2. Classic futures CTA strategy example
Newton once said: If I see further than others, it is because I stand on the shoulders of giants.
The CTA strategies publicly available on the market include the SMA strategy, the Bollinger band strategy, the turtle trading rules, the momentum strategy, the arbitrage strategy, and so on. Quantitative trading strategies have one characteristic, that is, they will slowly fail once they are made public. But this does not affect us to learn from these strategies and learn from the essence of them, so that we can solve problems on the shoulders of giants.
2.1 Analysis of futures fundamentals (inventory, basis difference, price)
The fundamental analysis does not need to care about the short-term price trend. It is believed that the value will be reflected in the price ultimately. It is more about analyzing the factors behind the price to determine how much the variety is worth. Generally, the top-down analysis method is adopted: from macro factors, variety factors and other factors.
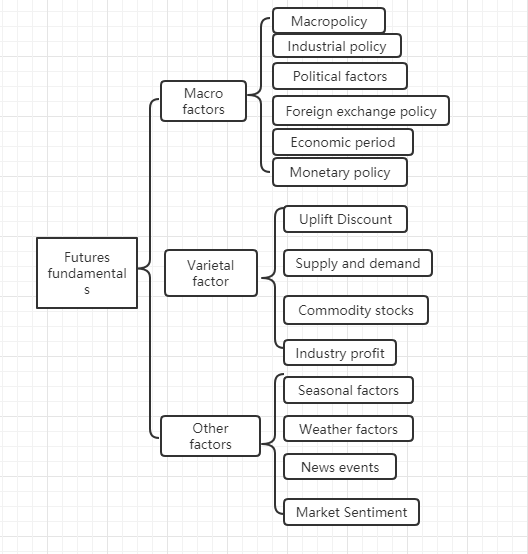
We can see from the above chart that there are many factors that affect commodity prices, and these data are changing constantly. It is beyond the ability of individual retail investors to obtain these huge data, let alone objective analysis.
In fact, the fundamental analysis of commodity futures is not to analyze all the factors. We only need to grasp the core elements of fundamental analysis to find out the rules from the complex information.
Macro factors
Macroeconomic data is complex and changeable. Every day, every moment, there are many economic data published, from national politics, central banks, investment banks, official and unofficial. In addition to the political and economic crisis, macro-analysis is a good material for chatting, but not practical. Peter Lynch, a famous fund management expert in the United States, once said: "I spend no more than 15 minutes on the analysis of the economic situation every year".
Variety factor
In the fundamental analysis, the variety analysis is mainly to analyze premium and discount, supply and demand relationship, commodity inventory, industrial profit, etc. It can be said that mastering the variety factor analysis of commodity futures can judge most of the market trend.
As friends who have done futures know, domestic commodity futures can be simply divided into industrial products and agricultural products. The analysis methods of industrial products and agricultural products are different. We will elaborate on the two aspects of supply and demand. In industrial products, supply is relatively stable. Unless there is a major technological breakthrough, production capacity is unlikely to change significantly in a short period of time. Therefore, the main factor affecting the price of industrial products is demand. The demand for agricultural products is relatively stable. In the long run, the demand for agricultural products changes, but in the short run, the demand for agricultural products tends to be stable, so the main factor affecting the price of agricultural products is supply.
Therefore, according to the laws of economics, it is the relationship between supply and demand that determines the price of goods ultimately. In theory, as long as the data of supply and demand can be obtained, the future price of goods can be determined. For industrial products, the supply data is easy to obtain, but it is difficult to obtain the demand data. For agricultural products, the demand data is easy to obtain, and it is difficult to obtain the supply data.
In fact, we can further subtract. The mutual result of supply and demand in the economic market is inventory. We can judge the strength of the relationship between market supply and demand through inventory data. If the inventory of a commodity is very high, it means that the market supply is greater than the demand, and the commodity price will decrease on the premise that the external conditions remain unchanged. If the inventory of a commodity is very low, it means that the market demand is greater than supply, and the commodity price will increase on the premise that the external conditions remain unchanged.
In addition to analyzing commodity inventory, we also need to analyze the price difference between the spot market and the futures market, which is also called the basis difference. If the futures price is greater than the spot price, we call it the futures premium; If the futures price is less than the spot price, we call it the futures discount. According to the futures delivery system, on the futures delivery date, the futures price should be equal to the spot price.
Regardless of the premium or discount, due to the constraints of the futures delivery system, the futures price on the delivery date should be equal to the spot price in theory. As the delivery date approaches, both the spot price and the futures price will tend to be consistent. One is the return of futures to spot, and the other is the return of spot to futures.
According to the above principle, we can use inventory and basis difference to determine future futures prices at the same time. If the inventory of a commodity is low, and if the futures price is much lower than the spot price, we can judge that the demand of the spot market is greater than the supply, and the probability of the spot price increasing in the future is large; Also due to the futures delivery system, as the delivery date approaches, the futures price will rise, and it will be equal to the spot price. The probability of futures price increasing is greater in the future.
Finally, we judge the probable direction of the future price through the inventory and basis difference, but there is no accurate point of buying and selling, so we need to cooperate with technical analysis to give a clear signal of entry and exit. The structure of the whole fundamental analysis is: low inventory + deep discount + technical analysis long position signal = go long; High inventory + substantial premium + technical analysis short position signal = go short.
2.2 Turtle trading rules
When it comes to trading strategies, we have to talk about the representative turtle trading rules. The turtle trading rule comes from the most famous experiment in the history of trading. Richard Dennis, a commodity speculator, wants to know whether great traders are born or trained. To this end, in 1983, he recruited 13 people and taught them the basic concepts of futures trading, as well as his own trading methods and principles. These students were called "turtles".
In the following four years, the Turtles achieved an average annual compound interest of 80%. Dennis proved that with a simple system and rules, people with little or no trading experience can become excellent traders. However, some turtles sell turtle trading rules on the website for profit. In order to prevent this behavior, two original turtles, Curtis Firth and Arthur Maddock, decided to make the turtle trading rules available to the public free of charge on the website.
After the truth came out, people found that the Turtle trading rules adopted the optimized Donchian channel and used ATR indicators for position management. After decades of historical tests, it has become an easy trading method for ordinary retail investors to make profits. It still works today in some varieties.
Turtle core principles
- Mastering advantages: find a trading strategy with positive expectations, because in the long run, it can create positive returns.
- Manage risk: control risk and hold your position, otherwise you may not wait for a day to make profits.
- Perseverance: Only by unswervingly implementing your strategy, can you truly achieve systematic results.
- Simple and clear: In the long run, simple systems have more vitality than complex systems.
So next, let's see what the Turtle trading rules say.
- Market - what to buy and sell, essentially in which markets to trade. Turtles are futures traders. They choose the markets with large trading volume and high liquidity only. Because choosing the markets with inactive trading will increase the extra slippage of entry and exit, and will also miss many opportunities of trend.
- Position size - how much to buy or sell is a very important part of the whole strategy, which is usually ignored or wrongly treated by most people. The Turtle trading rule adopts ATR, that is, the average real volatility index, to calculate the open position, increase position signal and stop loss signal. This is a very ingenious design. The original intention is to adjust the size of the position through the absolute volatility of the market. When the market volatility is strong, reduce the position, and when the market volatility is weak, increase the position. It first defines a unit whose formula is: (total assets * 1%)/ATR. The initial position is 1 unit. Even if the decline of the variety on that day reaches the level of ATR, the loss on that day can be controlled within 1% of the total asset. If the price rises by 0.5 unit, the long position will increase their positions by 1 unit, up to 4 units.
- Market entry - Turtle's market entry is based on the Donchian channel. When the price rises above the highest price of the first 20 or 55 K lines, it will enter the market to go long. When the price falls below the lowest price of the first 20 or 55 K lines, it will enter the market to go short. When the signal appears, enter the market for trading, without waiting for the close or the next K-line.
- Stop loss - In the long run, transactions that do not stop loss will not succeed, but most traders are holding loss positions and trying to take chances to hope that the market will turn over. Turtle rules stipulate when to withdraw from the loss position strictly. If you hold long position orders and the price drops by 2 units, the long position is closed with a stop loss. If you hold a short position order and the price rises by 2 units, the short position will be closed with a stop loss.
- Stop profit - In Turtle rules, stop profit means losing a lot of floating profits, which is also an unacceptable part for many traders. If you currently hold long position orders and the price falls below the track of the Donchian channel of ten days, close all long orders; If the current short position order is held and the price rises above the track of the Donchian channel of ten days, close all short positions.
Thus we can see that although the Turtle trading rules look very simple, in fact it has formed a real sense of the prototype of the trading system. It covers all aspects of a complete trading system, leaving no room for traders to make subjective imaginative decisions, which just makes the advantages of programmed operation of the system play, including: entry and exit rules, fund management and risk control, etc.
The biggest advantage of the turtle trading method is to help us establish a set of effective trading methods. It is a combination of batch opening, dynamic stop profits and stop loss, and the trend following strategy of the market, especially the use of ATR value and the concept of position management, which is very worth learning. Of course, it also has a common problem with trend tracking strategy, that is, floating profit and taking back. It is likely that all the floating profits gained from buying the winners will be taken out due to the following wave of sharp falls. It is very strong in the general trend, and not as good as expected in the volatile market.
3. Develop futures CTA strategy in practice
3.1 Development of CTA trend strategy based on MyLanguage
At the end of the last century, a very amazing trading method began to prevail in the field of financial investment in the United States. After thousands of people's practice, people found that this method has effectiveness and great practical value. At the same time, it has been recognized by many investment experts and professional traders. Until now, it can be applied to almost all financial investment fields perfectly, whether foreign exchange, gold, stocks, futures, crude oil, or index and bond, which is chaos operation method.
The word chaos refers to the description of the chaotic state of the universe originally. Its idea is that the result is inevitable, but because the existing knowledge cannot calculate the result, because the calculation itself is also changing the result, the maximum or minimum result may appear at last, but there is no inevitable result. This is very similar to the trading market. Participants also change the market when they analyze the market and buy and sell. The market has eternal variability. When the participants understand the new form of the market, the market also understands that it is recognized by the participants, so the variation occurs. And it will tend to change in the unknown direction of the participants. It has enough wisdom to prevent the participants from catching its change rules, that is, the market is not stable, and the understanding of the past of the market cannot represent the future.
The chaos operation method is a complete set of investment ideas, trading strategies and entry and exit signals, invented by Bill Williams. At present, many investors in the world adopt chaos operation to participate in market transactions. Because the development of China's financial market lags behind, and chaos theory is also a relatively new idea, there are few people studying chaos operation methods in China. Since chaos operation method is a trading strategy with high universality and can be applied to almost all financial investment fields, including stocks, bonds, futures, foreign exchange, and digital currency, this course uses a simplified version of chaos strategy as a starting point to improve your investment interest and income.
As the name implies, the theoretical basis of chaos operation method is chaos theory, which was proposed by meteorologist Edward Lorenz. It was one of the greatest scientific discoveries at the end of the 20th century. He put forward the famous "butterfly effect". Bill Williams applied chaos theory to the field of financial investment creatively, combined with fractal geometry, nonlinear dynamics and other disciplines, and created a series of very effective technical analysis indicators.
The entire Chaos operation method is composed of five major dimensions (technical indicators):
Alligator
The Fractal
The Momentum
Acceleration
The Balance Line
Let's look at the above chart. The Alligator is a set of equilibrium lines using fractal geometry and nonlinear dynamics. Its essence is to extend the exponentially weighted moving average, which is a kind of mean line, but its calculation method is slightly more complicated than the ordinary mean line. Next, let's look at how to define the Alligator in MyLanguage:
// Parameters
N1:=11;
N2:=21;
// Defining the price median
N3:=N1+N2;
N4:=N2+N3;
HL:=(H+L)/2;
// Alligator
Y^^SMA(REF(HL,N3),N4,1);
R:=SMA(REF(HL,N2),N3,1);
G:=SMA(REF(HL,N1),N2,1);
First, we define 2 external parameters N1 and N2, and then calculate the average HL of the highest price and the lowest price according to the external parameters, and then calculate the average HL with different parameters. For teeth, it is the average of the middle period of the midline, and the jaw is the average of the large period of the midline. In this strategy, we use the jaw.
In the chaos operation method, a fractal concept is defined vividly. We can make an analogy: open the palm of the hand, with the fingers facing up, the middle finger is the upper fractal, the left little finger and the ring finger, and the right index finger and thumb respectively, represent the K-line with no record high. A basic fractal is composed of these five K-lines. Then you can define fractal with the following code:
// Fractal
TOP_N:=BARSLAST(REF(H,2)=HHV(H,5))+2;
BOTTOM_N:=BARSLAST(REF(L,2)=LLV(L,5))+2;
TOP:=REF(H,TOP_N);
BOTTOM:=REF(L,BOTTOM_N);
MAX_YRG^^MAX(MAX(Y,R),G);
MIN_YRG^^MIN(MIN(Y,R),G);
TOP_FRACTAL^^VALUEWHEN(H>=MAX_YRG,TOP);
BOTTOM_FRACTAL^^VALUEWHEN(L<=MIN_YRG,BOTTOM);
After calculating the alligator and fractal, we can write a simple chaos operation strategy based on these two conditions, and use a group of exponentially weighted moving average lines as the benchmark price for calculating the alligator and fractal index. Of course, the original chaotic operation strategy will be more complex. The code is as follows:
// If there are no current long position orders and the closing price rises above the upper fractal and the upper fractal is above the alligator, open a long position.
BKVOL=0 AND C>=TOP_FRACTAL AND TOP_FRACTAL>MAX_YRG,BPK(1);
// If there are no current short position orders and the closing price falls below the lower fractal and the lower fractal is below the alligator, open a short position.
SKVOL=0 AND C<=BOTTOM_FRACTAL AND BOTTOM_FRACTAL<MIN_YRG,SPK(1);
// Long positions are closed if the closing price falls below the jaws of the alligator.
C<Y,SP(BKVOL);
// Short positions are closed if the closing price rises above the jaws of the alligator.
C>Y,BP(SKVOL);
For ease of understanding, I wrote the detailed comments into the code directly. We can simply list the trading logic of this strategy as follows:
- Long opening position: if there are no long position orders at present, and the closing price rises below the upper fractal, and the upper fractal is above the alligator.
- Short opening position: if there are no short position orders at present, and the closing price falls below the lower fractal, and the lower fractal is below the alligator.
- Long closing position: if the closing price falls below the alligator chin.
- Short closing position: if the closing price rises above the alligator chin.
Next, let's see what the results of this simple chaos operation strategy backtest actually look like. In order to make the backtest more close to the real market environment, the commission is set to twice the exchange rate, and the opening and closing positions are subject to a sliding point of two jumps each. The backtest data type is the rebar index, and the trading type is the rebar main force continuous, with a fixed 1 lot opening position. The following is the preliminary backtest performance report at the 1-hour level.
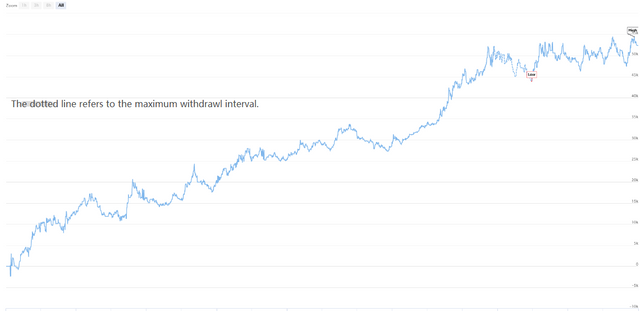
From the capital curve and backtest performance data, the strategy performed well, and the overall capital curve was steadily upward. However, since the end of 2016, the market characteristics of rebar varieties have changed, from the unilateral trend of high volatility to the broad volatility trend. From the perspective of capital curve, the profit from 2017 to now is obviously weak.
In a word, the essence of chaos operation method is to find a turning point, without caring about how the market goes or whether it is true or false breakout. If it breaks through the fractal, it will enter the market directly. Never try to predict the market, but be an observer and follower.
3.2 Development of CTA arbitrage strategy based on JavaScript language
George Soros put forward an important proposition in "The Alchemy of Finance" written in 1987: I believe the market prices are always wrong in the sense that they present a biased view of the future. He believed that the market efficiency hypothesis is only a theoretical hypothesis. In fact, market participants are not always rational, and at each time point, participants cannot completely obtain and objectively interpret all information. Moreover, even if it is the same information, everyone's feedback is different. That is to say, the price itself already contains the wrong expectations of market participants, so in essence, the market price is always wrong. This may be the profit source of arbitrageurs.
According to the above principles, we can know that in an ineffective futures market, the reason why the market impact on delivery contracts in different periods is not always synchronous, and the pricing is not completely effective. Then, based on the delivery contract price of the same transaction object in different periods, if there is a large price difference between the two prices, we can buy and sell futures contracts in different periods at the same time for cross-period arbitrage.
Like commodity futures, digital currency also has a cross-period arbitrage contract portfolio. For example, in the OKEX exchange, there are: ETC current week, ETC next week, ETC quarter. For example, suppose that the price difference between the current week of ETC and the quarter of ETC remains around 5 for a long time. If the price difference reaches 7 one day, we expect that the price difference will return to 5 in the future. Then we can sell ETC that week and buy ETC quarter at the same time to go short the price difference, vice versa.
Although this price difference exists, there are many uncertainties in manual arbitrage due to time-consuming manual operations, poor accuracy and the impact of price changes. The charm of quantitative arbitrage lies in capturing arbitrage opportunities through quantitative models and formulating arbitrage trading strategies, as well as placing trading orders automatically to exchanges through programmed algorithms, so as to capture opportunities quickly and accurately and make profits efficiently and stably.
This course will teach you how to use the FMZ Quant Trading Platform and the ETC futures contract in the OKEX exchange to demonstrate how to capture the instantaneous arbitrage opportunities, seize the profits that can be seen every time, and hedge the risks that may be encountered in the digital currency trading with a simple arbitrage strategy.
Create a cross-period arbitrage strategy for digital currency
Difficulty: Normal
Strategy environment
- Transaction object: Ether Classic (ETC)
- Spread data: ETC current week - ETC quarter (omit cointegration test)
- Transaction period: 5 minutes
- Transaction period: 5 minutes
- Transaction type: cross period of the same type
Strategy logic
- Conditions for opening positions with going long the price difference: if the current account has no positions and the price difference is less than the lower bound of the ball, then go long the price difference. That is, buy opening positions ETC for the week, sell opening positions ETC for the quarter.
- Conditions for opening positions with going short the price difference: if there is no position in the current account, and the price difference is greater than the upper bound of the ball, then go short the price difference. That is, sell opening positions ETC for the week, buy opening positions ETC for the quarter.
- Conditions for closing positions with going long the price difference: if the current account holds going long orders of ETC in the current week and holds going short orders of ETC quarter, and the price difference is greater than the middle bound of the ball, then close long the price difference. That is, sell closing positions ETC for the week, buy closing positions ETC for the quarter.
- Conditions for closing positions with going short the price difference: if the current account holds going short orders of ETC in the current week, and holds going long orders of ETC quarter, and the price difference is less than the middle bound of the ball, then close short the price difference. That is, buy closing positions ETC for the week, sell closing positions ETC for the quarter.
The above is a simple logic description of the cross-period arbitrage strategy of digital currency. So how to implement our ideas in the program? We try to build the framework on the FMZ Quant Trading Platform.
function Data() {} // Basic data function
Data.prototype.mp = function () {} // Position function
Data.prototype.boll = function () {} // Indicator function
Data.prototype.trade = function () {} // Order placement function
Data.prototype.cancelOrders = function () {} // Order withdrawal function
Data.prototype.isEven = function () {} // Processing single contract function
Data.prototype.drawingChart = function () {} // Drawing function
function onTick() {
var data = new Data(tradeTypeA, tradeTypeB); // Create a basic data object
var accountStocks = data.accountData.Stocks; // Account balance
var boll = data.boll(dataLength, timeCycle); // Calculate the technical indicators of boll
data.trade(); // Calculate trading conditions to place an order
data.cancelOrders(); // Cancel orders
data.drawingChart(boll); // Drawing
data.isEven(); // Processing of holding individual contract
}
//Entry function
function main() {
while (true) { // Enter the polling mode
onTick(); // Execute onTick function
Sleep(500); // Sleep for 0.5 seconds
}
}
Imagine what our trading process is like in supervisory trading. There is no essential difference in system transactions. It is nothing more than acquiring data, calculating data, placing an order transaction, and processing after placing an order. The same is true in the program. First, the program will execute the main function in line 20, which is a convention. When the program completes the trading strategy preprocessing (if any), it will enter the infinite loop mode, that is, the polling mode. In the polling mode, the onTick function will be executed repeatedly.
Then in the onTick function, it is our trading process in the subjective transaction: first, obtain the basic price data, then obtain the account balance, then calculate the index, then calculate the trading conditions and place the order, and finally the processing after placing the order, including order cancellation, drawing, and processing a single contract.
The strategy framework can be easily set up according to the strategy idea and transaction process. The whole strategy can be simplified into three steps:
- Pre-processing before transaction.
- Get and calculate data.
- Place an order and deal with it later.
To be continued...