4. Ternary operation module
This module is also called the assertion module, and its function is similar to the ternary operator in some programming languages.

This module can also be nested. The essence of the ternary operation module is also conditional judgment logic, and its function is similar to that of the conditional module.
Use the ternary operation module to reconstruct the teaching example of the "conditional module" above.
The following example:
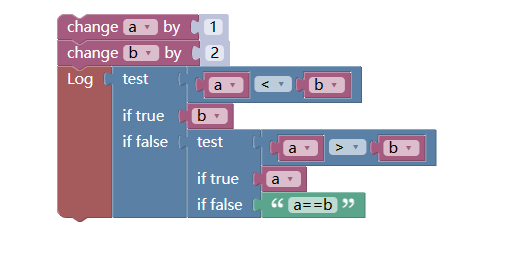
As the strategy code written in JavaScript:
function main () {
var a = 1
var b = 2
Log(a < b ? b : (a > b ? a : "equal"))
}
If you are interested, you can adjust the values of a and b and run the backtest.
Mathematics module type
In many of the previous examples, we have used some mathematics modules to a greater or lesser extent.
Next we explain some mathematics modules that have not studied yet.
1. Trigonometric module
Note that the parameter filled in the tenon (concave) position of this module is an angle value, not a radian value.
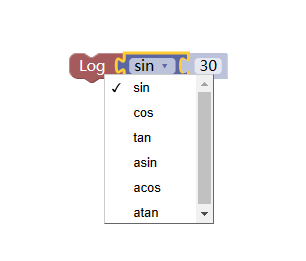
2. Circumference numerical module

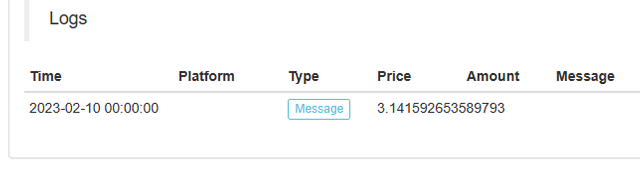
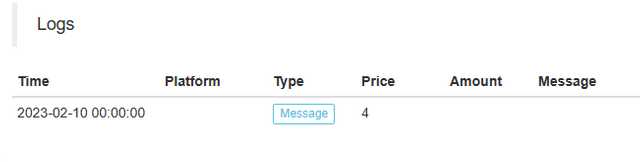
Backtesting prints:
3. Get a random number module within a range of values
This module takes a random number within a set range of values, and the module tenon (concave) position can directly fill in the value, or use a variable as the start and end value of the random range.
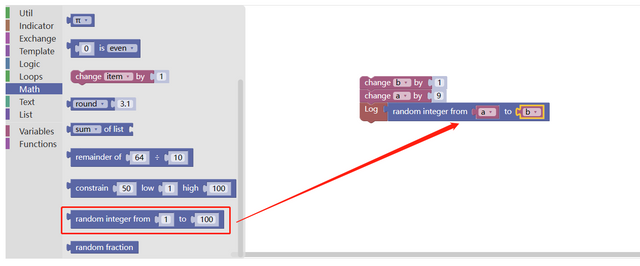
As the strategy code written in JavaScript:
function main () {
var a = 1
var b = 9
Log(_N(a + Math.random() * (b - a), 0))
}
4. Limited value range module
This module will limit the variable filled in the first tenon (concave) position, and take the value according to the range set by the second and third tenon (concave) positions.
If it is greater than the maximum value of this range, the module returns to the maximum value of this range, and if it is less than the minimum value of this range, the module returns to the minimum value.
If it is within this range, the value of the variable itself that takes the first tenon (concave) position is returned.
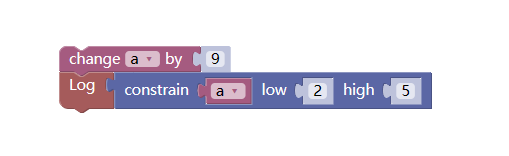
As the strategy code written in JavaScript:
function main () {
var a = 9
Log(Math.min(Math.max(2, a), 5))
}
5. Remainder module
This module performs numerical remainder operation on the numerical module set at the tenon (concave) position.
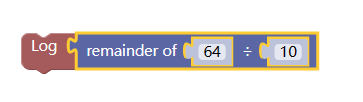
Divide 64 by 10 to get 6 and the remaining 4.
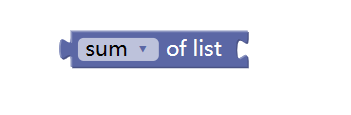
6. List calculation module
This module performs calculations on a certain list module (functions such as calculating the sum of the elements in the list).
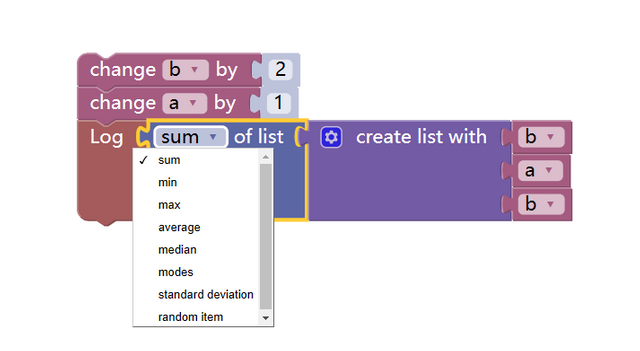
As the strategy code written in JavaScript:
function sum (arr) {
var ret = 0
for (var i in arr) {
ret += arr[i]
}
return ret
}
function main () {
var b = 2
var a = 1
Log(sum([b,a,b,a,a]))
}
Visualization example strategy:
- https://www.fmz.cn/strategy/121404
- https://www.fmz.cn/strategy/129895
- https://www.fmz.cn/strategy/123904
- https://www.fmz.cn/strategy/122318
More strategies are available at: https://www.fmz.cn/square
Other articles in the series
- Visualization Module to Build Trading Strategy - Advanced Understanding
- Visualization Module to Build Trading Strategy - First Acquaintance
Boring programming can be easily done by building blocks, try it out, it's very interesting!
From: https://blog.mathquant.com/2022/07/11/visualization-module-to-build-trading-strategies-in-depth.html