, stimulates the generation and survival of new hippocampal neurons, and enhances the resistance of neurons to stress injury and disease.
In addition to BHB and BDNF, fasting can also promote the expression of mitochondrial master regulators, namely the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC1α).
PGC1α is a central inducer of mitochondrial biogenesis, which can stimulate the formation of mitochondria and increase the number of mitochondria, thereby enhancing neuronal synaptic plasticity and having a positive effect on neuronal bioenergetics.
→ Fasting helps glucose metabolism
Fasting for 3–5 days in humans can reduce blood sugar levels by 30%-40% and inhibit glycolysis. Fasting every other day for 3 consecutive weeks can reduce insulin levels on the day of fasting by 50%-60%.

Generally speaking, fasting for 3–5 days in humans will also cause a 60% decrease in the main growth factor insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), one of its main binding proteins, IGF-1 binding protein (IGFBP1), to increase 5–10 times, and growth hormone (GH) to increase 2–3 times (increased growth hormone ensures muscle mass).
→ Fasting inhibits mTOR and increases AMPK, which is beneficial to autophagy
The balance between cell synthesis and degradation is regulated by two major metabolic regulators, namely the rapamycin target (mTOR) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
Under high-nutrient conditions, mTOR stimulates protein synthesis and cell growth.
In contrast, during fasting, neurons in the brain enter a “resource-saving” mode, and AMPK downregulates mTOR to minimize protein synthesis and stimulate autophagy.
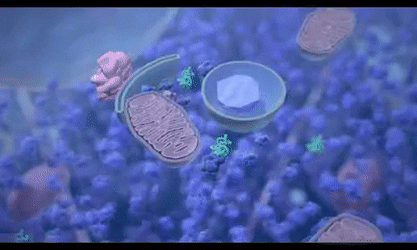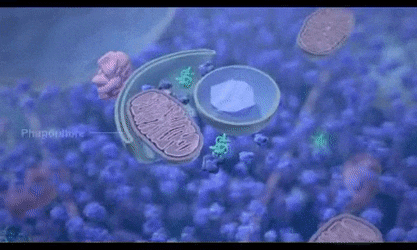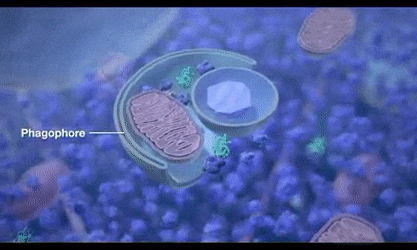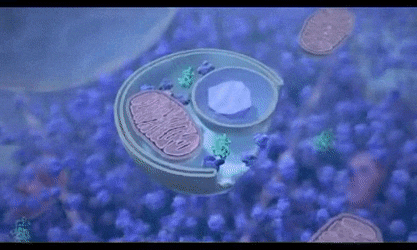
Autophagy can remove waste from cells, thereby achieving cell regeneration.
In the process of neurodegeneration, misfolded proteins (β-amyloid plaques and tau proteins) accumulate in the brain and cause damage. Autophagy helps to remove misfolded proteins and damaged organelles, perform DNA repair, recycle nutrients and promote energy production. ③
→ Fasting protects neurons and neural pathways
Fasting affects fat metabolism by reducing leptin (associated with a proinflammatory state), increasing adiponectin (enhancing insulin sensitivity and inhibiting inflammation) and the hormonal activity of growth hormone releasing peptide (enhancing insulin sensitivity).
In addition, growth hormone releasing peptide stimulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis, which is beneficial for protecting neurons and neural pathways.
→ Fasting inhibits inflammation and improves neuronal survival
Fasting can also inhibit inflammation and reduce the expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 6 (IL6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα).
Since inflammation is the pathogen of many different neurological diseases, the ability of fasting to inhibit neural and systemic inflammation will improve neuronal survival.
→Fasting makes you more adapted to your circadian rhythm
Intermittent fasting, eating within the most active 6–10 hours during the day, can adjust the peripheral rhythm clock to synchronize it with the central rhythm clock, thereby enhancing insulin sensitivity, improving metabolic health and cognitive function.
Eating at a time that does not match the body’s natural circadian rhythm can disrupt the way our organs work. A study of shift workers found that they are prone to chronic diseases such as sleep disorders, cardiovascular disease, peptic ulcers, metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer. ④
A 2021 study of 883 adults in Italy found that those who restricted their food intake to 10 hours a day were less likely to suffer from cognitive impairment than those who did not have a time-restricted diet. ⑤

→Fasting can balance gut microbes
Gut microbiota is closely related to brain health. Intermittent fasting can change the composition of gut microbiota, affecting the brain through neural, endocrine and immune pathways, thereby improving cognitive function.
Research on fasting and brain health
→Fasting reduces the risk of dementia
A 2022 study interviewed 411 non-demented elderly people and subjected them to multimodal neuroimaging examinations of brain β-amyloid protein (Aβ) and tau deposition, glucose metabolism, and cerebrovascular damage. ⑥

The results showed that compared with high meal frequency (HMF), LMF (less than 3 meals a day) was significantly associated with lower Aβ deposition and reduced the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
→ Reduce inflammation and enhance immunity
A study recruited 50 healthy volunteers (21 men and 29 women) to practice Ramadan fasting and found that the number of proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor α and immune cells was significantly reduced. ⑦
→ Improve mild cognitive impairment in the elderly
A longitudinal study of a healthy longevity neuroprotection model in the elderly followed up 99 participants with mild cognitive impairment aged 60 years and over for 36 months. ⑧

Among the study participants, the subjects were divided into three groups, namely those who practiced intermittent fasting regularly (r-IF), those who practiced intermittent fasting irregularly (i-IF), and those who practiced non-intermittent fasting (n-IF).
The results showed that the subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in the r-IF group had no cognitive impairment and disease (24.3%) compared with the i-IF group (14.2%) and n-IF group (3.7%).
Significant increase in superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the body, decrease in body weight, insulin level, fasting blood sugar, malondialdehyde (MDA), C-reactive protein (CRP) and DNA damage, and higher cognitive scores.
→ Reduce oxidative stress and enhance cognition and learning ability
Because oxidative stress can induce cell damage and impaired cognitive function, it is a known factor leading to brain aging, so in order to measure the brain oxidative stress index, a mouse study studied the protective effect of intermittent fasting on the brain. ⑨
There were 15, 19 and 15 mice in the control group, intermittent fasting group and high-fat diet group, respectively, and the observation was carried out for a total of 11 months.
The study found that the CA1 pyramidal cell layer (improved learning and memory) of the mice in the intermittent fasting group was thicker than that of the control group mice, and the expression of drebrin (a dendritic protein) in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus was increased, and the expression of the synaptic protein synaptophysin in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus (improved memory and cognition) showed an increasing trend.
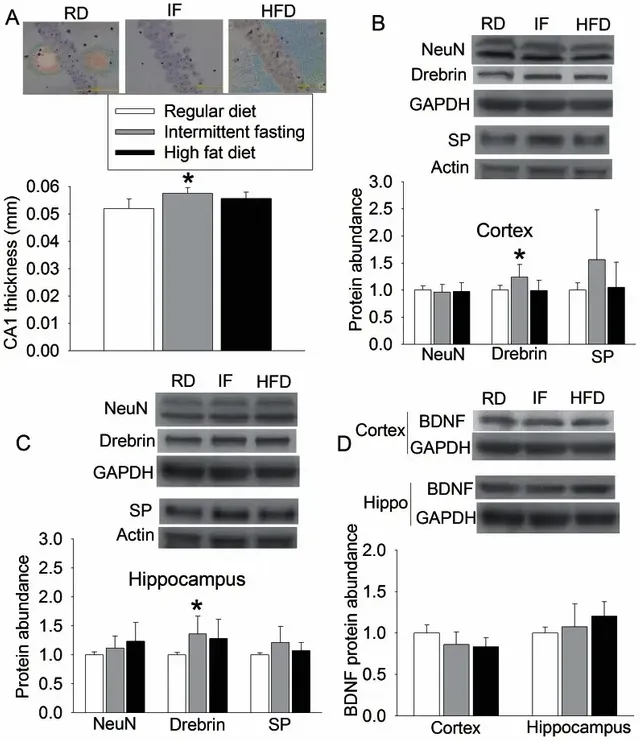
In addition, the intermittent fasting group reduced the protein levels of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) and nitrotyrosine, two indicators of oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex, and also reduced the level of glutathione disulfide (GSSG), which led to a significant increase in the glutathione/GSSG ratio.
The final results of the experiment showed that intermittent fasting can reduce oxidative stress in the brain, slow down neurodegeneration, and enhance cognitive ability and learning ability.
The key Grace said
Smile, you are ten years younger.
Hunger, you are ten years younger.
Intermittent fasting has many benefits for brain health, including reducing oxidative stress and enhancing memory and cognitive abilities.

Intermittent fasting can prevent chronic, excessive and possibly dysregulated glucose metabolism, while maintaining insulin sensitivity and growth factor signaling, all of which are beneficial to neurons.
The longer you stick to intermittent fasting, the more benefits you get.
Nowadays, many elderly people don’t eat three meals a day. In fact, eating two meals is more appropriate.
Two meals a day or one meal a day saves money, energy and time, and also gains a healthy body.
If the elderly want to try it, it is recommended to get up at 5 or 6 in the morning. If you are not hungry, you can do some housework or exercise first. When you come back, you feel hungry at 9 or 10 o’clock before eating the first meal, and eat the second meal at 4 or 5 o’clock in the afternoon.
Go to bed around 8 or 9 o’clock in the evening. In this way, intermittent fasting is easy, in line with the circadian rhythm, and the mind is clear and the body is healthy.
Of course, in addition to fasting, we also recommend taking in nutrients that are very important for the brain.
Reference links:
①https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27528626/ ②https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6836141/ ③https://www.adrc.wisc.edu /dementia-matters/intermittent-fasting-and-its-effects-brain
④https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22010477/⑤https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7827225/⑥https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9646955/⑦https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih .gov/23244540/⑧https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32872655/⑨https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3670843/
Greetings friend @gracex
Welcome to Steemit, we are pleased that you have integrated into the platform. We hope you find a space to share original and interesting content.
I invite you to fulfill the achievements in the Newcomers community.
I recommend that you learn about the internal policies that you must take into account when publishing content on Steemit.
https://steemit.com/faq.html#What_is_considered_spam_or_abuse
On the other hand, it is important to let you know that the use of artificial intelligence is not allowed to generate content.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit